CTO at NCSC Summary: week ending April 28th
Edge network devices a focus of threat actors once more..
Welcome to the weekly highlights and analysis of the blueteamsec subreddit (and my wider reading). Not everything makes it in, but the best bits do.
Operationally this week it has once again been around edge network devices proving to be of interest.
In the high-level this week:
Cyber Assessment Framework 3.2 - from the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre - “In the two years since the last version of the NCSC Cyber Assessment Framework (CAF) was published, its application has gone well beyond the original regulatory context. During this time, we have also seen an increase in the cyber threat to critical national infrastructure (CNI). Both these developments have been major drivers behind the decision to update the CAF.”
[US] National Security Division; Provisions Regarding Access to Americans' Bulk Sensitive Personal Data and Government-Related Data by Countries of Concern - National Security Division, Department of Justice - " The Executive order of February 28, 2024, “Preventing Access to Americans' Bulk Sensitive Personal Data and United States Government-Related Data by Countries of Concern” (the Order) … This advance notice of proposed rulemaking (ANPRM) seeks public comment on various topics related to the implementation of the Order.”
Data broker provisions in draft privacy legislation too weak, lawmakers say - The Record reports - “Under APRA’s current draft a consumer would have to individually visit 871 data brokers’ websites and affirmatively delete their personal data,”
Vote on EU cybersecurity label delayed to May, sources say - Reuters reports - “National cybersecurity experts have shelved a vote on a draft EU cybersecurity label allowing Amazon, , Alphabet's Google and Microsoft to bid for highly sensitive EU cloud computing contracts to May, people familiar with the matter said on Tuesday.”
France questions latest EU cloud certification scheme - EU Active reports - “France has questioned the latest draft of the EU Cloud Certification Scheme (EUCS) that would allow member states to set national sovereignty requirements at the highest cybersecurity level of the scheme, according to a leaked letter sent to the European Council of the EU’s Legal Service.”
'My hell in Myanmar cyber slavery camp' - BBC reports - “The centres are fed by a steady stream of aspiring migrant workers from all over the world. The Sri Lankan authorities say they know of at least 56 of its citizens alone who are trapped in four different locations in Myanmar”
EU Introduces New Cybersecurity Rules As EVs Are Deemed “Spying Machines On Four Wheels” - Car Scoops reports - “All new vehicles sold in the European Union from July 7, 2024 onwards have to comply with the UN regulations R155 and R156 which have already been in force for the approval of new models since July 2022. In short, the R155 requires a management system by automotive OEMs, while the R156 ensures that the vehicle software updates are safer from cybersecurity threats.”
Defending Democracy
Russian US election interference targets support for Ukraine after slow start - Microsoft reports - “China is using a multi-tiered approach in its election-focused activity. It capitalizes on existing socio-political divides and aligns its attacks with partisan interests to encourage organic circulation.”
Poll Vaulting: Cyber Threats to Global Elections - Google reports their key judgements
Mandiant assesses with high confidence that Russian state-sponsored cyber threat activity poses the greatest risk to elections in regions that Russia closely monitors, such as the U.S., the UK, and the EU.
Mandiant expects PRC state-sponsored intrusions to focus on election-related targets for intelligence collection while pro-PRC influence operations generally praise China and undermine its adversaries.
What an Indian Deepfaker Tells Us About Global Election Security - Bloomberg Reports - “It has never been easier, faster or cheaper to make a deepfake. Jadoun and five co-workers need just three days — and 600,000 rupees (about $7,200) — to create and edit an effective AI, using text-to-video systems in a workshop in Pushkar, a small tourist town in the western state of Rajasthan. They use tools like Dall.E, Midjourney, Stable Diffusion and Pika.”
[Australia’s] Peter Dutton backs laws to crack down on ‘above the law’ social media companies over misinformation - The Guardian reports - “has expressed support for a crackdown on the spread of dangerous lies on social media platforms, renewing focus on the government’s misinformation legislation which was shelved late last year.”
Reporting on/from China
FBI says Chinese hackers preparing to attack US infrastructure - Reuters reports - “Chinese government-linked hackers have burrowed into U.S. critical infrastructure and are waiting "for just the right moment to deal a devastating blow," FBI Director Christopher Wray said on Thursday.
The big hack at VW - China in focus - ZDF Heute reports - “Suspected Chinese state hackers targeted the Volkswagen Group for several years starting in 2010. The hackers managed to penetrate deeply into Volkswagen's networks on several occasions and steal intellectual property. “
The founding meeting of the Information Support Force of the Chinese People's Liberation Army was held in Beijing. Xi Jinping awarded the military flag to the Information Support Force and delivered a speech - Chinese Government reports.
Xi Jinping tightens grip on China’s military with new information warfare unit - Financial Times reports - “The shift of information warfare to the direct command of the Central Military Commission — the top Communist party and state organ that controls the People’s Liberation Army — would hand Chinese leader Xi Jinping even more direct control over the military, analysts said.”
Chinese police arrest over 1,500 in campaign targeting online rumours - South China Morning Post reports - “China shuts down 63,000 illegal accounts in crackdown on social media posts with false information about hot issues such as pandemic and disasters”
Chinese Auto Tech Should Be Banned at US Bases, Lawmakers Say - Bloomberg reports - “US lawmakers urged the Pentagon to bar Internet-connected vehicles with Chinese technology from entering US military bases, building on a Biden administration probe into security risks posed by the cars.”
Ericsson Lays Off More Than 200 Employees in China - Wall Street Journal reports - “One of the people said the R&D team recently had been excluded from working on at least two large projects in the U.S. and Australia.”
Action Plan for Accelerating the Cultivation of Digital Talents to Support the Development of the Digital Economy (2024-2026) announcement of - Chinese Government- “Carry out international exchange activities for digital talents. Increase the emphasis on digital talents, introduce a group of high-level overseas digital talents, support the innovation and entrepreneurship of a group of digital talents who have returned from studying abroad, and organize a group of high-level overseas digital talents to return to China to serve. Strengthen the construction of entrepreneurship parks for overseas students and support digital talents to innovate and start businesses in the parks”
China Orders Apple to Remove Popular Messaging Apps - Wall Street Journal reports - “WhatsApp, Signal and Telegram among apps cut from iPhone app store to comply with censorship demand”
China: The rise of digital repression in the Indo-Pacific - Article 19 reports - “This report shows that dual infrastructure and policy support from China, in the hands of authoritarian states, has contributed to increasing restrictions on freedom of expression and information, the right to privacy, and other acts of digital repression.”
Artificial intelligence
US seeks alliance with Abu Dhabi on artificial intelligence - Financial Times reports - “The Biden administration is proactively encouraging US tech groups to seek artificial intelligence deals and partnerships in the United Arab Emirates, seeking to cultivate an alliance that would provide it with an edge over China in developing the revolutionary technology.”
Japan's Sakura Internet snags $130m of Nvidia's next-gen chip - Nikkei Asia reports - “Osaka-based Sakura will install multiple AI chips at its facility in Hokkaido, the northernmost of Japan's main islands, by March next year, to provide computing power for companies wanting to train advanced AI algorithms. It said it will make additional investments, both in AI computing power and data centers, totalling 100 billion yen by March 2031.”
No, LLM Agents can not Autonomously Exploit One-day Vulnerabilities - “While LLM agents, and the foundational models that power them, are indeed making leaps in capabilities there is still little evidence to suggest they can discover or exploit complex or novel software security vulnerabilities.”
Cyber proliferation
Markets Matter: A Glance into the Spyware Industry - Digital Forensic Research Lab (DFRLab) at the Atlantic Council reports - “This paper argues that policymakers must approach the market as a whole, a large and complex but interlinked system, in designing future policy interventions against these vendors and their respective supply chains. In closing, the paper offers several tangible impacts and insights into this market, calling for greater transparency writ large, but also for increased attention into the individuals and investors that facilitate the proliferation of spyware. “
Promoting Accountability for the Misuse of Commercial Spyware - US State Department reports - "the Department is taking steps to impose visa restrictions on 13 individuals who have been involved in the development and sale of commercial spyware or who are immediate family members of those involved. "
2023 Country Reports on Human Rights Practices: Greece - US State Department reports - "(PEGA) found the country did not use spyware “as part of an integral authoritarian strategy,” but applied spyware against “journalists, politicians and businesspersons,” and exported spyware to countries with poor human rights records"
Spain reopens a probe into a Pegasus spyware case after a French request to work together - Associated Press reports - “A Spanish judge has reopened a probe into the suspected spying on the cellphone of Spain’s prime minister after receiving a request to collaborate with a similar investigation in France.
The judge with Spain’s National Court said Tuesday there is reason to believe that the new information provided by France can “allow the investigations to advance.”
The heroines of Onet's reportages, victims of molestation in the Military Police, were under surveillance with Pegasus - Onet reports - “The information about the use of Pegasus against them is the latest discovery in this multi-threaded case”
How the armed forces got involved with a spy company with connections to Russia - Der Standard reports in Germany - “There, a company called Machine Learning Solutions MLS presented them with their spy software Subzero. This emerges from internal documents from the armed forces, which DER STANDARD was able to see.”
Bounty Hunting
Exploring Law Enforcement Hacking as a Tool Against Transnational Cyber Crime - “Yet another growing trend challenges this notion: Western law enforcement agencies (LEAs) also have been expanding their own abilities to cross both technical and national boundaries to take on cyber criminals. This trend is creating new opportunities and challenges for both domestic and international cyber policy.”
The FSB detained a Muscovite involved in distributing malware via Telegram - TASS reports - “Moskvich found buyers of malware through a website he administered. “To purchase the program, the client had to contact the resource administrator in the Telegram messenger. After receiving information about the payment made, the seller sent the buyer a file containing the software, an activation key and an explanatory video,” the intelligence service added.”
Russian FSB Counterintelligence Chief Gets 9 Years in Cybercrime Bribery Scheme - Krebs on Security reports - “The head of counterintelligence for a division of the Russian Federal Security Service (FSB) was sentenced last week to nine years in a penal colony for accepting a USD $1.7 million bribe to ignore the activities of a prolific Russian cybercrime group that hacked thousands of e-commerce websites.”
Moldovan Botnet Operator Indicted for Role in Conspiracy to Unlawfully Access Thousands of Infected Computers Throughout the United States - US Department of Justice reports - “Lefterov and his co-conspirators stole victims’ login credentials—i.e., usernames and passwords—from the infected computers and then used the credentials to gain access to victim accounts at financial institutions, payment processers, and retail establishments as means to steal money from the victims”
Justice Department Announces Charges Against Four Iranian Nationals For Multi-Year Cyber Campaign Targeting U.S. Companies - US Department of Justice reports - “As alleged, the defendants participated in a cyber campaign using spearphishing and other hacking techniques in an attempt to compromise private companies with access to defense-related information.”
Reflection this week is around the response to the Cisco ASA issue. Having been on the inside and seeing industry and Governments work together is a thing of wonder. This is truly our super power against our adversaries…
Think someone else would benefit? Share:
All attribution is by others and not the UK Government unless specifically stated as such, please see the legal text at the end.
Have a lovely Friday..
Ollie
Cyber threat intelligence
Who is doing what to whom and how allegedly.
Reporting on Russia
Analyzing Forest Blizzard’s custom post-compromise tool for exploiting CVE-2022-38028 to obtain credentials
Microsoft provides insight into to post compromise tradecraft by this alleged Russian threat actor.
Since at least June 2020 and possibly as early as April 2019, Forest Blizzard has used the tool, which we refer to as GooseEgg, to exploit the CVE-2022-38028 vulnerability in Windows Print Spooler service by modifying a JavaScript constraints file and executing it with SYSTEM-level permissions. Microsoft has observed Forest Blizzard using GooseEgg as part of post-compromise activities against targets including Ukrainian, Western European, and North American government, non-governmental, education, and transportation sector organizations. While a simple launcher application, GooseEgg is capable of spawning other applications specified at the command line with elevated permissions, allowing threat actors to support any follow-on objectives such as remote code execution, installing a backdoor, and moving laterally through compromised networks.
UAC-0133 (Sandworm) plans for cyber sabotage on almost 20 objects of critical infrastructure of Ukraine
Ukraine’s CERT alleged that Russia was going after industrial control systems in ten (yes you read that right) regions of Ukraine. The scale of the ICS focused operation will be of note.
In March 2024, the government computer emergency response team of Ukraine CERT-UA revealed a malicious plan of the Sandworm group, aimed at disrupting the stable functioning of the information and communication systems (ICS) of about twenty enterprises in the energy, water and heat supply industry (OKI) in ten regions of Ukraine.
In addition to the QUEUESEED (KNUCKLETOUCH, ICYWELL, WRONGSENS, KAPEKA) backdoor known since 2022, a new toolkit of attackers, namely the LOADGRIP and BIASBOAT (Linux variant of QUEUESEED) malware, was discovered during the immediate incident response. on a computer (Linux OS) designed for the automation of processes of technological process management (ASUTP) using specialized software (SPZ) of domestic production. It should be noted that BIASBOAT was presented as a file encrypted for a specific server, for which the attackers used the previously obtained "machine-id" value.
https://cert.gov.ua/article/6278706
Unpacking the Blackjack Group's Fuxnet Malware
Team82 detail an interesting campaign which is notable for its scale, the type of technology being targeted and the country within which it happened (Russia).
Blackjack said that the JSON files it made public were only a sample of the full extent of their activity, and that the attack was carried out against 2,659 sensor-gateways, about 1,700 of which were “reachable and successfully attacked.”
The group also said it never claimed to have destroyed 87,000 sensors, rather disabled them by destroying the gateways and fuzzing the sensors using a dedicated M-Bus fuzzer within the malware’s code.
Blackjack claims its initial compromise of Moscollector began in June 2023, and since then the group said it has worked slowly in an attempt to cripple the industrial sensors and monitoring infrastructure managed by the company. On Tuesday, the hackers publicly released information about their activities against Moscollector and the information stolen in the attack on the ruexfil website. Some of their claims include:
Gaining access to Russia’s 112 emergency service number.
Hacking and bricking sensors and controllers in critical infrastructure (including airports, subways, gas-pipelines), all of which have been disabled.
Sharing details about and code from the Fuxnet malware used in the attack
Disabling network appliances such as routers and firewalls
Deleting servers, workstations and databases; 30 TB of data has been wiped, including backup drives.
Disabling access to the Moscollector office building (all keycards have been invalidated).
Dumping passwords from multiple internal services
https://claroty.com/team82/research/unpacking-the-blackjack-groups-fuxnet-malware
Reporting on China
Unplugging PlugX: Sinkholing the PlugX USB worm botnet
Felix Aimé and Charles M show both how relatively easily it is to take control of some latent compromises. Second is the scale of this alleged Chinese campaign - doesn’t feel proportionate.
In September 2023, we successfully sinkholed a command and control server linked to the PlugX worms. For just $7, we acquired the unique IP address tied to a variant of this worm, which had been previously documented by Sophos.
Almost four years after its initial launch, between ~90,000 to ~100,000 unique public IP addresses are still infected, sending distinctive PlugX requests daily to our sinkhole. We observed in 6 months of sinkholing more than 2,5M unique IPs connecting to it.
https://blog.sekoia.io/unplugging-plugx-sinkholing-the-plugx-usb-worm-botnet/
Note: these is also a video of this talk - you can see it here.
ToddyCat is making holes in your infrastructure
Andrey Gunkin, Alexander Fedotov and Natalya Shornikova provide some insight into alleged Chinese state aligned post compromise activity on Windows hosts. They used at least four different tunneling tools to maintain their footholds within networks - this is noteworthy.
During the observation period, we noted that this group stole data on an industrial scale. To collect large volumes of data from many hosts, attackers need to automate the data harvesting process as much as possible, and provide several alternative means to continuously access and monitor systems they attack. We decided to investigate how this was implemented by ToddyCat. Note that all tools described in this article are applied at the stage where the attackers have compromised high-privileged user credentials allowing them to connect to remote hosts. In most cases, the adversary connected, transferred and run all required tools with the help of PsExec or Impacket.
https://securelist.com/toddycat-traffic-tunneling-data-extraction-tools/112443/
China's Military Cyber Operations
Pukhraj Singh provides their summary of alleged Chinese military cyber operations, their structure and similar.
i-SOON Toolkit: What is “TZ”?
Natto Thoughts doing what they do best (i.e. analysis). They continue their analysis of the alleged i-Soon leaks.
The Natto Team started by looking into the context when TZ appeared in phrases in the i-SOON leaked documents. Here are TZ phrases we discovered:
TZ业务: TZ business
TZ实战业务: TZ live combat business
TZ 工作: TZ work
TZ平台: TZ platform
TZ 武器装备: TZ weapon and equipment
…
To conclude, The Natto Team replaced “TZ” with “reconnaissance” in the following paragraphs from the preface section of i-SOON’s Integrated Combat Platform marketing paper that previously mentioned. Does this all make sense now?
nattothoughts.substack.com/p/i-soon-toolkit-what-is-tz?triedRedirect=true
Reporting on North Korea
From BYOVD to a 0-day: Unveiling Advanced Exploits in Cyber Recruiting Scams
Luigino Camastra shows why no one should underestimate North Korea if this alleged campaign is indeed them. Noteworthy due to the level of technical capability around vulnerability research and exploitation on show.
[We] discovered a new campaign targeting specific individuals through fabricated job offers.
[We] uncovered a full attack chain from infection vector to deploying
“FudModule 2.0”rootkit with 0-dayAdmin -> Kernelexploit.[We] found a previously undocumented
KaolinRAT, where it could aside from standard RAT functionality, change the last write timestamp of a selected file and load any received DLL binary from C&C server. We also believe it was loading FudModule along with a 0-day exploit.Our investigation has revealed that the Lazarus group targeted individuals through fabricated job offers and employed a sophisticated toolset to achieve better persistence while bypassing security products. Thanks to our robust telemetry, we were able to uncover almost the entire attack chain, thoroughly analyzing each stage. The Lazarus group’s level of technical sophistication was surprising and their approach to engaging with victims was equally troubling. It is evident that they invested significant resources in developing such a complex attack chain. What is certain is that Lazarus had to innovate continuously and allocate enormous resources to research various aspects of Windows mitigations and security products. Their ability to adapt and evolve poses a significant challenge to cybersecurity efforts.
Multi-level Dropbox commands and TutorialRAT behind APT43
Genians detail an alleged North Korean campaign which continues to be rather rudimentary in terms of initial access tradecraft.
As of the first quarter of 2024, the activity level of APT attacks in Korea remains high, and in the case of spear phishing, 'shortcut (LNK)' type attacks continue, requiring special attention.
Luring people by impersonating them as policy meetings, advisory meetings, surveys, lecture guides, etc.
Initial approach begins with a normal email and uses a reactive spear phishing strategy.
Legitimate use of Dropbox's multi-level attack chain and TutorialRAT attack
Confirmed to be an extension of the APT43 group's BabyShark threat campaign
Identify North Korea's K-defense company hacking attack
South Korean Police detail various alleged North Korean campaigns. The techniques include compromise of Internet exposed servers as well as malware for initial access. Putting the P in Persistent.
North Korean hacking organization Lazarus ‧ Andariel ‧ Kim Soo-ki is all targeting defense technology.
Defense industry companies, etc. “Change e-mail passwords periodically.”
https://www.police.go.kr/user/bbs/BD_selectBbs.do?q_bbsCode=1002&q_bbscttSn=20240423132830276
Reporting on Iran
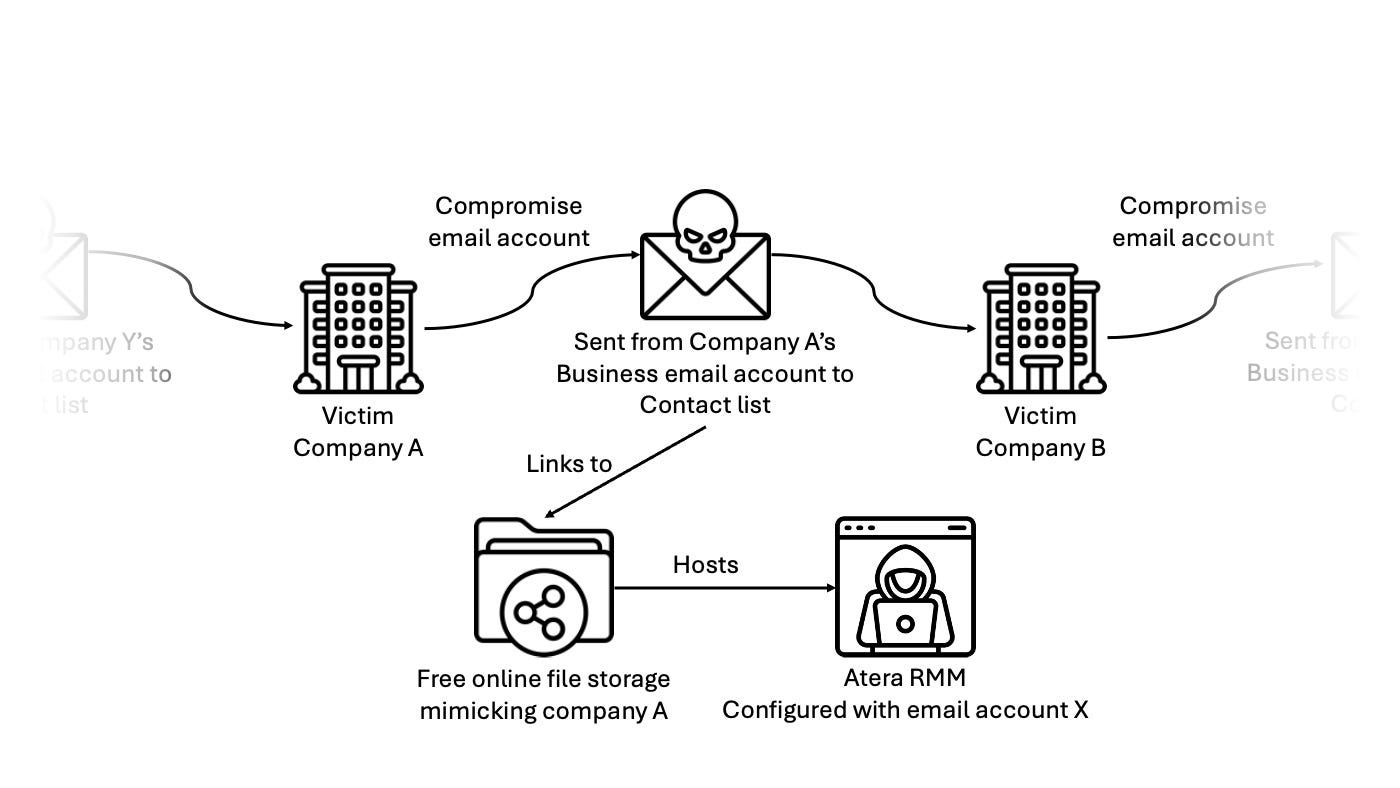
MuddyWater campaign abusing Atera Agents
An alleged Iranian operation detailed here by Harfang Lab. Of note is the use of one victim to target another coupled with the specific remote monitoring and management tool in use.
We have been closely monitoring the activities of the Iranian state-sponsored threat actor MuddyWater since the beginning of 2024. Our investigations reveal an active campaign that has been ramping up since October 2023, aligning with the Hamas attack that took place that month1. In this latest campaign, MuddyWater has been heavily relying on a legitimate remote monitoring and management (RMM) tool called Atera Agent.
https://harfanglab.io/en/insidethelab/muddywater-rmm-campaign/
Reporting on Other Actors
ArcaneDoor - New espionage-focused campaign found targeting perimeter network devices
Cisco have detailed this campaign which is noteworthy due to the level of sophistication even if unattributed.
Cisco was initially alerted to suspicious activity on an ASA device in early 2024. The investigation that followed identified additional victims, all of which involved government networks globally. During the investigation, we identified actor-controlled infrastructure dating back to early November 2023, with most activity taking place between December 2023 and early January 2024. Further, we have identified evidence that suggests this capability was being tested and developed as early as July 2023.
We at the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre also released a number of related notes:
https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/news/ncsc-partners-advice-mitigate-cisco-firewall-targeting
https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/news/exploitation-vulnerabilities-affecting-cisco-firewall-platforms
These included two bits of malware analysis.
https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/static-assets/documents/malware-analysis-reports/line/ncsc-tip-line-dancer.pdf
LightSpy Malware Variant Targeting macOS
Stuart Ashenbrenner and Alden Schmidt evidence the increased sophistication against macOS by this unattributed threat actor. Also of note if how the macOS version has more operational security than the iOS version.
It’s also important to note that while we were able to find the Android version of this malware on the same C2 as the macOS version, it doesn't appear the iOS version is also present. In this article, we'll only be focusing on the macOS implant.
Generally, the macOS version seems to be more refined than the iOS version. The operational security (opsec) is significantly improved, the development practices seem more mature, and things are generally more organized.
https://www.huntress.com/blog/lightspy-malware-variant-targeting-macos
DuneQuixote campaign targets Middle Eastern entities with “CR4T” malware
Kaspersky provide reporting on this unattributed campaign. Shows a degree of op-sec savviness.
In February 2024, we discovered a new malware campaign targeting government entities in the Middle East. We dubbed it “DuneQuixote”; and our investigation uncovered over 30 DuneQuixote dropper samples actively employed in the campaign.
The group behind the campaign took steps to prevent collection and analysis of its implants and implemented practical and well-designed evasion methods both in network communications and in the malware code.
..
We discovered victims in the Middle East, as per our telemetry, as early as February 2023. Additionally, there were several uploads to a semi-public malware scanning service at a later stage, more specifically starting on December 12 2023, with more than 30 submissions of the droppers in the period up to the end of January 2024. The majority of these uploads also originated from the Middle East. Other sources we suspect to be VPN exit nodes geo-located in South Korea, Luxembourg, Japan, Canada, Netherlands and the US.
https://securelist.com/dunequixote/112425/
Malvertising campaign targeting IT teams with MadMxShell
Roy Tay details a campaign which is interesting due to who is being targeted.
Beginning in March of 2024, [we] observed a threat actor weaponizing a cluster of domains masquerading as legitimate IP scanner software sites to distribute a previously unseen backdoor. The threat actor registered multiple look-alike domains using a typosquatting technique and leveraged Google Ads to push these domains to the top of search engine results targeting specific search keywords, thereby luring victims to visit these sites.
https://www.zscaler.com/blogs/security-research/malvertising-campaign-targeting-it-teams-madmxshell
Threat Group FIN7 Targets the U.S. Automotive Industry
BlackBerry detail a campaign which is noteworthy due to the sector being targeted and as with the MaxMxShell campaign who in the organisations were being targeted. Not sure that IT teams in all cases understand they are deeply interesting to adversaries.
n late 2023, [our] analysts identified a spear-phishing campaign by threat group FIN7 that targeted a large automotive manufacturer based in the United States. FIN7 identified employees at the company who worked in the IT department and had higher levels of administrative rights. They used the lure of a free IP scanning tool to run their well-known Anunak backdoor and gain an initial foothold utilizing living off the land binaries, scripts, and libraries (lolbas).
https://blogs.blackberry.com/en/2024/04/fin7-targets-the-united-states-automotive-industry
Discovery
How we find and understand the latent compromises within our environments.
Blauhaunt: A tool collection for filtering and visualizing logon events
A tool which will materially help teams undertaking hunting.
Designed to help answering the "Cotton Eye Joe" question (Where did you come from where did you go) in Security Incidents and Threat Hunts
https://github.com/cgosec/Blauhaunt
Shining Light into the Tunnel: Understanding and Classifying Network Traffic of Residential Proxies
Ronghong Huang, Dongfang Zhao, Xianghang Mi and Xiaofeng Wang attempt to detect residential proxies with this work.
Emerging in recent years, residential proxies (RESIPs) feature multiple unique characteristics when compared with traditional network proxies (e.g., commercial VPNs), particularly, the deployment in residential networks rather than data center networks, the worldwide distribution in tens of thousands of cities and ISPs, and the large scale of millions of exit nodes. All these factors allow RESIP users to effectively masquerade their traffic flows as ones from authentic residential users, which leads to the increasing adoption of RESIP services, especially in malicious online activities.
https://chasesecurity.github.io/bandwidth_sharing/
Hunting for a Sliver in a haystack
Zawadi Done and Borys Avdieiev provide some practical detection techniques for this implant framework.
Finally, we discussed the network protocols Sliver supports to communicate with targeted systems, the use of which can be detected by fingerprinting the TLS configurations of C2 servers. We explored other methods of detecting abnormal network traffic initiated by Sliver and finished with a discussion about the various detection possibilities.
https://www.huntandhackett.com/blog/hunting-for-a-sliver
Investigating Industrial Control Systems using ICSpector open-source framework
Maayan Shaul provides a walk through on real-world ICS hunting with this framework. Something the world needs to get more practised at.
ICSpector, an open-source framework that facilitates the examination of the information and configurations of industrial programmable logic controllers (PLCs). This framework simplifies the process of locating PLCs and detecting any anomalous indicators that are compromised or manipulated. This can assist you in safeguarding the PLCs from adversaries who intend to harm or disrupt their operations.
Defence
How we proactively defend our environments.
Cyber Security Incident Response Planning: Practitioner Guidance
Updated April, 2024 by the Australian Cyber Security Centre.
KB5025885: How to manage the Windows Boot Manager revocations for Secure Boot changes associated with CVE-2023-24932
Gary Blok shows how tricky some things are to patch, especially when they involve cryptographic keys.
Once you’ve applied the mitigations outlined in the KB, the device is difficult to work with when it comes to boot media / reimaging. Personally, I’d only do this on some lab test machines, and not rollout to larger groups until MS provides a better story for managing post mitigated machines. My assumption is that this will be a horror story until October when 24H2 is released.
related Microsoft also released the new phase in Revoking vulnerable Windows boot managers
Guidance for Incident Responders
Microsoft provides some learnings from the field
This set of guides not only boosts analytical capabilities but also contextualizes the evidence within the security frameworks developed by Microsoft over years of incident response
Incident Writeups & Disclosures
How they got in and what they did.
MITRE Response to Cyber Attack in One of Its R&D Networks
MITRE shows incidents can and do happen to anyone.
MITRE today disclosed that despite its fervent commitment to safeguarding its digital assets, it experienced a breach that underscores the nature of modern cyber threats. After detecting suspicious activity on its Networked Experimentation, Research, and Virtualization Environment (NERVE), a collaborative network used for research, development, and prototyping, compromise by a foreign nation-state threat actor was confirmed.
https://www.mitre.org/news-insights/news-release/mitre-response-cyber-attack-one-its-rd-networks
https://medium.com/mitre-engenuity/advanced-cyber-threats-impact-even-the-most-prepared-56444e980dc8
Vulnerability
Our attack surface.
Electron security is closely related to you and me
Chinese research into Electron based application attack techniques. Also shows the long list of vulnerabilities which have stemmed from it.
Offense
Attack capability, techniques and trade-craft.
Sniping at web applications to discover input-handling vulnerabilities
The Journal of Computer Virology and Hacking Techniques was a new one on me.
Ciro Brandi, Gaetano Perrone and Simon Pietro Romano provide this paper which shows there is still value in combining fuzzing techniques.
However, existing literature has often underemphasized the nuances of web-centric fuzzing methodologies. This article presents a comprehensive exploration of fuzzing techniques specifically tailored to web applications, addressing the gap in the current research. Our work presents a holistic perspective on web-centric fuzzing, introduces a modular architecture that improves fuzzing effectiveness, demonstrates the reusability of certain fuzzing steps, and offers an open-source software package for the broader security community.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11416-024-00518-0
MagicDot: A Hacker’s Magic Show of Disappearing Dots and Spaces
Or Yair shows compatibility layers continue to be a gift that keeps on creating vulnerability..
When a user executes a function that has a path argument in Windows, the DOS path at which the file or folder exists is converted to an NT path. During this conversion process, a known issue exists in which the function removes trailing dots from any path element and any trailing spaces from the last path element. This action is completed by most user-space APIs in Windows. By exploiting this known issue, I was able to uncover:
One remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability (CVE-2023-36396) in Windows’s new extraction logic for all newly supported archive types that allowed me to craft a malicious archive that would write anywhere I chose on a remote computer once extracted, leading to code execution.
Two elevation of privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities: one (CVE-2023-32054) that allowed me to write into files without the required privileges by manipulating the restoration process of a previous version from a shadow copy and another that allowed me to delete files without the required privileges.
https://www.safebreach.com/blog/magicdot-a-hackers-magic-show-of-disappearing-dots-and-spaces/
Exploitation
What is being exploited.
More on the PAN-OS CVE-2024-3400
Chandan B.N. leads by example of what all vendors should be doing when their products exhibit vulnerability. Also provides a write-up of what happened around this specific one.
Per our standard product security assurance process, we are performing a Root Cause Analysis to further identify these issues, ensure that they are identified and addressed during development, and continue to enhance product design, including resistance to such attacks.
https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/blog/2024/04/more-on-the-pan-os-cve/
CrushFTP
…
CrushFTP v11 versions below 11.1 have a vulnerability where users can escape their VFS and download system files. This has been patched in v11.1.0. Customers using a DMZ in front of their main CrushFTP instance are partially protected with its protocol translation system it utilizes. A DMZ however does not fully protect you and you must update immediately. (CREDIT:Simon Garrelou, of Airbus CERT)
Can you tell me how I can check if I have been exploited? Not really..the nature of this was common words that could be in your log already. So there is no silver bullet search term to check for. Looking for "<INCLUDE" is an indicator.
https://www.crushftp.com/crush11wiki/Wiki.jsp?page=Update
https://crushftp.com/version11_build.html
Tooling and Techniques
Low level tooling and techniques for attack and defence researchers…
patology: Python script to decrypt Synology .pat files
Expect more vulnerability research for these devices..
https://visit.suspect.network/reversing-adventures/decrypting-synology-patchfiles
https://github.com/sud0woodo/patology
Footnotes
Some other small (and not so small) bits and bobs which might be of interest.
Aggregate reporting
Deterministic storage and retrieval of telecom light from a quantum dot single-photon source interfaced with an atomic quantum memory - “We store single photons from an indium arsenide quantum dot in a high-bandwidth rubidium vapor–based quantum memory, with a total internal memory efficiency of (12.9 ± 0.4)%. The signal-to-noise ratio of the retrieved light field is 18.2 ± 0.6, limited only by detector dark counts.”
SCULI programme set to transform cybersecurity for large-scale infrastructure - “A major new research programme from the Universities of Bristol, Oxford, and Lancaster is set to address the grand challenge of providing cybersecurity at societal scale, following £6.8 million in funding from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC). “
Artificial intelligence
Books
Nothing this week.
Events
Botconf 2024 - videos
Building Community of Good Practice in Cybersecurity - not an event, but a publication - deadline for manuscript submissions: 25 January 2025
Unless stated otherwise, linked or referenced content does not necessarily represent the views of the NCSC and reference to third parties or content on their websites should not be taken as endorsement of any kind by the NCSC. The NCSC has no control over the content of third party websites and consequently accepts no responsibility for your use of them.
This newsletter is subject to the NCSC website terms and conditions which can be found at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/terms-and-conditions and you can find out more about how will treat your personal information in our privacy notice at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/privacy-statement.