CTO at NCSC Summary: week ending April 13th
Leveling up Boards coupled with more security solution vulnerability...
Welcome to the weekly highlights and analysis of the blueteamsec subreddit (and my wider reading). Not everything makes it in, but the best bits do.
Operationally this week more security solution vulnerability, both of which are trivial and shallow. Remember to ask your vendors where on their roadmaps implementation of the Guidance on digital forensics and protective monitoring specifications for producers of network devices and appliancess is and when it will be delivered (yes, this was also in last weeks).
In the high-level this week:
NCSC and partners share guidance for communities at high risk of digital surveillance - UK NCSC publishes - “GCHQ’s National Cyber Security Centre, international and industry partners share new details about spyware used to target individuals in Uyghur, Tibetan and Taiwanese communities.”
Cyber Governance Code of Practice - Department for Science, Innovation and Technology, National Cyber Security Centre and Feryal Clark MP -publish “directors can build resilience to a wide range of cyber risks across their organisation. The Code, which has been co-designed with technical experts from the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) and a range of governance experts across industry, focuses on the actions senior leaders should take to govern cyber risks effectively within their organisation.”
New online training helps board members to govern cyber risk - UK NCSC publishes
Cyber Governance for Boards - UK NCSC publishes
Cyber security breaches survey 2025 - Department for Science, Innovation & Technology and Home Office publish - “Just over four in ten businesses (43%) and three in ten charities (30%) reported having experienced any kind of cyber security breach or attack in the last 12 months. … This represents a decrease in prevalence among businesses compared to 2024 (where 50% experienced a breach or attack)”
Commission unveils ProtectEU – a new European Internal Security Strategy - European Commission announces - “The EU must enhance its resilience against hybrid threats by protecting critical infrastructure, reinforcing cybersecurity and combatting online threats:
Member States to fully implement the CER and NIS2 Directives,
A new Cybersecurity Act, and new measures to secure cloud and telecom services and developing technological sovereignty,
Measures to reduce dependencies on single foreign suppliers and de-risk our supply chains from high-risk suppliers including revision of procurement rules,
Reinforce the security of transport hubs, with an EU Ports Strategy, and new reporting systems to strengthen aviation security, transport and supply chains,
An Action Plan against chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear (CBRN) threats.”
An Analysis of the Cybersecurity Pillar of Australia’s New Counter-Terrorism Strategy - Observer Research Foundation analyses - “The Counter-Terrorism and Violent Extremism Strategy 2025 employs a multi-agency approach and collaborative efforts between ASIO, the Australian Federal Police (AFP), the Australian Cyber Security Centre, and the Five Eyes intelligence-sharing network.”
CHERIoT-Ibex Core is Open Sourced to Enable Memory Safe MCUs - EE Times reports - “The availability of the Sunburst Chip design repository is a key milestone in phase two of the U.K. government’s DSbD/UKRI-funded Sunburst Project (Grant Number: 107540).”
Securing the Digital and Orbital Frontiers in Ukraine - Center for Strategic & International Studies analyses - “Within hours of the announcement of a ceasefire in Ukraine that limited conventional attacks on critical infrastructure and military operations in the Black Sea, something interesting happened: a dueling series of cyberattacks.”
The UK’s New Take on Cyber - Abaigeal Lorge opines - “The United Kingdom views cyber power as the projection of cyber security. With aims to act as “a leading responsible and democratic cyber power” and strategies steeped in the language of both national power and big-picture thinking, the United Kingdom understands cyberspace as a battleground for Great Power Competition and a platform to export values, knowledge and norms.”
Connecting “Cyber Diplomacy” to “Cyber Deterrence” - Stimson Center think tanks - “Yet there is a long-running debate in the cybersecurity and cyber policy communities about the wisdom and practicality of attempting to apply traditional concepts of deterrence to the cyber domain.”
Reporting on/from China
In Secret Meeting, China Acknowledged Role in U.S. Infrastructure Hacks - The Wall Street Journal reports - ”Chinese officials acknowledged in a secret December meeting that Beijing was behind a widespread series of alarming cyberattacks on U.S. infrastructure, according to people familiar with the matter”
Wi-Fi Giant TP-Link’s US Future Hinges on Its Claimed Split From China - Bloomberg reports - “US investigators are probing the China ties of TP-Link Systems Inc., the new American incarnation of a consumer Wi-Fi behemoth, following its rapid growth and a spate of cyber attacks by Chinese state-sponsored actors targeting many router brands.”
Apps With Ties to Chinese Military - Tech Transparency Project shines a light - “TTP’s investigation found that one in five of the top 100 free virtual private networks in the U.S. App Store during 2024 were surreptitiously owned by Chinese companies”
Cyberspace Operations and Chinese Strategy: Unpacking China’s Approach to Digital Dominance - Rajesh Uppal thinks - “Adding fuel to these worries is the perception that China may leverage new technologies to strike directly at American infrastructure, military, and civilian alike. The latest Annual Threat Assessment from the U.S. Director of National Intelligence highlights that China could potentially deploy aggressive cyberspace operations to disrupt and deter American military responses, creating a new and challenging layer of modern warfare.”
Hackers spied on 100 US bank regulators’ e-mails for over a year - Straits Times reports - “Hackers intercepted about 103 bank regulators’ e-mails for more than a year, gaining access to highly sensitive financial information, according to two people familiar with the matter and a draft letter to Congress seen by Bloomberg News.”
House Republicans reintroduce bill to counter Chinese cyber threats to critical infrastructure - Industrial Cyber reports - a re-run of the 2024-2024 bill.
Can China and the West work together to fight cybercrime? - World Economic Forum opines - “History shows that even in the most fraught geopolitical environments, pragmatic, issue-specific cooperation can build trust and foster dialogue that can ultimately lead to greater stability between powers.
Taiwan authorities investigate China's SMIC for hiring engineers disguised as Samoan company - Reuters Japan reports - “According to the Ministry of Justice's investigating authorities, SMIC set up a subsidiary in Taiwan, posing as a Samoan company, to recruit engineers.”
Some Troubled Science Reporting at South China Morning Post - Zichen Wang opines - “Regrettably, alongside its wealth of credible reporting, SCMP has also developed a distinct genre of science stories based entirely on a single paper published in a Chinese (sometimes quasi-) academic journal.”
China built hundreds of AI data centers to catch the AI boom. Now many stand unused - MIT Technology Review observes - “The local Chinese outlets Jiazi Guangnian and 36Kr report that up to 80% of China’s newly built computing resources remain unused.”
Samsung turns to China to prop up ailing chip business - Financial Times reports - “The South Korean electronics group revealed last month that the value of its exports to China jumped 54 per cent between 2023 and 2024, as Chinese companies rush to secure stockpiles of advanced artificial intelligence chips in the face of increasingly restrictive US export controls.”
AI
CAI: An Open, Bug Bounty-Ready Cybersecurity AI - Alias Robotics, Johannes Kepler University and Alpen-Adria-Universität K forecasts - “By 2028 most cybersecurity actions will be autonomous, with humans teleoperating. We present the first classification of autonomy levels in cybersecurity and introduce Cybersecurity AI (CAI), an open-source framework that democratizes advanced security testing through specialized AI agents.”
VibeScamming - From Prompt to Phish: Benchmarking Popular AI Agents’ Resistance to the Dark Side - Guardio Labs analyses - “In this first round, we tested three popular platforms: ChatGPT, Claude, and Lovable. Each responded differently, revealing surprising gaps in resistance to abuse. Some offered tutorials, others delivered production-ready phishing kits with zero pushback.”
AI 2027 - Daniel Kokotajlo, Scott Alexander, Thomas Larsen, Eli Lifland and Romeo Dean forecasts - “We wrote a scenario that represents our best guess about what that might look like.1 It’s informed by trend extrapolations, wargames, expert feedback, experience at OpenAI, and previous forecasting successes.”
Announcing the Agent2Agent Protocol (A2A) - Google announce taking the human out of the loop - “This collaborative effort signifies a shared vision of a future when AI agents, regardless of their underlying technologies, can seamlessly collaborate to automate complex enterprise workflows and drive unprecedented levels of efficiency and innovation.”
Advances and Challenges in Foundation Agents: From Brain-Inspired Intelligence to Evolutionary, Collaborative, and Safe Systems - a cast of many publish - “This survey provides a comprehensive overview, framing intelligent agents within a modular, brain-inspired architecture that integrates principles from cognitive science, neuroscience, and computational research.”
Microsoft unveils AI assistant with ‘memory’ - Financial Times reports - “The Seattle-based group at an event on Friday to mark its 50th anniversary announced a personalised “Copilot” that develops a “memory” and can recall important details, such as family birthdays and hobbies.”
Africa’s first ‘AI factory’ could be a breakthrough for the continent - CNN reports - “last week’s announcement from Cassava Technologies, a tech firm founded by Zimbabwean telecoms billionaire Strive Masiyiwa, that it would be building Africa’s first “artificial intelligence factory,” in partnership with leading AI chipmaker Nvidia.”
PaperBench: Evaluating AI’s Ability to Replicate AI Research - OpenAI evaluates - “We introduce PaperBench, a benchmark evaluating the ability of AI agents to replicate state-of-the-art AI research… We evaluate several frontier models on PaperBench, finding that the best-performing tested agent, Claude 3.5 Sonnet (New) with open-source scaffolding, achieves an average replication score of 21.0%. Finally, we recruit top ML PhDs to attempt a subset of PaperBench, finding that models do not yet outperform the human baseline.”
Llama 4 - Meta releases - “Llama 4 Scout, a 17 billion active parameter model with 16 experts, is the best multimodal model in the world in its class and is more powerful than all previous generation Llama models, while fitting in a single NVIDIA H100 GPU.”
Cyber proliferation
Court document reveals locations of WhatsApp victims targeted by NSO spyware - TechCrunch reports - “The countries with the most victims of this campaign are Mexico, with 456 individuals; India, with 100; Bahrain with 82; Morocco, with 69; Pakistan, with 58; Indonesia, with 54; and Israel, with 51”
Spyware Maker NSO Group Is Paving a Path Back - WIRED reports - “The Israeli spyware maker, still on the US Commerce Department’s “blacklist,” has hired a new lobbying firm”
Bounty Hunting
ICC Office of the Prosecutor launches public consultation on policy on cyber-enabled crimes under the Rome Statute - International Criminal Court consults - “The Office welcomes the engagement of all stakeholders in this new initiative to advance accountability for crimes under the Rome Statute enabled by conduct in cyberspace.”
Operation Endgame follow-up leads to five detentions and interrogations as well as server takedowns - Europol announces - “In a coordinated series of actions, customers of the Smokeloader pay-per-install botnet, operated by the actor known as ‘Superstar’, faced consequences such as arrests, house searches, arrest warrants or ‘knock and talks’.”
Taiwan uncovers identity of Chinese hacker 'Crazyhunter' in Mackay Memorial Hospital cyberattack - Taiwan News reports - “Taiwan’s Criminal Investigation Bureau has uncovered the identity of “Crazyhunter,” who attacked Mackay Memorial Hospital and several medical institutions, schools, and companies in February and March.”
Marsh introduces CyberShore Bermuda exclusive excess cyber insurance facility - Resinsurance News reports- “CyberShore Bermuda offers up to $30 million in follow-form excess Bermuda coverage, with a threshold starting at $75 million.”
No reflections this week, but here is a podcast I recorded in December with Cynam - Secure By Design: Building Cyber Resilience.
Not getting this via email? Subscribe:
Think someone else would benefit? Share:
All attribution is by others and not the UK Government unless specifically stated as such, please see the legal text at the end.
Have a lovely Saturday..
Ollie
Cyber threat intelligence
Who is doing what to whom and how allegedly.
Reporting on Russia
Targeted espionage activity UAC-0226 against innovation centers, government and law enforcement agencies using the GIFTEDCROOK stealer
Ukrainian CERT detail this alleged Russian operation which is only notable due to the vintage tradecraft on show.
The initial compromise is achieved by distributing emails with attachments in the form of XLS documents with macros (extension ".xlsm"), the names/topics of which may relate to issues of demining the territory, administrative fines, UAV production, compensation for destroyed property, etc.
https://cert.gov.ua/article/6282946
Shuckworm Targets Foreign Military Mission Based in Ukrain
Symantec details this alleged Russian operation and whilst the initial access method is not detailed the use of Tor as a backup data exfiltration method is of note. The fact that fall back methods are being employed implies a want for a degree of operational resiliency.
Shuckworm’s relentless focus on Ukraine has continued into 2025, with the group targeting the military mission of a Western country based in the Eastern European nation.
In this campaign, the attackers appear to be using an updated version of their GammaSteel tool. GammaSteel is an infostealer that exfiltrates data from victim networks.
They are also seen using cURL alongside Tor as a backup method of data exfiltration.
https://www.security.com/threat-intelligence/shuckworm-ukraine-gammasteel
Gamaredon’s Flux-Like Infrastructure
Hunt.io gives a sense of the underlying infrastructure used by this alleged Russian actor to provide them some resilience.
Gamaredon continues to operate a wide infrastructure footprint, relying heavily on .ru domains registered through REGRU-RU. Between March 31 and April 7, Hunt.io scanners identified over 30 servers linked to the group.
The majority were hosted by DigitalOcean, with BL Networks making up a number of the IPs with resolving domains. This reinforces previous reporting that the actors rely on VPS providers.
https://hunt.io/blog/state-sponsored-activity-gamaredon-shadowpad
Windows Remote Desktop Protocol: Remote to Rogue
Rohit Nambiar details an alleged historic Russian campaign which exhibits a degree of technical novelty. Using RDP to only redirect resources is a subtle one..
In October 2024, Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) observed a novel phishing campaign targeting European government and military organizations that was attributed to a suspected Russia-nexus espionage actor we track as UNC5837. The campaign employed signed .rdp file attachments to establish Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) connections from victims' machines. Unlike typical RDP attacks focused on interactive sessions, this campaign creatively leveraged resource redirection (mapping victim file systems to the attacker servers) and RemoteApps (presenting attacker-controlled applications to victims). Evidence suggests this campaign may have involved the use of an RDP proxy tool like PyRDP to automate malicious activities like file exfiltration and clipboard capture. This technique has been previously dubbed as “Rogue RDP.”
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/windows-rogue-remote-desktop-protocol
Reporting on China
GOFFEE continues to attack organizations in Russia
Oleg Kupreev details an alleged Chinese operation against Russia. The use of a non-public version of Mythic agent is of note.
GOFFEE updated distribution schemes.
A previously undescribed implant dubbed PowerModul was introduced.
GOFFEE is increasingly abandoning the use of PowerTaskel in favor of a binary Mythic agent for lateral movement.
Currently, several infection schemes are being used at the same time. The starting point is typically a phishing email with a malicious attachment, but the schemes diverge slightly from there. We will review two of them relevant at the time of the research.
https://securelist.com/goffee-apt-new-attacks/116139/
How ToddyCat tried to hide behind AV software
Andrey Gunkin details an alleged Chinese operations which used a sideloading issue in ESET to mask their activities and achieve their aims. A level of technical sophistication on show here and ability to invest in the requisite R&D.
In early 2024, while investigating ToddyCat-related incidents, we detected a suspicious file named version.dll in the temp directory on multiple devices.
This 64-bit DLL, written in C++, turned out to be a complex tool called TCESB. Previously unseen in ToddyCat attacks, it is designed to stealthily execute payloads in circumvention of protection and monitoring tools installed on the device.
..
a component of ESET’s EPP solution – a scanner launched from the command line (ESET Command line scanner). Dynamic analysis showed that the scanner insecurely loads the system library version.dll, first checking for the file in the current directory, then searching for it in the system directories. This can result in a malicious DLL library being loaded, which constitutes a vulnerability.
https://securelist.com/toddycat-apt-exploits-vulnerability-in-eset-software-for-dll-proxying/116086/
Indictments and Leaks: Different but Complementary Sources
Natto Team show the value of multi-open-source intelligence..
Although the Natto Team have done a great deal of research into the leaked documents from i-SOON in the past year (see here, here, here and here), the recently unsealed official documents related to i-SOON – including the indictment, a Most Wanted poster for the indicted i-SOON employees, and a warrant for seizure of Internet domains controlled by sometime i-SOON associate Zhou Shuai – provide new information and can yield insights that we might have missed before. Therefore, in this post, we would like to use i-SOON as a case study to evaluate how to leverage sources such as leaks and indictments. The Natto Team believes this approach is very helpful to sharpen up CTI analysts’ analytic process and learn how to evaluate and maximize the value of research sources.
Reporting on North Korea
Suspected Kimsuky (APT-Q-2) attacks South Korean companies
QiAnXin Threat Intelligence Center detail this alleged North Korean operation which is notable for using stolen code signing certificates.
One of the samples released software signed by the South Korean software manufacturer BlueMoonSoft to confuse victims.
Russian accent in the DPRK related cyber operations
Blackbigswan asserts that through there analysis there is evidence of co-operation or influence between these two nations potentially in the cyber domain.
The evidence suggests these operators are consuming niche Russian military content rather than mainstream Western media, indicating their geographical and ideological positioning. It’s also the first time we encounter such specific choice of an avatar, as in most cases, these are generic. No other accounts within this cluster used any image of such type.
This finding adds to growing evidence of deepening Russia-DPRK cooperation beyond conventional military aid, potentially extending into the cyber domain with shared personnel or operational protocols.
https://www.ketman.org/russia-dprk-soft-connection.html
Reporting on Iran
Nothing of note this week
Reporting on Other Actors
Goodbye HTA, Hello MSI: New TTPs and Clusters of an APT driven by Multi-Platform Attacks
Sathwik Ram Prakki details an alleged Pakistani operation against Indian targets. Noteworthy for the fact that the threat actor is using a mixture of open source implants which they are evolving.
Usernames associated with attacker email IDs are impersonating a government personnel member with cyber security background, utilizing compromised IDs.
A fake domain mimicking an e-governance service, with an open directory, is used to host payloads and credential phishing login pages.
Thirteen sub-domains and URLs host login pages for various RTS Services for multiple City Municipal Corporations (CMCs), all in the state of Maharashtra.
The official domain of National Hydrology Project (NHP), under the Ministry of Water Resources, has been compromised to deliver malicious payloads.
New tactics such as reflective loading and AES decryption of resource section via PowerShell to deploy a custom version of C#-based open-source tool XenoRAT.
A modified variant of Golang-based open-source tool SparkRAT, is targeting Linux platforms, has been deployed via the same stager previously used for Poseidon and Ares RAT payloads.
A new RAT dubbed CurlBack utilizing DLL side-loading technique is used. It registers the victim with C2 server via UUID and supports file transfer using curl.
… targeted sector
Railways
Oil & Gas
External Affairs
Defence
Discovery
How we find and understand the latent compromises within our environments.
100 Days of KQL
Aura continues to pump out the goodness..
Execution from a Low Prevalence, Non-Signed or Invalidly Signed Binary from C:\Windows
Logon Attempts from LDAP Bind Accounts to System other than DCs
Hooking Context Swaps with ETW
Archie details a potentially super powerful technique here. It ones again shows that cyber lags the game cheat/anti-cheat arms race..
Many anti-cheat solutions have started hooking context swaps in an effort to create hidden memory regions that are only visible to certain threads in the system. One notable example is Riot Vanguard which uses a different method that I’ll definitely write about in the near future.
The hook can also be used to detect threads executing in unsigned memory, as there’s little preventing you from walking the stack of the old thread, and seeing whether code is running in any region it shouldn’t be.
https://archie-osu.github.io/etw/hooking/2025/04/09/hooking-context-swaps-with-etw.html
A Standard for Safe and Reversible Sharing of Malicious URLs and Indicators
Draft RFC for everyone to get involved in
This document defines a consistent and reversible method for sharing potentially malicious indicators of compromise (IOCs), such as URLs, IP addresses, email addresses, and domain names. It introduces a safe obfuscation format to prevent accidental execution or activation when IOCs are displayed or transmitted. These techniques aim to standardize the safe dissemination of threat intelligence data. This specification uses the URI syntax defined in RFC 3986 and follows the key word conventions from RFC 2119.
https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-grimminck-safe-ioc-sharing/
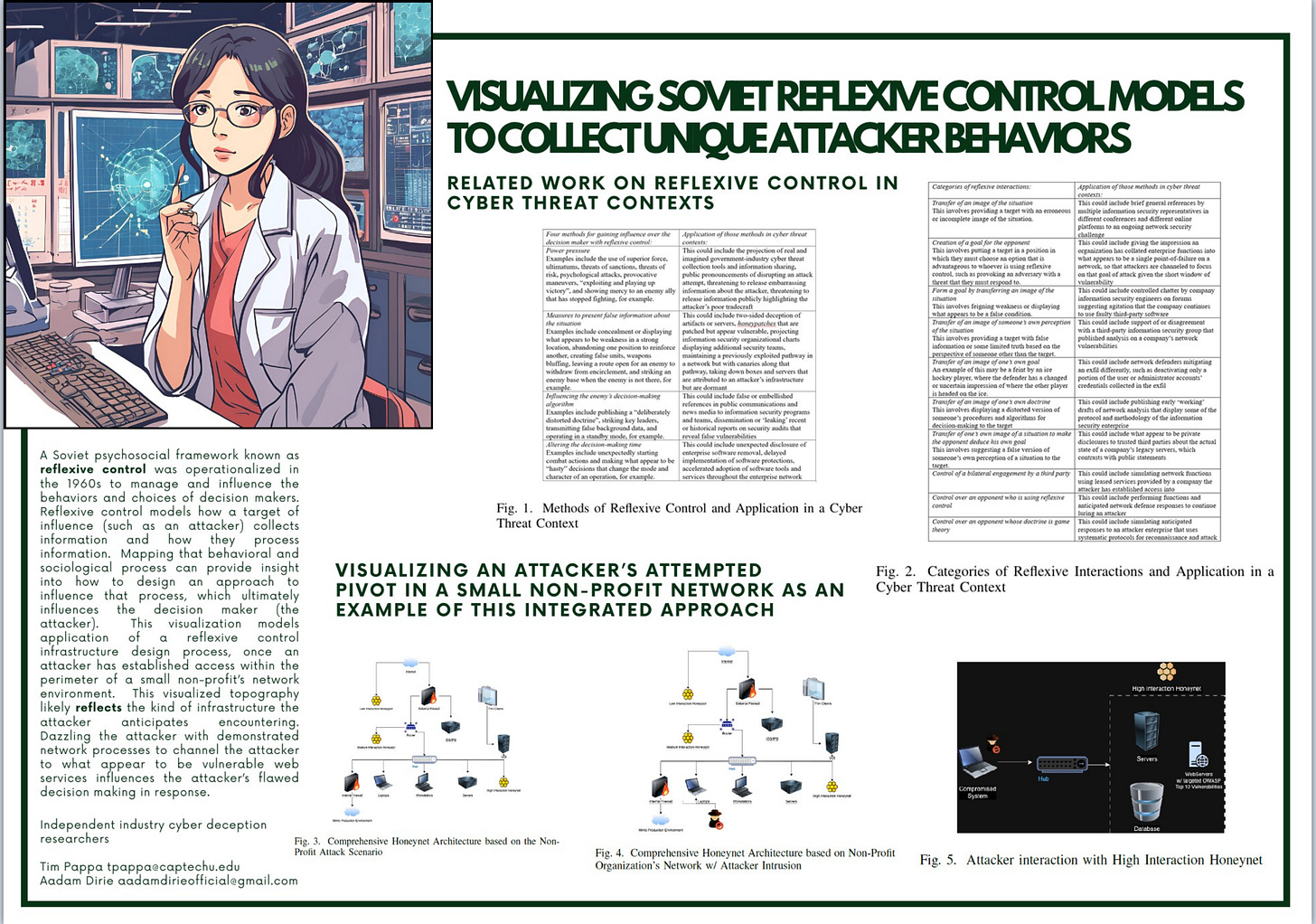
Poster on Cyber Deception
Tim Pappa and Aadam Dirie as shown at 20th International Conference on Cyber Warfare and Security. The full paper will be presented in June at the 24th European Conference on Cyber Warfare and Security.
Defence
How we proactively defend our environments.
Stopping attacks against on-premises Exchange Server and SharePoint Server with AMSI
Microsoft Threat Intelligence show that IIS modules are coming back into vogue..
In both SharePoint Server and Exchange Server, AMSI is integrated as a security filter module within the IIS pipeline to inspect incoming HTTP requests before they are processed by the application. The filter is triggered at the onBeginRequest stage through the SPRequesterFilteringModule for SharePoint Server and HttpRequestFilteringModule for Exchange Server, allowing it to analyze incoming requests before they reach authentication and authorization phases. This integration ensures that potential threats are identified before they interact with internal processing, mitigating the risk of exploitation.
Incident Writeups & Disclosures
How they got in and what they did.
Qilin affiliates spear-phish MSP ScreenConnect admin, targeting customers downstream
Anthony Bradshaw, Colin Cowie, Hunter Neal, Neal Rajguru and Sean Gallagher detail an incident of nightmares. This is why Managed Service Providers are a critical supply chain element.
Late in January 2025, a Managed Service Provider (MSP) administrator received a well-crafted phishing email containing what appeared to be an authentication alert for their ScreenConnect Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tool. That email resulted in Qilin ransomware actors gaining access to the administrator’s credentials—and launching ransomware attacks on the MSP’s customers.
Signed. Sideloaded. Compromised!
Ontinue detail a real-world instance of vishing(ish). You can decide if it meets what we might think of the definition.
the team identified a sophisticated multi-stage attack leveraging vishing, remote access tooling, and living-off-the-land techniques to gain initial access and establish persistence.
The threat actor exploited exposed communication channels by delivering a malicious PowerShell payload via a Microsoft Teams message, followed by the use of Quick Assist to remotely access the environment. This led to the deployment of signed binaries (e.g., TeamViewer.exe), a sideloaded malicious DLL (TV.dll), and ultimately a JavaScript-based C2 backdoor executed via Node.js.
..Our investigation revealed that the actor employed social engineering tactics to execute a vishing attack. This involved sending a message to the target through Microsoft Teams by creating an external chat. The actor transmitted a PowerShell command directly via the Teams message and also utilised the QuickAssist remote tool to gain access to the target device remotely.
https://www.ontinue.com/resource/blog-signed-sideloaded-compromised/
Check Point response to the BreachForum post on 30 March 2025
Check Point shows a degree of transparency..
On March 30th, 2025, a BreachForum post offered to sell alleged hacked Check Point data. This relates to an old, known, and pinpointed event from several months ago, which we addressed at the time and had no security implications.
This event included 3 organizations' tenants in a portal that does not include customers' systems, production or security architecture. The event did not include the description detailed in the post.
The event was addressed immediately and thoroughly investigated. These organizations were updated and handled at the time, and this post is recycling this old, irrelevant information.
We are sharing here some additional context which helps scope this event:
The post relates to an event from December 2024, stems from compromised credentials of a portal account with limited access.
It was limited to a list of several account names with product names, 3 customers' accounts with contact names, and a list of some Check Point employees' emails. As said, this does not include customers' systems, production, or security architecture.
The content of the post falsely implies exaggerated claims which never happened. The portal has different internal mitigations.
Our thorough investigation concluded that there is no risk to Check Point customers and there are no security implications.
https://support.checkpoint.com/results/sk/sk183307
Vulnerability
Our attack surface.
CVE-2024-48887: Unverified password change via set_password endpoint
https://fortiguard.fortinet.com/psirt/FG-IR-24-435
CVE-2025-22457: Ivanti Connect Secure, Policy Secure & ZTA Gateways
Ivanti making the case for CHERI, greater transparency around first party code and market incentives more generally
A stack-based buffer overflow in Ivanti Connect Secure before version 22.7R2.6, Ivanti Policy Secure before version 22.7R1.4, and Ivanti ZTA Gateways before version 22.8R2.2 allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to achieve remote code execution.
Further analysis
https://attackerkb.com/topics/0ybGQIkHzR/cve-2025-22457/vuln-details
Proof of concept
https://github.com/sfewer-r7/CVE-2025-22457
Unsafe at Any Speed: Abusing Python Exec for Unauth RCE in Langflow AI
Naveen Sunkavally provides further evidence that our AI future is built on sand currently..
We discovered an interesting code injection vulnerability, CVE-2025-3248, in Langflow, a popular tool used for building agentic AI workflows. This vulnerability is easily exploitable and enables unauthenticated remote attackers to fully compromise Langflow servers. The issue is patched in Langflow 1.3.0, and we encourage all users to upgrade to the latest version.
SoK: Security of Programmable Logic Controllers
Efrén López-Morales, Ulysse Planta, Carlos Rubio-Medrano, Ali Abbasi and Alvaro A. Cardenas provide a value piece of work.
In this study, we conduct the first comprehensive systematization of knowledge that explores the security of PLCs: We present an in-depth analysis of PLC attacks and defenses and discover trends in the security of PLCs from the last 17 years of research. We introduce a novel threat taxonomy for PLCs and Industrial Control Systems (ICS). Finally, we identify and point out research gaps that, if left ignored, could lead to new catastrophic attacks against critical infrastructures.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.00280
Enterprise equipment security equipment vulnerability analysis and utilization
Swing from China provides an overview of western security solutions and their vulnerabilities..
https://bestwing.me/Security-Equipment-Vulnerability-Research.html
GOP Complex: Image parsing bugs, EBC polymorphic engines and the Deus ex machina of UEFI exploit dev
ic3qu33n’s talk is now available..
This talk combines hardware hacking and platform firmware reverse engineering and exploit development and will cover the following:
UEFI software testing/debugging techniques with emulators
UEFI hardware debugging and testing techniques
UEFI reverse engineering
Assembly programming techniques for developing UEFI shellcode on different architectures (x86-64, aarch64 and EBC)
PCI Option ROM hacking
What happens when you combine the exploit primitives in a vulnerable image parsing driver impacted by LogoFAIL, PCI Option ROM hacking, the oft-forgotten and neglected EBC (EFI Byte code) architecture and a dash of low-level graphics programming? GOP Complex.
https://github.com/ic3qu33n/REcon2024-GOP-Complex
Offense
Attack capability, techniques and trade-craft.
peeko
b3rito provides a capability which detection engineers will want to get after..
peekois a browser-based XSS-powered C2 (Command and Control) tool that leverages the victim’s browser as a stealthy proxy inside internal networks.Through an injected XSS payload, peeko establishes a WebSocket connection to a central server, allowing an attacker to remotely control the victim’s browser to send requests to internal services, scan networks, exfiltrate data, or even execute arbitrary JavaScript — all without dropping a single binary.
https://github.com/b3rito/peeko
Weaponizing DCOM for NTLM authentication coercions
Andrew Oliveau provides a capability which should be able to detect..
We’ll briefly cover the fundamentals of COM and its distributed counterpart, Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM), dive into the RunAs setting and why authentication coercions are impactful and introduce a new credential harvesting tool - RemoteMonologue.
https://www.ibm.com/think/x-force/remotemonologue-weaponizing-dcom-ntlm-authentication-coercions
QuicCourier: Leveraging the Dynamics of QUIC-Based Website Browsing Behaviors Through Proxy for Covert Communication
Jianan Huang, Weiwei Liu, Guangjie Liu, Bo Gao and Fengyuan Nie out of China detail a technique which is novel to say the least. Might just want to have assurance you would detect it.
Network covert channels transmit secret messages by manipulating network traffic, including packet headers, timing intervals, and communication patterns. The growth of network services has spurred interest in exploring these channels. Yet, the practical application of these channels faces challenges in transmission rate and reliability due to unpredictable network interference. QUIC-based websites offer promising opportunities for covert communication, given their inherent dynamic nature from web resource updates and network interferences. Repeated visits or refresh actions on the same website generate substantial statistical redundancy. Furthermore, widely used proxy tools introduce additional traffic morphology changes. This paper presents QuicCourier, a covert channel leveraging web traffic's dynamic characteristics and proxy service encapsulation to hide messages in QUIC packets from the service node to the client. Guided by a generative model for web resource patterns, QuicCourier ensures that covert traffic closely resembles legitimate traffic, employing three packet-wise meta operations. The altered QUIC flows are then encased in proxy protocols, complicating the detection of embedded information. The covert receiver is incorporated into the proxy client. The efficacy of QuicCourier is evaluated using a dataset of over 30,000 web browsing traffic samples, demonstrating its exceptional undetectability against state-of-the-art traffic classification tools and a high covert transmission rate.
https://www.computer.org/csdl/journal/tq/5555/01/10916752/24TAwn09eRq
Exploitation
What is being exploited..
Analysis of Threat Actor Activity
Fortinet detail old-day permutations..
During this investigation, a threat actor was observed using known vulnerabilities (e.g. FG-IR-22-398, FG-IR-23-097, FG-IR-24-015) to gain access to Fortinet devices. The targeting of known, unpatched vulnerabilities by a threat actor is not new and has been previously examined; this specific finding is the result of a threat actor taking advantage of a known vulnerability with a new technique to maintain read-only access to vulnerable FortiGate devices after the original access vector was locked down. Immediately upon discovery, we activated our PSIRT response efforts, developed necessary mitigations and have communicated with affected customers. We continue to work directly with those customers to ensure they have taken steps to remediate the issue.
PoC for CVE-2025-22457
Stephen Fewer release an exploit.. now we get to watch the world burn..
A remote unauthenticated stack based buffer overflow affecting Ivanti Connect Secure, Pulse Connect Secure, Ivanti Policy Secure, and ZTA Gateways
This is a proof of concept exploit to demonstrate exploitation of CVE-2025-22457.
https://github.com/sfewer-r7/CVE-2025-22457
Tooling and Techniques
Low level tooling and techniques for attack and defence researchers…
GoResolver: Using Control-flow Graph Similarity to Deobfuscate Golang Binaries, Automatically
Killian Raimbaud and Paul Rascagneres releases a powerful tool which should inspire other applications.
Go language (Golang) is increasing in popularity with developers of both legitimate and malicious tooling.
Volexity frequently encounters malware samples written in Golang that apply obfuscators to hinder analysis.
Obfuscated Golang malware samples are significantly harder to statically analyze for reverse engineers.
Volexity has developed an open-source tool, GoResolver, to retrieve obfuscated functions names.
GoResolver’s control-flow graph similarity techniques offer a significant advantage in recovering symbol information.
Pishi Reloaded
Meysam helps surface shallow vulnerabilities..
XNU has a KASAN build (will describe this later) in KDK, or even you can build a KASAN version of it, but KEXTs are not included. So, whenever you fuzz a KEXT, a vulnerability may go unnoticed. This is why I decided to work on this project.
https://r00tkitsmm.github.io/fuzzing/2025/04/10/Pishi2.html
Using big models to explore the secrets of patch codes
Xiao Ming applies AI to do patch diffing and produce proof of concepts using DeepSeek. The boiling frog moment of AI continues..
This paper will explore how to use large language models (LLMs) to help us complete this process more efficiently.
..
This article explores in depth how to discover Android system vulnerabilities by analyzing patch codes, and elaborates on the complete call chain of the package name renaming mechanism in PackageManagerService
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bI-QTfiAeN9znFHOtA_3eQ
Footnotes
Some other small (and not so small) bits and bobs which might be of interest.
Annual report
Advanced Threat Research Report (2025 Edition) - by NSFOCUS in China
Panorama de la cybermenace 2024 - ANSSI published (in March) - “In total, 3004 reports2 and 1361 incidents3 were brought to ANSSI’s attention.”
Human resource management in cybercriminal organizations: an exploratory analysis - not a manual
Back in the Game: Privacy Concerns of Second-Hand Game Consoles
Use FAIR to Build an ISO 27001-Based Cyber Risk Management Program
Cybersecurity for space systems - BSI Germany
Tech’s security challenges in space - Politico
Bug Framework (BF): Formalizing Cybersecurity Weaknesses and Vulnerabilities - from summer 2024
Artificial intelligence
Books
Events
OpenAI Security Research Conference - after RSAC '25
UNIDIR Cyber Stability Conference 2025 - 12 May 2025, Hybrid, in person (Geneva) and online
Technical Innovations for AI Policy Conference, - Saturday, May 31 – Sunday, June 1 in Washington, D.C.
LLMSEC 2025 - Aug 1, 2025 in Vienna, Austria
Video of the week - Cybersecurity is Local, Too: Assessing the State and Local Cybersecurity Grant Program
Unless stated otherwise, linked or referenced content does not necessarily represent the views of the NCSC and reference to third parties or content on their websites should not be taken as endorsement of any kind by the NCSC. The NCSC has no control over the content of third party websites and consequently accepts no responsibility for your use of them.
This newsletter is subject to the NCSC website terms and conditions which can be found at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/terms-and-conditions and you can find out more about how will treat your personal information in our privacy notice at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/privacy-statement.



Hey OW, not for nothin...but who is Rajesh Uppal? Why did you cite him? One of his pieces?