CTO at NCSC Summary: week ending August 18th
The game this week... count the number of instances of phishing for initial access..
Welcome to the weekly highlights and analysis of the blueteamsec subreddit (and my wider reading). Not everything makes it in, but the best bits do.
Operationally this week nothing overly of note unless you consider phishing being sprayed around allegedly by Russia, North Korea and Iran to be notable.. also make sure you play along this week with how many times phishing was used for initial access.
In the high-level this week:
Post-quantum cryptography: what comes next? - NCSC UK details - “Longer term, we plan to be able to accredit suitable consultants and consultancies through our existing schemes. In the nearer term, we will be exploring efficient ways to connect organisations with the expertise they need, in a way that scales to a UK-wide migration.”… Focus is:
Support to regulation
Support to central government
Helping all organisations get good advice.
Building a nation-scale evidence base for cyber deception - NCSC UK announces - “As part of this endeavour, we see two primary use cases for the technologies and solutions to provide value in cyber defence:
low-interaction solutions such as digital tripwires and honeytokens to alert to unauthorised access – when deployed by all organisations
low-interaction and high-interaction honeypots to collect threat intelligence both at internet scale and as discrete instances – when deployed by organisations with mature security operations capabilities, as well as managed cyber security service providers”
Cyber Resilience Audit scheme open to applications - NCSC UK announces - “A new NCSC scheme assuring providers of CAF-based audits is now open for potential members.”
NIST Releases First 3 Finalized Post-Quantum Encryption Standards - NIST press releases - “The standards — containing the encryption algorithms’ computer code, instructions for how to implement them, and their intended uses — are the result of an eight-year effort managed by NIST, which has a long history of developing encryption.”
There is an urgent need to enact cyber security laws and revise espionage laws to protect national security and public safety - People Power Party of South Korea reflects - “Recently, investigative authorities discovered that key technology for the K-2 tank, the main tank of the Korean Army and exported to Poland, was leaked. In addition, it was confirmed that technical data related to the Baekdu and Geumgang reconnaissance planes, our military's core aerial reconnaissance asset against North Korea, were hacked by suspected North Korean forces. There is a growing possibility that North Korea will use stolen Korean technology to evade our military's surveillance. “
Warner, Lankford Announce Legislation to Strengthen Federal Cybersecurity Measures, Implement Mandatory Vulnerability Disclosure Policies - U.S. Sens. Mark R. Warner (D-VA), Chairman of the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence, and James Lankford (R-OK), a member of the Senate Committee on Homeland Security & Governmental Affairs announce - “the Federal Contractor Cybersecurity Vulnerability Reduction Act of 2024, legislation they will introduce to strengthen federal cybersecurity by ensuring that federal contractors adhere to guidelines set forth by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Companion legislation, introduced in the House of Representatives, is being led by Rep. Nancy Mace (R-SC-01).”
Moolenaar, Krishnamoorthi Call for Investigation into Chinese Wi-Fi Routers in U.S. Vulnerable to CCP Hacking & Data Harvesting - The Select Committee on the CCP announces - “the House Select Committee on the Strategic Competition Between the United States and the Chinese Communist Party identified the growing risk posed by Chinese Wi-Fi routers in the United States manufactured by TP-Link Technologies and called on the Department of Commerce to verify this threat and investigate the company.”
Biden-Harris Administration Releases Summary Report of 2023 RFI on Open Source-Software Security Initiative - The White House releases - “A defensible, resilient, and flourishing open-source ecosystem will require further collaboration and coordinated investment from public and private sectors alike.”
South Korea’s 2024 Cyber Strategy: A Primer - Center for Strategic & International Studies primes - “Another important feature of ROK’s new strategy is that it openly names North Korea as the biggest threat to ROK cybersecurity and proposes specific measures to counter the threat. In 2023, North Korea launched an estimated 1.3 million cyberattacks per day on ROK public institutions alone.”
[US] Army Cyber Protection Brigade-led exercise brings multiple service elements, components together - US Army announces - “Exercise Grungy Zion is the Cyber Protection Brigade’s annual certification exercise,” said Col. Christopher Stauder, CPB commander. “Historically, this exercise has been focused on certifying mission elements, cyber protection teams, and battalion-size task forces. This year the CPB took a giant step forward in certifying the brigade headquarters as a maneuver element and by incorporating multiple partners into this exercise.”
Triad panel informs SMD Symposium - DVIDS details “Over the past year, we’ve also postured our alert cyberattack to begin moving from experimentation into actual operations with the joint force,”
Rwanda National Cybersecurity Strategy 2024-2029 - Government of Rwanda publishes - “This strategy formalises an ambitious plan that will not only increase Rwanda’s cybersecurity level, but that will also support national strategies in other areas of country development (e.g., digitalisation) and that will promote the role of Rwanda in the international cybersecurity arena.”
Reporting on/from China
Tech Bros Are Betting They Can Help Win a War With China - Wall Street Journal reports - “The amount of private capital flowing into the venture-backed defense-tech industry has ballooned, with investors spending at least 70% more on the sector each of the past three years than any prior year. From 2021 through mid-June 2024, venture capitalists invested a total of $130 billion in defense-tech startups, according to data firm PitchBook. The Pentagon spends about $90 billion on R&D annually.”
Internationalizing Chinese standards through infrastructure experimentation: Engineering a pumped storage hydropower project in Israel - Sage Journals publishes - “This ethnographic study examines the implementation of Chinese engineering standards in a multinational pumped storage hydropower project in Israel. Using an ethnographic approach, the study investigates how Chinese standards are negotiated, accepted or rejected within local engineering practice and how Chinese engineers experience the international adoption of their knowledge.”
China-Backed Apollo Future Mobility Offloads Holding in Sensitive U.S. Business - Caixan Global reports - “Apollo Future Mobility Group Ltd., a Hong Kong-traded investment company with China backing, announced the sale of its holding in an American 3D printing company citing concerns over U.S. national security scrutiny.”
Artificial intelligence
What are the risks from Artificial Intelligence? - MIT evidences - “A comprehensive living database of over 700 AI risks categorized by their cause and risk domain “
Paper and Spreadsheet
Policy for the responsible use of AI in government [Australia] - v1.1 - Australian Government Digital Transformation Agency releases.
Cyber Risks Associated with Generative Artificial Intelligence - Monetary Authority of Singapore notes - “MAS has published an information paper on “Cyber Risks Associated with Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI)”. The paper aims to raise financial institutions’ (FIs) awareness by providing an overview of key cyber threats arising from GenAI, the risk implications, and some of the mitigation measures that FIs could take to address the risks. “
China wrestles with ‘quantity over quality’ in generative AI patents - Aljazeera reports - “China has emerged as the world’s top producer of generative AI patents, but it is struggling to turn many of its ideas into action thanks to US export controls and longstanding struggles with its innovation culture at home.”
Cyber proliferation
UK and France consult on commercial cyber intrusion capabilities - Foreign Commonwealth & Development Office issues - “Through this consultation, we invite stakeholders to share views on good practice relating to commercial cyber intrusion capabilities (CCICs) across 3 stakeholder groups:
states: as regulators and potential customers of the market for CCICs
industry organisations: involved in and around the market for CCICs, alongside their wider value chain
civil society, experts, and threats researchers : with relevant expertise on the threat presented by the market for CCICs, and responses to it “
Bounty Hunting
Suspected head of prolific cybercrime groups arrested and extradited - UK National Crime Agency press releases - “Investigators established that these individuals were responsible for the development and distribution of notorious ransomware strains, including Reveton and most recently Ransom Cartel, as well as exploit kits, including Angler, which have extorted tens of millions from victims worldwide.”
Russian Citizen Sentenced to 40 Months for Selling Stolen Financial Information on the Criminal Internet Marketplace Slilpp - US Department of Justice reports - ”According to court documents, between July 2016 and May 2021, Kavzharadze, using the name “TeRorPP,” listed over 626,100 stolen login credentials for sale on Slilpp and sold more than 297,300 of them on the illegal marketplace. Those credentials were subsequently linked to $1.2 million in fraudulent transactions.”
Cyber insurers are winners from the biggest ever IT outage - Financial Times reports - “Moreover, insurers can and should mitigate the risk by careful underwriting. In 2021, Beazley shed large numbers of policyholders that lacked adequate controls. It has pioneered cyber catastrophe bonds to offload some its risk. It also imposes exclusions and limits in case of war, a malware disruption of a sovereign state or a prolonged cloud outage of 72 hours or more.”
‘A market of constant change’: Cyber insurance evolution and opportunities - Insurance Business reports - “Overall, however, North is optimistic about the growth potential for the sector, telling IB that there are estimates predicting “multi-billion dollar growth in gross written premium for cyber insurance over the next few years.””
Reflections this week come off the back of the Post Quantum Computer crypt algorithm standardisation. There is a real risk that a faux rush will now begin to transition. Why? Well it risks being powered by marketing/vendor hype stoking fear. Jeremy’s post on Post-quantum cryptography: what comes next? is important as it outlines the reality and our perspective. We now need protocols to be updated, then implemented with the new algorithms and then those implementations tested and verified etc. No small amount of work..
This is why we are being very clear that we recommend that cataloguing cryptographic usage starts now whilst the rest of the implementation pipeline catches up. This is also why we are looking to certify/accredit consultants in the UK who have the skills and experience to provide the requisite professional advice on a national cryptographic transition project that will take over a decade in practice to complete...
Think someone else would benefit? Share:
All attribution is by others and not the UK Government unless specifically stated as such, please see the legal text at the end.
Have a lovely Friday..
Ollie
Cyber threat intelligence
Who is doing what to whom and how allegedly.
Reporting on Russia
Sophisticated Phishing Targets Russia’s Perceived Enemies Around the Globe
John Scott-Railton, Rebekah Brown, Ksenia Ermoshina, and Ron Deibert detail this alleged Russian campaign using… 🥁… phishing!
Sophisticated spear phishing campaign has been targeting Western and Russian civil society.
This campaign, which we have investigated in collaboration with Access Now and with the participation of numerous civil society organizations including First Department, Arjuna Team, and RESIDENT.ngo, engages targets with personalized and highly-plausible social engineering in an attempt to gain access to their online accounts.
We attribute this campaign to COLDRIVER (also known as Star Blizzard, Callisto and other designations). This threat actor is attributed to the Russian Federal Security Service (FSB) by multiple governments.
We identified a second threat actor targeting similar communities, whom we name COLDWASTREL. We assess that this actor is distinct from COLDRIVER, and that the targeting that we have observed aligns with the interests of the Russian government.
The Citizen Lab is sharing all indicators with major email providers to assist them in tracking and blocking these campaigns.
Access Now have also done some reporting:
https://www.accessnow.org/russian-phishing-campaigns/
Reporting on China
A Dive into Earth Baku’s Latest Campaign
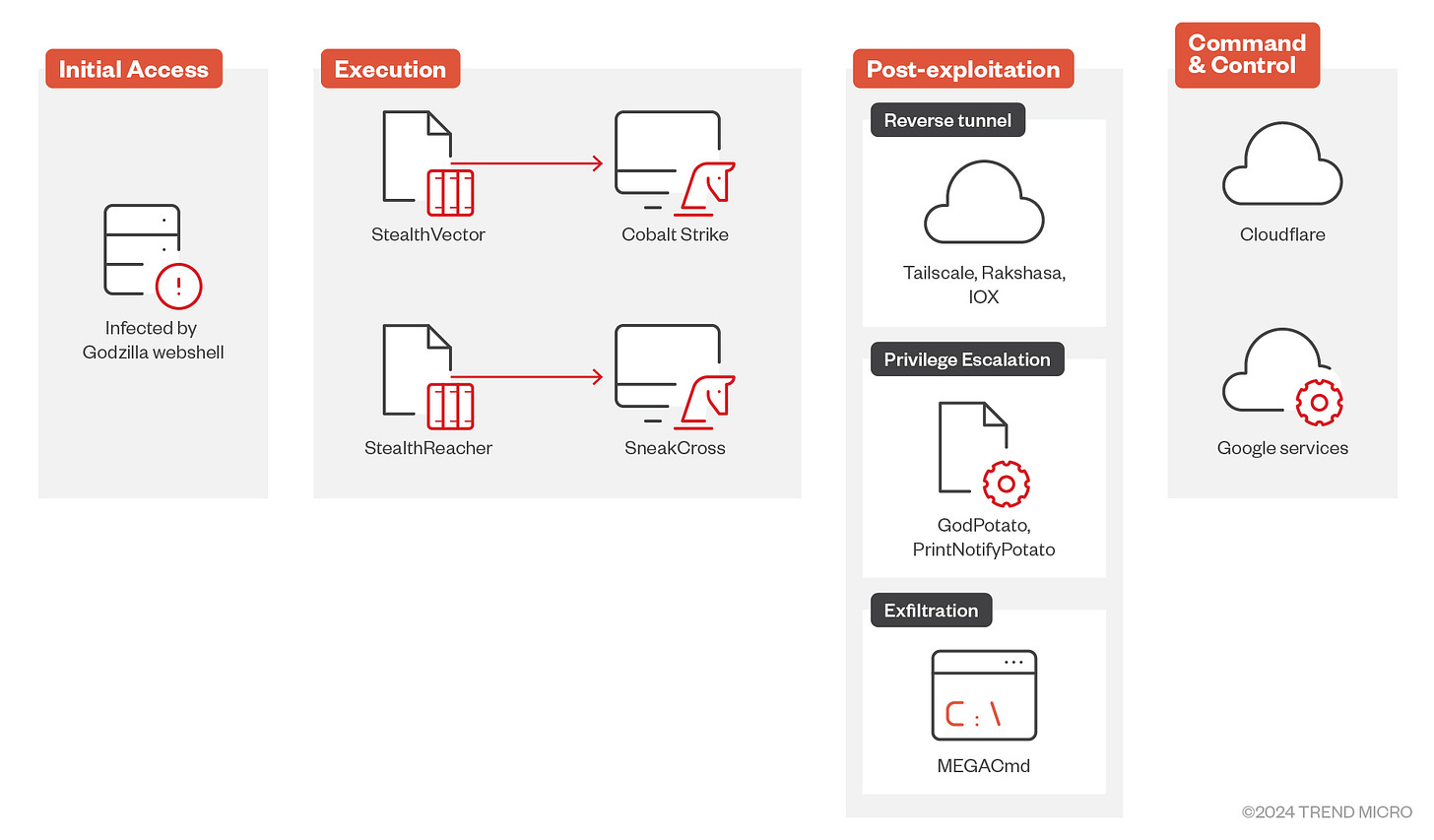
Ted Lee and Theo Chen detail this alleged Chinese campaign which involves exploiting web servers for initial access, then the deployment of webshells. As a reminder ShellSweep may help here..
In the group’s recent operations, Earth Baku’s attacks exploited public-facing applications, specifically IIS servers, as an entry point for attacks
Earth Baku (a threat actor associated with APT41) has expanded its activities beyond the Indo-Pacific region to Europe, the Middle East, and Africa — targeting countries like Italy, Germany, UAE, and Qatar, with suspected threat activity in Georgia and Romania.
The group uses public-facing applications such as IIS servers as entry points, deploying advanced malware toolsets such as the Godzilla webshell, StealthVector, StealthReacher, and SneakCross.
StealthVector and StealthReacher are customized loaders that deploy backdoor components while employing techniques such as AES encryption and code obfuscation for stealth. SneakCross, the group’s latest backdoor, uses Google services for command-and-control (C&C) activities and boasts a modular design for easer updates.
During post-exploitation, Earth Baku uses tools like a customized iox tool, Rakshasa, and Tailscale to maintain persistence, along with MEGAcmd for data exfiltration.
https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/research/24/h/earth-baku-latest-campaign.html
EastWind campaign: new CloudSorcerer attacks on government organizations in Russia
GREAT alleged Chinese intrusions into Russian government systems. The initial access was using… 🥁… phishing!!
The malware downloaded by the attackers from Dropbox has been used by APT31 since at least 2021. We named it GrewApacha.
The attackers updated the The CloudSorcerer backdoor (described by us in early July 2024) ) after we published our blogpost. It currently uses LiveJournal (a social network popular in Russia) and Quora profiles as initial C2 servers.
The attacks additionally deploy a previously unknown implant with a classic backdoor functionality, which we dubbed PlugY. It is loaded via the CloudSorcerer backdoor, and its command set is quite extensive. It supports three different protocols for communicating with C2, and what’s more, its code resembles that of the DRBControl backdoor (aka Clambling), which several companies attribute to the APT27 group.
Notably, the EastWind campaign bore traces of malware from two different Chinese-speaking groups: APT27 and APT31. This clearly shows that APT groups very often team up, actively sharing knowledge and tools. To successfully counter such collaborations, we closely monitor the techniques and tactics of APT groups operating around the world.
https://securelist.com/eastwind-apt-campaign/113345/
The i-Soon Leaks: Industrialization of Cyber Espionage
The German Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution releases the second part of the i-Soon leaks which they attribute to the Chinese state:
The leaked documents do not contain any indication of affected entities in Germany, however, the analysis offers an insight into the inner workings of private hacker companies and providers of malicious software and their close ties to the Chinese state. It also lays bare how hacking groups operate and how government agencies leverage them.
They also released their third report:
The evaluations show an industrialization of cyber espionage by privately organized companies that carry out cyber attacks on behalf of the state.
Reporting on North Korea
APT Group Kimsuky Targets University Researchers
Cyber Resilience reports on this alleged North Korean campaign using… 🥁… phishing!!!
Kimsuky is a North Korean APT group tasked with global intelligence collection operations aligned with the North Korean government’s interests. The group has been active since at least 2012 and has a particular interest in South Korean think tanks and government entities; however, it also targets the United States, the United Kingdom, and other European countries. Kimsuky specializes in targeted phishing campaigns, leveraging malicious attachments in follow-on emails after establishing trust through email correspondence
https://www.cyberresilience.com/threatintel/apt-group-kimsuky-targets-university-researchers/
Crypto Operations
ZachXBT details an alleged operation originating from North Korea which is yielding one group $300k to $500k a month.
Recently a team reached out to me for assistance after $1.3M was stolen from the treasury after malicious code had been pushed. Unbeknownst to the team they had hired multiple DPRK IT workers as devs who were using fake identities. I then uncovered 25+ crypto projects with related devs that have been active since June 2024.
Reporting on Iran
[APT42] Iranian backed group steps up phishing campaigns against Israel, U.S.
Google Threat Analysis Group detail this alleged Iranian campaign using… 🥁… phishing!!!!
Targeting military, defense, diplomats, academics, and civil society: APT42 attempted to use social engineering to target former senior Israeli military officials and an aerospace executive by sending emails masquerading as a journalist requesting comment on the recent air strikes. They also sent social engineering emails to Israeli diplomats, academics, NGOs and political entities. The emails were sent from accounts hosted by a variety of email service providers, and did not contain malicious content. These emails were likely meant to elicit engagement from the recipients before APT42 attempted to compromise the targets. Google suspended identified Gmail accounts associated with APT42.
Cyclops: a likely replacement for BellaCiao
Harfang Labs details this alleged Iranian implant framework..
we assess that Cyclops was likely developed as a sucessor to the BellaCiao malware
We attribute this new platform to “Charming Kitten” (also known as APT 35) due to significant overlaps in TTPs and targeting.
As far as we know, there are only a limited number of samples of this family, with evidence suggesting its development was completed in December 2023.
https://harfanglab.io/insidethelab/cyclops-replacement-bellaciao/
Iran Targeting 2024 US Election
Clint Watts details alleged Iranian activity using… 🥁… phishing!!!!!
Yet another Iranian group, this one connected with the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps, or IRGC, sent a spear phishing email in June to a high-ranking official on a presidential campaign from the compromised email account of a former senior advisor. The email contained a link that would direct traffic through a domain controlled by the group before routing to the website of the provided link. Within days of this activity, the same group unsuccessfully attempted to log into an account belonging to a former presidential candidate. We’ve since notified those targeted.
A fourth Iranian group compromised an account of a county-level government employee in a swing state. The compromise was part of a broader password spray operation and Microsoft Threat Intelligence did not observe the actor gain additional access beyond the single account, making it hard to discern the group’s ultimate objectives. Since early 2023, the group’s operations have focused on strategic intelligence collection particularly in satellite, defense, and health sectors with some targeting of US government organizations, often in swing states.
https://blogs.microsoft.com/on-the-issues/2024/08/08/iran-targeting-2024-us-election/
Reporting on Other Actors
FIN7: The Truth Doesn't Need to be so STARK
S2 Research Team show that good analytical tradecraft can find adversary infrastructure en masse..
Identification of two clusters of potential FIN7 activity, derived from collaborative analysis of indicators originally shared by Silent Push.
The two clusters indicate communications inbound to FIN7 infrastructure from IP addresses assigned to Post Ltd (Russia) and Smart Ape (Estonia), respectively.
Identification of 25 Stark-assigned IP addresses used to host domains associated with FIN7 activities.
https://www.team-cymru.com/post/fin7-the-truth-doesn-t-need-to-be-so-stark
Discovery
How we find and understand the latent compromises within our environments.
ET-BERT: A Contextualized Datagram Representation with Pre-training Transformers for Encrypted Traffic Classification
This is from 2022 but worth a call out as it surfaced on a Chinese website this week. Xinjie Lin, Gang Xiong, Gaopeng Gou, Zhen Li, Junzheng Shi and Jing Yu show how their pre-trained models can do things that JA3 / JA3S are not be able to.
The pre-trained model can be fine-tuned on a small number of task-specific labeled data and achieves state-of-the-art performance across five encrypted traffic classification tasks, remarkably pushing the F1 of ISCX-VPN-Service to 98.9% (5.2%↑), Cross-Platform (Android) to 92.5% (5.4%↑), CSTNET-TLS 1.3 to 97.4% (10.0%↑). Notably, we provide explanation of the empirically powerful pre-training model by analyzing the randomness of ciphers. It gives us insights in understanding the boundary of classification ability over encrypted traffic. The code is available at:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3485447.3512217
https://github.com/linwhitehat/ET-BERT
Understanding Application Control event IDs (WDAC)
There was talk on social media of using WDAC policies to block drivers of EDRs loading. As a result you may wish to monitor logs for new for 3099 events etc.
Pythia
Efstratios Lontzetidis provides an uplift in capability here, will be interesting to see how it gets adopted.
Pythia offers a generic standardized query format (pretty similar to, and inspired from Sigma) that is easily convertable to multiple infrastructure hunting platforms. Such platforms are designed to scan daily (at different frequencies) multiple IP ranges and collect data (snapshots of a state in time). An important tip is to validate your findings with multiple tools to verify your results and even get more up-to-date results. That's why Pythia was developed.
Pythia aims to be for publicly-discoverable data, what Snort is for network files, YARA is for files and Sigma is for log files.
https://github.com/EfstratiosLontzetidis/pythia
Defence
How we proactively defend our environments.
Enabling Trusted Types in a Complex Web Application: A Case Study of AppSheet
Kian Jamali and Aaron Shim detail the effort it took to employ this mitigation is a real large scale web application. Between this and the BeyondCorp and the long tail of Zero Trust work - Google really are providing insights into what it really takes..
Trusted Types are a powerful web defense mechanism that effectively protects applications against XSS vulnerabilities. In this blog post, we'll take a closer look at Trusted Types and describe how we adopted and rolled out Trusted Types in AppSheet, a Google product.
..
Although implementing Trusted Types is not a trivial task, it is a worthwhile endeavor. Trusted Types contributes to the scalable safe coding platform that Google Security has been building for so many years. By mitigating the risks associated with malicious code execution, Trusted Types can help protect your users and your organization against critical threats posed by DOM XSS vulnerabilities.
GraphWeaver: Billion-Scale Cybersecurity Incident Correlation
Scott Freitas and Amir Gharib detail the correlation engine behind Microsoft Defender.
We introduce GraphWeaver, an industry-scale framework that shifts the traditional incident correlation process to a data-optimized, geo-distributed graph based approach. GraphWeaver introduces a suite of innovations tailored to handle the complexities of correlating billions of shared evidence alerts across hundreds of thousands of enterprises. Key among these innovations are a geo-distributed database and PySpark analytics engine for large-scale data processing, a minimum spanning tree algorithm to optimize correlation storage, integration of security domain knowledge and threat intelligence, and a human-in-the-loop feedback system to continuously refine key correlation processes and parameters. GraphWeaver is integrated into the Microsoft Defender XDR product and deployed worldwide, handling billions of correlations with a 99% accuracy rate, as confirmed by customer feedback and extensive investigations by security experts.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.01842
Incident Writeups & Disclosures
How they got in and what they did.
Unicoin breach
The four days must have been fraught..
On August 9, 2024, Unicoin Inc. (the “Company”) detected an unknown threat actor had gained access to the Company’s Google G-Suite account and changed passwords of all users of the Company’s G-Suite products (i.e., G-Mail, G-Drive and other related G-Suite functionality), thereby denying access to all users having an “@unicoin.com” email address (the “Event”). On or about August 13, 2024, the Company was able to remove the threat actor’s access to the G-Suite accounts and restore access to its internal users. The Company is examining the information accessed to determine and mitigate the impact of the Event. The Company also continues to investigate the extent of the Event, and the following details are known at the time of this Current Report:
.Unauthorized access to corporate G-Suite services was gained by unknown persons.
During a personal check of corporate users of internal services, discrepancies were found in the personal data of employees and/or contractors in the Company’s accounting department.
Traces of hacked messages and email accounts of certain managers of the Company were found.
Traces of identity forgery of one of the contractors of the Company were found and such contractor subsequently was terminated.
https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1740742/000182912624005571/unicoin_8k.htm
Vulnerability
Our attack surface.
SMM Lock Bypass on AMD
When CPUs have vulnerabilities…
it may be possible for an attacker with ring 0 access to modify the configuration of System Management Mode (SMM) even when SMM Lock is enabled.
https://www.amd.com/en/resources/product-security/bulletin/amd-sb-7014.html
allegedly will not be fixed on the 3000 series:
Android Vulnerability Impacting Millions of Pixel Devices Around the World
Needs local access to enable, but the scale of deployment is the thing of wonder.
iVerify discovered an Android package, "Showcase.apk," with excessive system privileges, including remote code execution and remote package installation capabilities, on a very large percentage of Pixel devices shipped worldwide since September 2017
The application downloads a configuration file over an unsecure connection and can be manipulated to execute code at the system level
The application retrieves the configuration file from a single US-based, AWS-hosted domain over unsecured HTTP, which leaves the configuration vulnerable and can makes the device vulnerable
The app vulnerability leaves millions of Android Pixel devices susceptible to man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, giving cybercriminals the ability to inject malicious code and dangerous spyware
Removal of the app is not possible through a user’s standard uninstallation process, and at this time, Google has not offered a patch for the vulnerability
It appears that Showcase.apk is preinstalled in Pixel firmware and included in Google’s OTA image for Pixel devices
The press reporting said..
iVerify disclosed its findings to Google at the beginning of May, and the tech giant has not yet released a fix for the issue. Google spokesperson Ed Fernandez tells WIRED in a statement that Showcase “is no longer being used” by Verizon, and Android will remove Showcase from all supported Pixel devices with a software update “in the coming weeks.”
https://www.wired.com/story/google-android-pixel-showcase-vulnerability/
Offense
Attack capability, techniques and trade-craft.
Breach the Gates Initial Access Craft in 2024
Emeric Nasi provides a shopping list of capabilities for cyber defence teams to go through in turn to ensure they are resilient against then..
Covers Windows and maCOS..
Also this rang an socio-tech alarm bell. It is clear from the authors experience that 5-6 clicks / actions is not outside the realm of possibility to achieve initial access.
Targets can be phished into 5-6 click actions
Less then 3 Clicks is almost RCE!
MSC, LNK, ClickOnce for shortest path
But nothing replaces the quality of good Social Engineering
Execution Guardrails: No One Likes Unintentional Exposure
Brandon McGrath details opsec considerations which will make detection and response more complicated for cyber defence teams if adopted more broadly..
I made several mistakes here:
Having easy access to the VDI made me lower my guard/paranoia
Used a single key
Used an embedded payload
Points 2 and 3 above are directly fueled by point 1 because it’s not something I typically do. Alas, here we are.
In this blog, I want to discuss how these mistakes can be avoided by using a collection of different keying variations and mechanisms. The code shown in this blog is merely an example/proof of concept and will have OpSec considerations—this is purely to demonstrate the ideas and methodology.
https://trustedsec.com/blog/execution-guardrails-no-one-likes-unintentional-exposure
Bring Your Own Vulnerable DLL (BYOVDLL)
Clément Labro details a regression technique which should be relatively easy to detect (i.e. the addition of catalogue files).
I will explore yet another avenue for bypassing LSA Protection in Userland. I will also detail the biggest challenges I faced while developing a proof-of-concept, and discuss some novel techniques and tricks to load an arbitrary DLL in LSASS, or even dump its memory.
..
We can thus extract both the vulnerable DLL and the catalog file containing its signature. After copying the catalog file to the
CatRootfolder of a fully updated Windows 11 machine, we can confirm that the signature of the importedkeyiso.dllfile is now recognized by the OS.
https://blog.scrt.ch/2024/08/09/ghost-in-the-ppl-part-1-byovdll/
DriverJack
Klez weaponizes a technique which should be detectable if you have sufficient file system telemetry.
DriverJack is a tool designed to load a vulnerable driver by abusing lesser-known NTFS techniques. These method bypass the registration of a Driver Service on the system by hijacking an existing service, and also spoof the image path presented in the Driver Load event. To further masquerade the presence of a vulnerable driver, the attack also abuses an Emulated Filesystem Read-Only bypass to swap the content of a driver file on a mounted ISO before loading it.
..
Hijacking valid driver services to load arbitrary (signed) drivers abusing native symbolic links and NT paths
https://github.com/klezVirus/DriverJack
TrickDump
Ricardo Ruiz weaponizes this approach which should be easy enough to detect due to the opening of the process.
TrickDump dumps the LSASS process without creating a Minidump file, generating instead 3 JSON and 1 ZIP file with the memory region dumps. In three steps:
Lock: Get OS information using RtlGetVersion.
Shock: Get SeDebugPrivilege privilege with NtOpenProcessToken and NtAdjustPrivilegeToken, open a handle with NtGetNextProcess and NtQueryInformationProcess and then get modules information using NtQueryInformationProcess and NtReadVirtualMemory.
Barrel: Get SeDebugPrivilege privilege, open a handle and then get information and dump memory regions using NtQueryVirtualMemory and NtReadVirtualMemory.
https://github.com/ricardojoserf/TrickDump
Exploitation
What is being exploited.
CVE-2024-38077 MadLicense
The only thing of note this week got pulled by the author, it is the RDP license server exploit which was Chinese origin.
The service needs to be manually enabled.
There is a copy here - https://github.com/qi4L/CVE-2024-38077
Tooling and Techniques
Low level tooling and techniques for attack and defence researchers…
Traceeshark
Ofek Shaked and Idanrg give the work a powerful analysis capability here..
Traceeshark brings the world of Linux runtime security monitoring and advanced system tracing to the familiar and ubiquitous network analysis tool Wireshark.
Using Traceeshark, you can load Tracee captures in JSON format into Wireshark, and analyze them using Wireshark's advanced display and filtering capabilities.
https://github.com/aquasecurity/traceeshark
Grimoire
Christophe Tafani-Dereeper gives the world a synthetic data generator for AWS logs.
Grimoire is a "REPL for detection engineering" that allows you to generate datasets of cloud audit logs for common attack techniques. It currently supports AWS.
https://github.com/dataDog/grimoire
BadZure
Mauricio Velazco provides a re-written work-aid in Python.
BadZure is a Python tool that utilizes Terraform to automate the setup of Azure Active Directory (now Entra ID) tenants, populating them with various entities and introducing common security misconfigurations to create vulnerable tenants with multiple attack paths.
https://github.com/mvelazc0/BadZure
Footnotes
Some other small (and not so small) bits and bobs which might be of interest.
Aggregate reporting
July 2024 APT attack trend report (domestic) - South Korea
Adversarial Threat Report - Meta
A Five Year Retrospective on Detection as Code - “Reflecting on the past five years since co-authoring the initial paper on Detection as Code, it’s clear that the landscape of detection engineering has evolved and matured significantly. By integrating DevOps principles, we’ve seen notable improvements in the way detection logic is managed and deployed.”
Logic Gone Astray: A Security Analysis Framework for the Control Plane Protocols of 5G Basebands
A quick research overview of the Research Handbook on Cyberwarfare
Post CrowdStrike:
Artificial intelligence
DecodingTrust Comprehensive Assessment of Trustworthiness in GPT Mode - Illinois University publishes - “This project is organized around the following eight primary perspectives of trustworthiness, including:
Toxicity
Stereotype and bias
Adversarial robustness
Out-of-Distribution Robustness
Privacy
Robustness to Adversarial Demonstrations
Machine Ethics
Fairness”
Books
Events
Threat Analyst Summit 2024 威脅分析師高峰會, December, Taipei
Unless stated otherwise, linked or referenced content does not necessarily represent the views of the NCSC and reference to third parties or content on their websites should not be taken as endorsement of any kind by the NCSC. The NCSC has no control over the content of third party websites and consequently accepts no responsibility for your use of them.
This newsletter is subject to the NCSC website terms and conditions which can be found at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/terms-and-conditions and you can find out more about how will treat your personal information in our privacy notice at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/privacy-statement.