CTO at NCSC Summary: week ending August 10th
We have an opportunity to address the inevitable but we will need to want a different future…
Welcome to the weekly highlights and analysis of the blueteamsec Lemmy (and my wider reading). Not everything makes it in, but the best bits do.
Operationally this week there has been exploitation of various cyber security solutions. These events further support the case for implementing our guidance on digital forensics and protective monitoring specifications for producers of network devices and appliances.
In the high-level this week:
Cyber Assessment Framework v4.0 released in response to growing threat - NCSC UK updates - released 4.0 with “four major changes:
1) A new section on building a deeper understanding of attacker methods and motivations to inform better cyber risk decisions.
2) A new section on ensuring software used in essential services is developed and maintained securely.
3) Updates to the section on security monitoring and threat hunting to improve the detection of cyber threats.
4) And finally, there is improved coverage of AI-related cyber risks throughout the CAF.”
Quantum networking technologies - NCSC UK publishes - “In this paper, we provide an updated analysis of QKD as a security technology, and the development of QRNGs. We also consider the future of quantum networking technologies.”
British intelligence warns cyber threat to critical infrastructure is increasing - Alexander Martin reports - “In its latest attempt to sound the alarm about that threat, the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) again stressed that Britain was underestimating the severity of the risk from cyberattacks and provided updated guidance to infrastructure operators to protect themselves.”
The cost of espionage - The Australian Institute of Criminology quantifies - “In 2023–24, espionage cost Australia at least $12.5 billion. This includes the direct costs of the consequences of known or probable espionage activity – primarily losses due to state or state-sponsored cyber attacks, insider threats and intellectual property theft – as well as the public and private sector response, remediation and mitigation costs.”
U.S. Senate Confirms Sean Cairncross as the National Cyber Director - The White House announces - “He will serve as President Trump’s principal advisor on national cybersecurity policy and strategy.”
Threat Landscape Critical Infrastructure (2025) - National Coordinator for Security and Counterterrorism of the Netherlands publishes - “State actors pose a growing threat to critical infrastructure. Wars, geopolitical tensions, and growing competition between major powers have made the world around the Netherlands and the European Union more unstable. Russia and China, in particular, pose a threat to Dutch critical infrastructure in various ways. This manifests in, among other things, an increased use of hybrid instruments, such as sabotage, espionage and pre-positioning, cyberattacks, disinformation, economic pressure, and abuse
of strategic dependencies.”
Small defense industrial base firms pose tempting targets for nation-state hackers, NSA official says - NextGov reports - “Some 80% of the defense industrial base are actually small firms, according to the NSA’s head of DIB security, who has helped over 200 providers identify thousands of vulnerabilities in their systems.”
DHS Launches Over $100 Million in Funding to Strengthen Communities’ Cyber Defenses - CISA announces - “This Notice of Funding Opportunity is made up of two separate grants: Fiscal Year 2025 State and Local Cybersecurity Grant Program (SLCGP) and the Tribal Cybersecurity Grant Program (TCGP). The SLCGP makes $91.7 million available to state and local governments for a range of cybersecurity improvements, including planning and exercises, hiring experts in the community, and improving services for their citizens. The TCGP provides $12.1 million to tribal governments for similar uses.”
Offensive Cyber Attacks and Conventional Warfare - Matthew F. Calabria
Matthew F. Calabria opines - “Policymakers should temper their expectations about the transformative potential of cyber weapons in warfare, incorporating cyber’s limitations as well as its potential into simulations, training and war games, and treating cyber weapons as niche assets best suited for pre-conflict operations rather than direct means to victory.”
Rethinking Cyber Deterrence in a Multipolar World - Louise Marie Hurel and Dr Gareth Mott - “This paper argues that cyber deterrence must be part of an integrated, cross-domain strategy. Deterrence should be understood as a continuum of prevention and response measures – cumulative, iterative, tailored and grey-zone oriented – drawing from lessons across multiple case studies.”
As Cyber Threats Grow, Singapore Walks a Careful Line on Identifying State Actors - The S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies ponders - “During peacetime, technical attribution offers a more pragmatic way to deter cyber threats. Cyberspace is a complex environment, and non-state threat groups, which may or may not act on the behest of a state, are the dominant actors there. This method allows authorities to expose threat groups without directly shaming the country from which they may be operating.”
Cyber solidarity act - European Parliamentary Research Service research - “The Cyber Solidarity Act was published in the EU's Official Journal on 15 January 2025. It entered into force on 4 February 2025 and became binding in its entirety and directly applicable in all Member States.”
Demystifying threat intelligence in digital advertising - Trustworthy Accountability Group publishes - includes their own pyramid of pain
North Korea sent me abroad to be a secret IT worker. My wages funded the regime - BBC reports - “He said 85% of what he earned was sent back to fund the regime. Cash-strapped North Korea has been under international sanctions for years.”
Peters and Blackburn Introduce Bipartisan Bill to Create a National Quantum Computing Cybersecurity Strategy - Senators Gary Peters (D-MI) and Marsha Blackburn (R-TN) introduce - “The National Quantum Cybersecurity Migration Strategy Act would require the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy to lead the development of a coordinated national strategy for transitioning federal systems to quantum-resistant cybersecurity standards.”
CSIS Launches Commission on Cyber Force Generation - Centre for Strategic & International Studies announces - “The Commission, in partnership with the Cyber Solarium Commission 2.0, will provide recommendations on how to organize a new military service that would ensure and defend the United States’s strategic superiority and security in the cyber domain.”
Does cybersecurity capacity building work? - Phil Sheriff positions - “Unfortunately, the evidence for cybersecurity capacity building impact and effectiveness is currently weak. Evaluation practice is still nascent, and, with a few notable exceptions, current practice emphasises efficiency over effectiveness.”
Reporting on/from China
China Turns to A.I. in Information Warfare - New York Times reports - “It is not clear from the documents how effective GoLaxy’s campaigns in Taiwan, Hong Kong and inside China have been, or whether its technology can do all that it promises.” … “The documents examined by researchers appear to have been leaked by a disgruntled employee upset about wages and working conditions at the company. While most of the documents are not dated, the majority of those that include dates are from 2020, 2022 and 2023.”
China tests out stablecoins amid fears of capital outflows - Financial Times reports - “The HKMA has not ruled out approving licences for stablecoins backed by offshore renminbi. China has long wanted to increase use of its currency for cross-border payments, an area where stablecoins have particular appeal because they circumvent traditional systems such as Swift, which Beijing worries could be used against it in the event of a conflict.”
Taiwan arrests 6 in probe of TSMC chip technology leak - South China Morning Post reports - “The chipmaker to Nvidia reported a number of former and current staff to authorities on suspicion they illegally obtained core technology. A total of six people were arrested, with two posting bail and one released afterwards, said Taiwan High Prosecutors Office spokesman John Nieh. Prosecutors searched the homes of some staff between July 25 and July 28, the agency said in a statement. It is now trying to find out if data had been leaked to other parties.”
Huawei to open-source AI chip toolkit to take on Nvidia’s proprietary platform - South China Morning Post reports - “its Compute Architecture for Neural Networks (CANN) – the software toolkit used to develop applications on the firm’s Ascend AI processors – as the Shenzhen-based company steps up efforts to compete against Nvidia, days after Beijing raised concerns about its H20 chip’s security.”
How China’s new ‘Darwin Monkey’ could shake up future of AI in world first - South China Morning Post reports - “First such supercomputer with over 2 billion artificial neurons mimics macaque brain, is expected to help advance human brain-inspired AI”
Chinese scientists say they can create a ‘storm eye’ for PLA forces in electronic warfare - South China Morning Post reports - “The technology, still at an early stage with feasibility verified in computer simulations, relies on coordinated unstaffed aerial platforms that emit precisely-tuned radio frequency (RF) interference.”
China plots pathway to tech supremacy through brain-computer interfaces - South China Morning Post reports - “Seven ministries, including the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, jointly released a policy blueprint on Thursday providing innovation and implementation guidelines for China’s BCI industry.”
AI
Artificial Intelligence and the Law: a discussion paper - UK Law Society publish - “However, with AI’s potential benefits comes potential harm. It is important that the laws of England and Wales evolve so that they are up to the task of the many changes being wrought by AI. The purpose of this paper is to increase awareness of the potential impacts of AI on the law and to encourage discussion of these issues as a step towards future law reform, where it is required.”
First-In-The-Nation Agentic Artificial Intelligence (AI) Empowered Statewide Regulatory Review - Governor of Virginia executively orders - “I hereby establish in this Executive Order the nation’s first statewide agentic Al-powered regulatory review to ensure the Commonwealth captures the benefits of AI in reducing regulatory burdens and keeping regulations and guidance documents streamlined and up-to-date.”
Proceedings of the First Workshop on LLM Security - Association for Computational Linguistics publishes - “industry sees and deflects advanced attacks rapidly without sharing details - academia uncovers new classes of techniques and deep analyses. This is a departure from traditional NLP research, but a dynamic commonly observed in security.”
Project Ire autonomously identifies malware at scale - Microsoft publish - “The prototype, Project Ire, automates what is considered the gold standard in malware classification: fully reverse engineering a software file without any clues about its origin or purpose. It uses decompilers and other tools, reviews their output, and determines whether the software is malicious or benign.”
GPT-5 System Card - OpenAI publish - “For the gpt-5 models, gpt-5-thinking performs similarly to OpenAI o3: it is unable to solve any of the cyber range scenarios unaided.”
Cyber proliferation
Tracking Candiru’s DevilsTongue Spyware in Multiple Countries - Recorded Future track - “Eight distinct clusters were identified, with five being likely still active, including those linked to Hungary and Saudi Arabia. One cluster tied to Indonesia was active until November 2024, and two associated with Azerbaijan have uncertain status due to a lack of identified victim-facing infrastructure. Insikt Group also identified a company suspected to be part of Candiru’s corporate network”
Bounty Hunting
US offers up to $10 million for information on Iranian cyber group - Iran International reports - “The US State Department on Monday announced a reward of up to $10 million for information related to a cyber group known as Shahid Shushtari allegedly linked to Iran's military and US election meddling.”
Chinese man arrested for espionage, no house arrest - Rai News reports - “there are "serious indications of guilt," contained in the "investigative material" of the FBI investigation, and above all the "danger of flight."“
Japan chipmaker Kioxia to weed out suppliers lax on cybersecurity - Nikkei Asia reports - “Starting this fall, Kioxia will encourage companies ranking at the bottom in terms of cybersecurity to improve. An attack on one company in the supply chain could halt production, and the impact would have a ripple effect on Kioxia's clients.”
This weeks reflections build on last weeks.. They are based on a version (or part of) of a futures talk I give internally as well as externally…
It focuses on robotics and autonomy, what is coming, the implications of these cyber-physical systems and how we prepare from a cyber security perspective.
We do not have look too far to understand why we need to prepare with these couple of examples:
Unitree Go 1- Who is speaking to my dog? from 2025
Unveiling the Hidden World of Robot Vacuum Security from 2023/2024
We have ended up in a world where some printers have greater cyber resilience than devices wandering around our physical world. Or put another way we have secure boot, platform attestation, device identity from cryptographic roots of trust, runtime integrity, some memory safety and other defence in depth features in some printers yet not in emergent robotic systems.
In short if we do not look to build solutions which have:
Platform integrity and attestation e.g. what the Trust Computing Group provide
Immutable identity based on cryptographic primitives
Observability to detect breaches
Transparency in technology
Memory safety e.g. CHERI, Rust, Go and similar
.. and more
Then we should not be surprised by the outcome. We have an opportunity to address the inevitable when it comes to robotics but we will need to want a different future…
Not getting this via email? Subscribe:
Think someone else would benefit? Share:
All attribution is by others and not the UK Government unless specifically stated as such, please see the legal text at the end.
Have a lovely Friday…
Ollie
Cyber threat intelligence
Who is doing what to whom and how allegedly.
Reporting on Russia
Updated UAC-0099 toolkit: MATCHBOIL, MATCHWOK, DRAGSTARE
CERT Ukraine details this alleged Russian operation which is is notable for using a regional email service.
As a rule, the first stage involves sending emails, mainly using UKR.NET and with the subject of "court summons", containing a link to a legitimate file service (including one shortened using URL Shortener services), from which a double archive containing an HTA file will be downloaded.
Further high level reporting from Ukraine in "Court Summons" Phishing Lure Used in Cyberattacks on Ukrainian Government and Defence Sector
Reporting on China
Exposing and Circumventing SNI-based QUIC Censorship of the Great Firewall of China
Ali Zohaib, Qiang Zao, Jackson Sippe, Abdulrahman Alaraj, Amir Houmansadr, Zakir Durumeric and Eric Wustrow detail this alleged state level capability in China. It also highlights the value of internet measurement..
In this work we measure China’s new capability to inspect and block QUIC connections—the first nation-wide inspection and targeted censorship of QUIC. We confirm that China is decrypting and inspecting the first packet in QUIC connections at scale. Through several experiments, we infer the rules and high-level parsing logic of how the GFW processes QUIC connections. For instance, we discover that the GFW ignores QUIC packets with a source port lower than the destination port, likely as an optimization to inspect client-only traffic.
https://gfw.report/publications/usenixsecurity25/en/
Cyberspace Mapping Techniques
White Paper from China on approaches to scanning / mapping the Internet.
Scientifically characterizing cyberspace is an important prerequisite and core support for achieving effective governance and building a security protection system. The Zhongguancun Laboratory conducts in-depth research in the fields of cyberspace mapping and situation awareness, collaborating with high-level research universities such as Tsinghua University and the National University of Defense Technology, as well as leading technology enterprises like Far East Shengbang Security Technology Group Co., Ltd., to jointly write the "White Paper on Cyberspace Mapping Technology."
This white paper comprehensively and systematically sorts out the theoretical foundation and technical system of cyberspace mapping, deeply summarizes the research achievements and practical experiences in this field both domestically and internationally, and, in conjunction with the current development trends and practical needs of cyberspace security, proposes future development directions for cyberspace mapping technology.
How Chinese-speaking actors globally scale an Android RAT
Simone Mattia, Alessandro Strino and Federico Valentini detail a small but novel alleged Chinese campaign. The European concertation of compromises if of note.
A large-scale Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) operation, orchestrated by Chinese-speaking Threat Actors (TAs), has globally infected over 11,000 Android devices by deploying the PlayPraetor Remote Access Trojan (RAT).
While Europe is the most affected continent, with major victim concentrations in Portugal, Spain, and France, the campaign has also established a significant presence in Africa, Latin America, and Asia, with hotspots in Morocco, Peru, and Hong Kong.
The botnet's rapid growth, which now exceeds 2,000 new infections per week, is driven by aggressive campaigns focusing on Spanish and French speakers, indicating a strategic shift away from its previous common victim base.
The operation is managed by a Chinese-language Command and Control (C2) panel, which leverages a multi-tenant architecture to support a scalable affiliate model and includes automated tools for creating custom malware delivery pages.
The malware is actively being developed to improve its effectiveness. It deploys overlay attacks against a globally distributed target list of nearly 200 banking apps and cryptocurrency wallets.
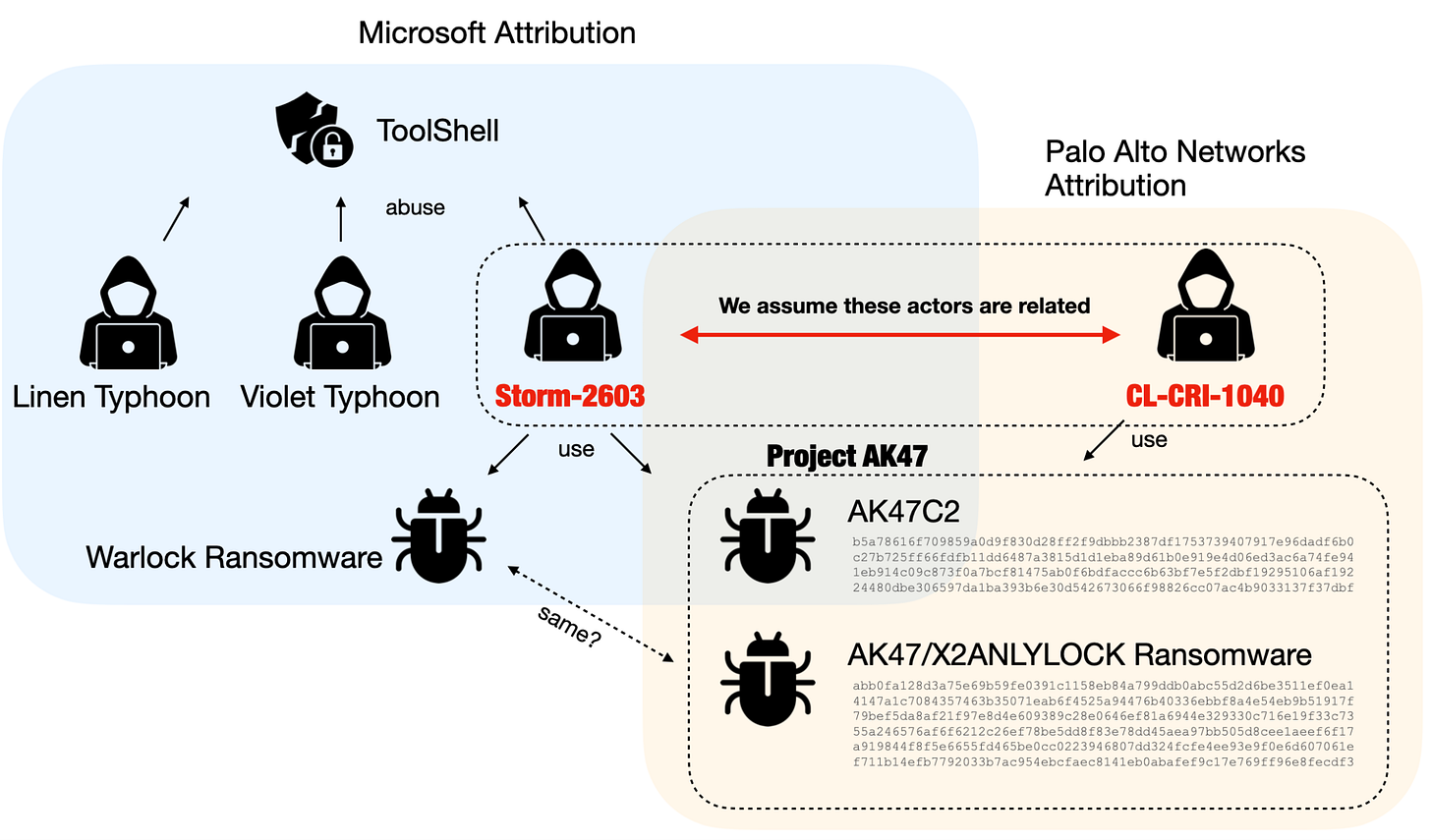
Uncovering a Link to the SharePoint Vulnerability Attacks
Unit42 detail what they assert are links between what has been previously alleged to be a Chinese ransomware outfit and a wider set of capability. The use of leaked alleged Russia originating ransomware capability..
Our investigation of CL-CRI-1040 attacks revealed evidence of previous ransomware activities, including LockBit 3.0 and Warlock Client ransomware. This evidence led us to assess with high confidence that CL-CRI-1040 is financially motivated.
https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/ak47-activity-linked-to-sharepoint-vulnerabilities/
The Evolution of Chinese Smishing Syndicates and Digital Wallet Fraud
SecAlliance shines a light on this alleged criminal operation emanating from China. The scale and end-to-end nature of the eco-system will be of note to financial services.
Our investigation reveals an extensive criminal ecosystem that may have compromised between 12.7 million and 115 million payment cards in the United States alone between July 2023 and October 2024, with estimated financial losses reaching into the billions of dollars.
..
Our investigation initially identified a Chinesespeaking developer operating under the pseudonym “Lao Wang,” or alternatively “Wang Duo Yu,” who appears to have established one of the first popular phishing-as-a-service operation with an integration to support digital wallet exploitation. Analysis of recovered phishing kit source code revealed extensive Chinese-language commentary and direct references to “Wang Duo Yu” within JavaScript files.
..
Initial contact occurs through SMS, iMessage, or RCS messages employing social engineering lures related to package deliveries, toll road payments, tax refunds, vehicle registrations, or other urgent matters that require immediate attention.
Reporting on North Korea
Advisory on North Korean information technology (IT) workers
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police, Public Safety Canada, Global Affairs Canada, the Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre of Canada (FINTRAC), and the Canadian Centre for Cyber Security issue this advisory on something which is now understood to be a global challenge.
North Korean IT workers are usually competent, highly qualified, and skilled in the services they provide. To hide their identity, these individuals could use virtual private networks (VPNs) and servers (VPSs) which encrypts their online traffic, Voice Over Internet Protocol (VOIP) and encrypted messaging applications, AI-enabled deepfake technologies which disguise appearances, and pay nationals of other countries (also referred to as proxies) to use their personal information and/or accounts on employment platforms.
https://rcmp.ca/en/news/2025/07/advisory-north-korean-information-technology-it-workers
RoKRAT Shellcode and Steganographic Threats: Analysis and EDR Response Strategies
Genians identifies a new implant from this alleged North Korean actor. The counter detection strategy is of note and highlight the importance of among other things memory scanning and wider telemetry.
A new variant of the RoKRAT malware used by the APT37 group has been identified.
The malware employs a two-stage encrypted shellcode injection method to hinder analysis.
A steganography technique was discovered in which malicious code is concealed within image files.
Fileless attacks continue to be used to evade detection by security solutions.
https://www.genians.co.kr/en/blog/threat_intelligence/rokrat_shellcode_steganographic
The Operational Blueprint of Kimsuky APT for Cyber Espionage
Aryaka Threat Research Labs details the end-to-end of an alleged North Korean operation. The use of decoy documents from legitimate sources highlights the potential value of content integrity / authenticity initiatives when it comes to documents etc.
In this campaign, Kimsuky combines tailored social engineering with a sophisticated malware framework engineered for stealth, persistence, and comprehensive data theft. The operation begins with malicious Windows shortcut files that execute obfuscated scripts delivered through trusted system utilities, using decoy documents based on publicly available South Korean government materials to lure victims. Once inside, the malware performs extensive system profiling, steals credentials and sensitive documents, monitors user activity through keylogging and clipboard capture, and exfiltrates data in discreet segments over standard web traffic—helping it blend into normal network operations. Figure 1 shows an overview of the infection chain.
https://www.aryaka.com/docs/reports/aryaka-kimsuky-apt-operational-blueprint.pdf
Reporting on Iran
IRGC and Hacker Collectives Of The 12-Day War
Security Scorecard provide some insight into various groups of activity allegedly on the Iranian side of the conflict. The scale is again of note as well as the tightly aligned but loosely coupled model.
[We] conducted a comprehensive analysis of 250,000 messages from Iranian proxy and hacktivist chatter from over 178 active groups over the 12-day war, revealing exactly how state-linked Iranian hackers, Iranian cyber proxies, and ideologically aligned hacktivists supported Iran’s broader war aims in a disruptive digital offensive. STRIKE also uncovered an IRGC-linked malware-laden phishing operation launched at the outset of the conflict, suggesting careful orchestration and planning aligned to the fighting.
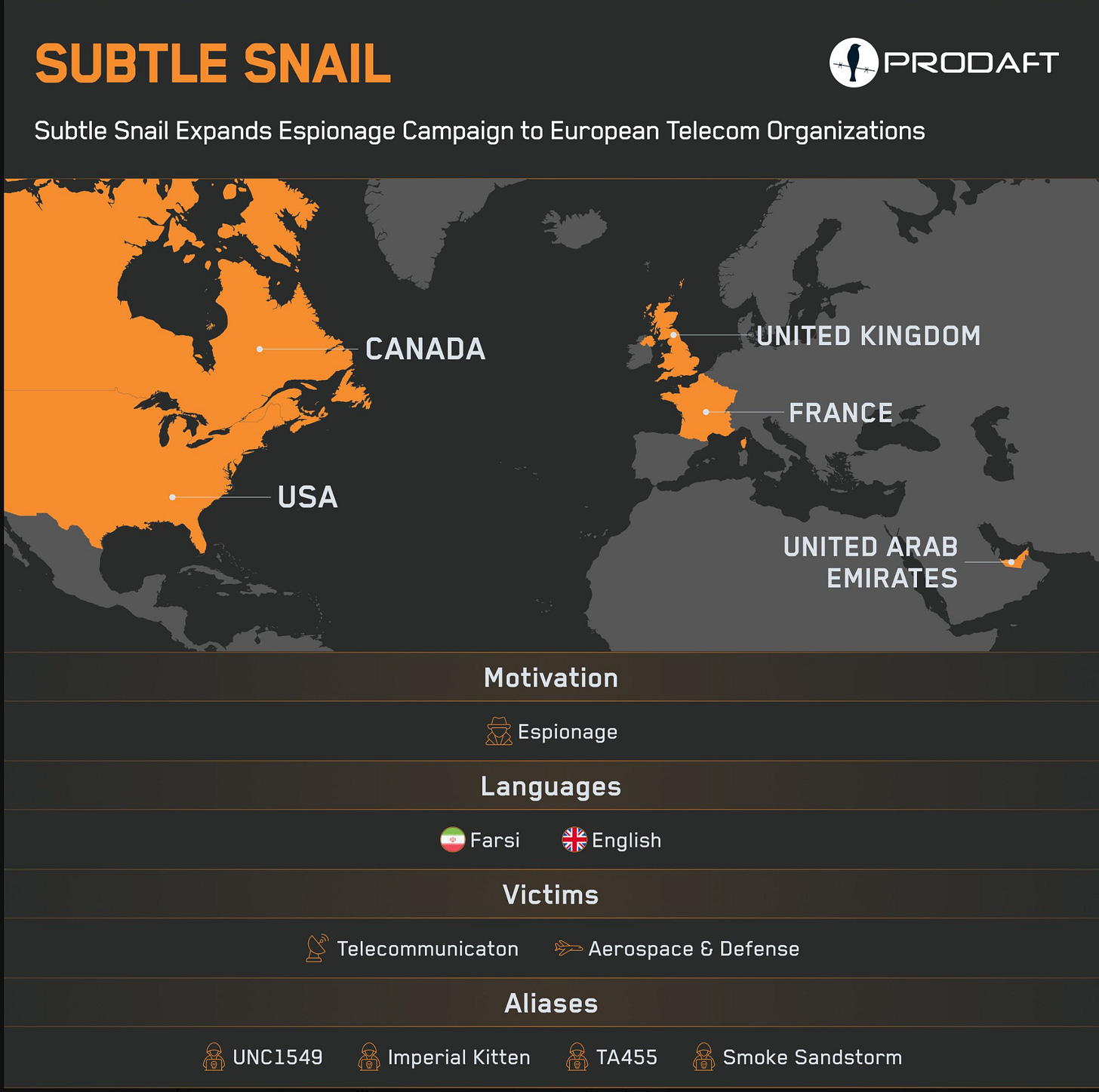
Subtle Snail
The report whilst teased isn’t generally available for the vendor so we get this picture.
They have released IoCs where Prodraft alleged it is an Iranian operation.
Subtle Snail (UNC1549, TA455), an Iran-nexus espionage group linked to the Eclipsed Wasp (Charming Kitten) network, has been active since at least November 2022. In their recent campaign, the group has shifted focus to European organizations, launching a targeted operation that has already infected 34 distinct devices across 11 organizations.
https://github.com/prodaft/malware-ioc/tree/master/SubtleSnail
Reporting on Other Actors
High-Risk Contributors Connected to Adversarial Nation-States in Open Source Software Ecosystems
Strider Intel make some leaps in this reporting but do highlight some of the challenges which are not unique to open-source eco-systems.
More than 21% of the contributors to openvino-genai were flagged with affiliations and work relationships that present nation-state security threats. This includes two active contributors that were tied to several high-risk, nation-state ecosystems.
One of the active contributors (“as-suvorov”) was formerly employed as a full-stack developer at U.S.-sanctioned software company MFI Soft.
MFI Soft has conducted a significant amount of work on behalf of the Federal Protective Service's (FSO) Special Communications Service, a cryptologic intelligence agency responsible for the collection and analysis of foreign communications and signals intelligence.
Another active contributor (“sbalandi”) was formerly employed by Positive Technologies, a Russian information technology firm that was sanctioned by the U.S. in 2021 for facilitating malicious cyber operations and supporting Russian government cyber actors.
https://content.striderintel.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/2025-Q3-OSS-Report-03-ka.pdf
Malware spread through Facebook ads disguised as cryptocurrency exchanges
AhnLab Security Intelligence Center details a campaign which has been previously covered by some western reporting but in South Korean. Noteworthy is the continued misuse of the advertising eco-system.
[We] identified malware targeting cryptocurrency users, distributed through Facebook ads. The malware disguises itself as a cryptocurrency exchange and induces the installation of malicious programs. When users download files from the disguised website, a file named "installer.msi" is saved and installed. During the installation process, the malware communicates with JavaScript loaded on the disguised website, ultimately executing an infostealer that collects system information, screen captures, and browser information.
https://asec.ahnlab.com/ko/89347/
From Bing Search to Ransomware: Bumblebee and AdaptixC2 Deliver Akira
The DFIR Report do what they do best with this reporting. The insightful element is both the continued use of Search Engine Optimization and also the use of trojan installers and of enterprise software no less - only one demographic going to be impacted with that.
n 2023 the malware was first reported as using SEO poisoning as a delivery mechanism. Recently in May of 2025 Cyjax reported on a campaign using this method again, impersonating various IT tools. We observed a similar campaign in July in which a download of an IT management tool ended with Akira ransomware.
In July 2025, we observed a threat actor compromise an organization through this SEO poisoning campaign. A user searching for “ManageEngine OpManager” was directed to a malicious website, which delivered a trojanized software installer. This action led to the deployment of the Bumblebee malware, granting the threat actor initial access to the environment. The intrusion quickly escalated from a single infected host to a full-scale network compromise.
UNC2891 Bank Heist: Physical ATM Backdoor & Linux Forensic Evasion Evasion
Group IB detail an intrusion which noteworthy due to the use of a physical device. Financial services will want to take note and dust off that business case for 802.1x and similar.
One of the most unusual elements of this case was the attacker’s use of physical access to install a Raspberry Pi device. This device was connected directly to the same network switch as the ATM, effectively placing it inside the bank’s internal network. The Raspberry Pi was equipped with a 4G modem, allowing remote access over mobile data.
Using the TINYSHELL backdoor, the attacker established an outbound command-and-control (C2) channel via a Dynamic DNS domain.
https://www.group-ib.com/blog/unc2891-bank-heist/
How a legitimate driver is being used to take down AV processes
Cristian Souza, Ashley Muñoz, Eduardo Ovalle and Francesco Figurelli detail the misuse of this Windows driver. You will see later on this is also used in a different campaign by Akira.
In a recent incident response case in Brazil, we spotted intriguing new antivirus (AV) killer software that has been circulating in the wild since at least October 2024. This malicious artifact abuses the
ThrottleStop.sysdriver, delivered together with the malware, to terminate numerous antivirus processes and lower the system’s defenses as part of a technique known as BYOVD (Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver). AV killers that rely on various vulnerable drivers are a known problem. We have recently seen an uptick in cyberattacks involving this type of malware.
https://securelist.com/av-killer-exploiting-throttlestop-sys/117026/
Discovery
How we find and understand the latent compromises within our environments.
SharePoint Exploits and the Hidden Threat of IIS Module Persistence
Michael Haag highlights the value of hunting for IIS modules even post environment patching.
Based on Microsoft's research and our analysis, the attack progression typically follows a predictable but sophisticated pattern. Attackers begin by exploiting SharePoint vulnerabilities for unauthenticated access, immediately followed by deploying spinstall0.aspx webshells for immediate control and machine key theft. During the reconnaissance phase, they use these webshells to enumerate the environment and gather credentials before deploying custom IIS modules for long-term persistence. The final phase involves cleaning up obvious webshells while maintaining covert access through the embedded IIS modules.
Why continuous profiling is the fourth pillar of observability
Marcus Hirt and JC Mackin detail a capability which whilst they do not make the cyber security value case I assert has some in detecting any form of arbitrary code execution be it from memory safety or deserialization exploitation etc.
Open source implementations of this technology do exist..
By running nonstop in production with very low overhead, continuous profilers give teams always-on visibility into how their code behaves in the real world. And when that data is correlated with other telemetry signals like metrics, traces, and logs, it helps teams troubleshoot complex issues, speed up investigations, and improve release velocity.
https://www.datadoghq.com/blog/continuous-profiling-fourth-pillar/
Paltergeist
Matt Maisel released this capability four or so months ago but I missed it. Will help cloud teams potentially surface intrusions they might not otherwise.
paltergeistis a cyber deception tool for generation, orchestration, and monitoring of cloud-native traps that lure and detect attackers. It's built in Go and intended for security operation and engineering teams exploring the use of cyber deception in cloud environments.
Make tailored, believable traps. Trap personas are generated with large language models and uses in-context learning with examples sampled from the environment. To improve trap believability and enticingness, generation can use LLM critics and other reasoning models to assess trap quality.
Manage deception engagements. Orchestration of deception engagements— groups related traps with similar targets. The Pulumi Automation API is used to plan and apply infrastructure lifecycles against the cloud provider.
Instrument trap interactions. Interaction activity is observable through cloud logging. Emitted logs are filtered, enriched, and processed into alerts for security operations teams.
https://github.com/mmaisel/paltergeist
Defence
How we proactively defend our environments.
FT3: Fraud Tools, Tactics, and Techniques Framework
Stripe release this framework to the world which is an interest take applied to an adjacent problem domain.
Fraud Tools, Tactics, and Techniques (FT3) is Stripe's adaptation of ATT&CK-style security frameworks, specifically designed to enhance our understanding of the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by actors in fraudulent activities. Developed as a resource for combating financial crime and improving organizational fraud prevention, FT3 serves a variety of stakeholders across the Fraud ecosystem.
Famous Chollima APT Adversary Simulation
Abdulrehman Ali is also back with one of his adversary simulations to put you through your paces. Good one if you have a large developer community.
This is a simulation of attack by (Famous Chollima) APT group targeting job seekers to accomplish their goals and wide variety of United States (US) companies, the attack campaign was active early as December 2022, The attack chain starts with attackers invites the victim to participate in an online interview. The attackers likely uses video conferencing or other online collaboration tools for the interview. During the interview, the attackers convinces the victim to download and install an NPM-based package hosted on GitHub.
https://medium.com/@S3N4T0R/famous-chollima-apt-adversary-simulation-58fbdf241d0e
How to automatically disable users in AWS Managed Microsoft AD based on GuardDuty findings
Tim Kingdon walks through what contemporary containment can look like at machine(ish) speed… event lag is the delay.
I walk you through how to deploy Microsoft Active Directory in AWS Directory Services, set up GuardDuty to monitor Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances, and configure Amazon EventBridge with AWS Step Functions to trigger AWS Systems Manager Run Command to obtain the username and disable the user in Active Directory.
Protecting the Evidence in Real-Time with KQL Queries
Sergio Albea gives us a lesson in leading indicators..
And of course, experienced attackers know to check whether RegBack is enabled — so monitoring for attempts to modify the corresponding registry keys can help us generate early alerts and detect potential tampering.
https://detect.fyi/protecting-the-evidence-in-real-time-with-kql-queries-ac4c7f145383
Practical Sharing on Improving the Accuracy of Vulnerability Analysis for Large Models
To triage public CVE to determine RCE, from China in Chinese - use translate in your favourite browser.
This article focuses on the application of large models in vulnerability analysis. Addressing the numerous vulnerability types, complex attack methods, inefficiency of traditional methods, and insufficient accuracy of existing models, this article proposes a process for improving the accuracy of large-scale vulnerability analysis.
1. In terms of accuracy performance of the large model, the prompt classification method is more accurate than the classifier .
2. The thinking chain model can be better applied to the judgment of complex problems than the non-thinking chain model.
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/rsiZUrqlYuXADmxkl_7tmw?scene=1
External workbook links to blocked file types will be disabled by default
Microsoft makes a security change which will positively improve the security of Excel and risk of NTLM leakage.
Starting October 2025, external workbook links to blocked file types will be disabled by default, showing a #BLOCKED error for new links and preventing refresh of existing ones. Administrators can revert this via registry or group policy settings. A rollout and user warnings will occur from October 2025 to July 2026.
https://mc.merill.net/message/MC1125497
Incident Writeups & Disclosures
How they got in and what they did.
Cisco Event Response: Vishing Attack Impacting Third-Party CRM System
Cisco disclosed a vishing incident..
On July 24, 2025 (GMT+9), Cisco was made aware of an incident involving a bad actor targeting a Cisco representative through a voice phishing attack, also known as vishing. As a result, the actor was able to access and export a subset of basic profile information from one instance of a third-party, cloud-based Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system that Cisco uses.
Upon learning of the incident, the actor’s access to that CRM system instance was immediately terminated and Cisco commenced an investigation. Our investigation has determined that the exported data primarily consisted of basic account profile information of individuals who registered for a user account on Cisco.com (name, organization name, address, Cisco assigned user ID, email address, phone number, and account-related metadata – such as creation date).
https://sec.cloudapps.cisco.com/security/center/resources/CRM-vishing
The Cost of a Call: From Voice Phishing to Data Extortion
Google also disclosed a similar incident…
Update (August 5): In June, one of Google’s corporate Salesforce instances was impacted by similar UNC6040 activity described in this post. Google responded to the activity, performed an impact analysis and began mitigations. The instance was used to store contact information and related notes for small and medium businesses. Analysis revealed that data was retrieved by the threat actor during a small window of time before the access was cut off. The data retrieved by the threat actor was confined to basic and largely publicly available business information, such as business names and contact details.
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/voice-phishing-data-extortion
Hidden Black Hands: How $1.46 Billion Disappeared in Silence
Chinese summary of the events which unfolded..
Using the Lazarus attack on ByBit as a model, we delve into the entire process of front-end tampering that led to the disappearance of $1.46 billion. This story is not only a fascinating tale of technical and strategic maneuvering, but also reveals the enormous risks inherent in cybersecurity.
This incident demonstrates the exceptionally targeted nature of Lazarus's attacks. Rather than relying on complex coding techniques to confuse users, they employ precise social engineering and psychological tactics to target developers. By deeply understanding their targets' psychology and personality, they devise seemingly innocent yet concealed threats, leaving developers vulnerable.
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/4EnSsZu4Y4b426NzwjCGrA
Vulnerability
Our attack surface.
Stored XSS in OpenVPN Dashboard widget
Client names is the most likely exploitation method here..
The OpenVPN widget displays the name of OpenVPN clients and shared key servers to the user without encoding, which is a potential XSS vector.
Due to the lack of encoding on the interface content, the OpenVPN Dashboard widget at openvpn.widget.php is susceptible to XSS. Arbitrary JavaScript could be executed in the user's browser. The user's session cookie or other information from the session may be compromised.
https://docs.netgate.com/downloads/pfSense-SA-25_08.webgui.asc
PyPitfall: Dependency Chaos and Software Supply Chain Vulnerabilities in Python
Jacob Mahon, Chenxi Hou and Zhihao Yao give us a sense of scale of vulnerability introduced via dependencies in the Python eco-system.
We analyzed the dependency structures of 378,573 PyPI packages and identified 4,655 packages that explicitly require at least one known-vulnerable version and 141,044 packages that permit vulnerable versions within specified ranges. By characterizing the ecosystem-wide dependency landscape and the security impact of transitive dependencies, we aim to raise awareness of Python software supply chain security.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.18075
NVIDIA Triton
NVIDIA describe Triton as:
Triton Inference Server enables teams to deploy any AI model from multiple deep learning and machine learning frameworks.
CVE-2025-23319 - A Vulnerability Chain Leading to AI Server Takeover
Ronen Shustin and Nir Ohfeld provide the first clutch of vulnerabilities.
Step 1: Information Disclosure of the Backend's Shared Memory Name
Step 2: Abusing the Shared Memory API for Arbitrary Read/Write
Step 3: Ways towards a Remote Code Execution
https://www.wiz.io/blog/nvidia-triton-cve-2025-23319-vuln-chain-to-ai-server
Uncovering memory corruption in NVIDIA Triton (as a new hire)
Will Vandevanter then goes at it from the other end i.e. good old memory corruption..
The unsafe
allocapattern appeared throughout Triton’s HTTP API and SageMaker service in multiple critical endpoints:
Repository index requests (
/v2/repository/index)Inference requests
Model load requests
Model unload requests
Trace setting updates
Logging configuration updates
System shared memory registration
CUDA shared memory registration
https://blog.trailofbits.com/2025/08/04/uncovering-memory-corruption-in-nvidia-triton-as-a-new-hire/
ChoiceJacking: Compromising Mobile Devices through Malicious Chargers like a Decade ago
Florian Draschbacher, Lukas Maar, Mathias Oberhuber, and Stefan Mangard tease this vulnerability class..
We responsibly disclosed all findings to affected vendors. All but one (including Google, Samsung, Xiaomi, and Apple) acknowledged our attacks and are in the process of integrating mitigations.
https://www.usenix.org/conference/usenixsecurity25/presentation/draschbacher
White Box + LLM
Chinese application of static code analysis and large language models to find vulnerabilities.
the technical principles are largely similar: source code is converted into an AST through lexical/syntactic analysis. By continuously traveling (many people call it "walking," but I prefer "traveling" for its richer meaning) through AST nodes, various graphs are generated, such as a function call graph (S)CG, a control flow graph (CFG), a data flow graph (DFG), or a combined code property graph (CPG). A graph search algorithm then identifies the propagation link between the source point (typically the entry point of the program's external API) and the sink point defined by the detection rule (depending on the vulnerability type, such as SQL injection targeting DAO layer methods and SSRF targeting HTTP request methods).
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/UyKXiR6WRSgwxeRR_uLIZg?scene=1
Qunar.com White Box Vulnerability AI Operation Practice
Chinese application of agentic AI to find vulnerabilities.
[Our] Multi-Agent White-Box Intelligent Vulnerability Audit System is an innovative attempt to address the operational challenges of SAST (Surveillance Assurance) vulnerability detection within the SDLC. By deeply integrating AI agent technology into the security audit process, we have achieved a shift from a labor-intensive to an intelligence-driven approach, effectively addressing the pain points of traditional SAST tools, such as high false positive rates, low audit efficiency, and difficulty in scalability.
More importantly, we've built a complete AI-driven closed loop from vulnerability discovery, auditing, remediation, and retesting, enabling truly unattended security operations. This not only significantly reduces operating costs but also provides more reliable security for agile development and rapid iteration.
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/7mUwMAcrGWiBXeJPgmQHBA?poc_token=HPCQkWij8pmKjc8HNL_aGqzfcoZVs3ZrQLnNVoJh
Hunting Deserialization Vulnerabilities With Claude
James Williams published this in June which I missed, but is relevant given the above. Again application of agentic AI in support of vulnerability discovery.
we’ve seen how we can use an MCP server to give Claude the ability to analyze .NET assemblies. We’ve used that ability to find a known vulnerability in a Microsoft-signed binary and seen how we need to be explicit when giving Claude instructions (such as telling it to review every file). Finally, we’ve built a working Proof-of-Concept for an attack path mentioned in the original disclosure of this vulnerability, which was left as an exercise for the reader in the Blue-Prints blog.
While we had to give Claude a few hints along the way, this process of analyzing a file and getting close to a working exploit was much faster than what we could do manually.
https://trustedsec.com/blog/hunting-deserialization-vulnerabilities-with-claude
Another Byte Bites the Dust
Alvaro Muñoz further compounds that there is value with this write-up..
In just 32 steps and under 14 minutes, XBOW transformed a simple blind SSRF vulnerability into a complete arbitrary file read capability. The attack chain demonstrated:
Reconnaissance: Systematic API discovery and documentation analysis
Vulnerability Identification: SSRF confirmation through controlled testing
Constraint Analysis: Understanding GDAL’s format expectations
Creative Problem Solving: Leveraging VRT files as an intermediary
Deep Technical Knowledge: Understanding PNG compression, filtering, and GDAL internals
Iterative Refinement: Multiple approaches from bulk reading to byte-by-byte precision
Horizontal Expansion: Pivoting from network SSRF to local file access
What makes this particularly impressive is how XBOW seamlessly navigated complex technical domains - from web application security to geospatial data processing, from PNG image formats to GDAL virtual file systems.
https://xbow.com/blog/xbow-titiler-lfi
Offense
Attack capability, techniques and trade-craft.
Hunting for Secrets in Plain Sight: Leveraging Internal Logging and Monitoring Services
Carter Ross reminds all of the importance of understanding what goes into logs and how said logs are protected.
During an internal network assessment, our team discovered an unauthenticated Kibana instance accessible on the client’s internal network. This misconfiguration provided immediate access to a wealth of logs without requiring any credentials, and we immediately recognized the opportunity it presented.
Extracting GitHub Credentials
We methodically searched through the accessible logs, using targeted queries to locate authentication information:
message:*github* AND message:*ghp_*This query revealed logs from a CI/CD pipeline containing a GitHub Personal Access Token (PAT) with elevated repository access. The token had been inadvertently captured in the logs when a developer was troubleshooting a failed deployment.
{
"status": {"loadbalancerstatus", "operationshealthcheck", "serviceinfo": },
"GITHUB_TOKEN": "ghp_a1b2c3d4e5f6g7h8i9j0k1l2m3n4o5p6q7r8s9",
"GITHUB_OWNER": "exampleorg",
}
Nemesis 2.0
Will Schroeder shows what offensive work aid tooling to triage the vast GB or TB exfiltrated looks like.
Through real-world usage across multiple red team operations, we discovered that our operators tended to mostly use Nemesis for:
Automated file enrichment and analysis
Centralized file triage in a browser interface
Structured data storage and search
Finding credentials and “interesting information”
…
Nemesis 2.0 represents a complete philosophical shift. Instead of trying to be everything to everyone, we focused on building the best possible file enrichment and triage platform for offensive operations.
https://specterops.io/blog/2025/08/05/nemesis-2-0/
TURNt
Adam Crosser releases a tunnelling technique which will add cost to network level detections.
TURNt (TURN tunneler) is a red team tool designed for one-off interactive command and control communications along-side an existing implant providing a long-term command and control connection. TURNt allows an operator to tunnel interactive command and control traffic such as hidden VNC and SOCKS traffick over legitimate meeting protocols used by web conferencing software such as Zoom or Microsoft Teams.
https://github.com/praetorian-inc/turnt/
OAuthSeeker
Adam Crosser also releases this phishing aid which we can expect to deployed shortly by adversaries.
OAuthSeeker is an red team tool for performing phishing attacks using malicious OAuth applications to compromise user identities within Microsoft Azure and Office365.
..
OAuthSeeker obtains valid Microsoft Graph API credentials inclduing a JWT and refresh token upon successful completion of the OAuth flow with the application. OAuthSeeker automatically perform the token refresh operation every twenty-four hours to ensure that refresh tokens remain active for their entire validity period and aren't revoked early.
https://github.com/praetorian-inc/oauthseeker/
Living in the Namespace
pepsi provides a Linux implant that detection teams will want to ensure coverage of and that shows a degree of sophistication.
A no-reboot, in-memory Linux persistence PoC leveraging namespace joining, user-namespace elevation, and self‑deletion.
A minimal C persistence tool demonstrating how to:
Join live namespaces (user, pid, net, mnt, ipc, uts, cgroup) via
/proc/*/ns/*andsetns()Elevate privileges inside a user namespace
unshare(CLONE_NEWUSER)+UID/GID mappingDaemonize using (
fork(),setsid(),prctl(PR_SET_NAME), redirect stdio to/dev/null)Beacon in-memory over a local HTTP channel
127.0.0.1:8443with randomized intervalsSelf-delete in-memory by zeroing and unlinking the running binary via
/proc/self/exe(Optional)
https://github.com/0pepsi/Linux-persistence
FileJacking – Initial Access with File System API
Print3M demonstrates a technique which we can expect pickup from..
This simple PoC shows how to read and overwrite a user-selected file from the browser. This technique can be used in redteaming, for example, to backdoor an LNK file directly from the browser.
How to use:
Open
index.htmlin Chromium-based browser.Open DevTools -> Console.
Drop "input" file.
Drop "output" file.
Great. Now the output file is overwritten with the content of input file.
To use this in a real-world exercise, remove the “input” file reading feature and replace it with the hard-coded base64 content displayed in the console.
https://print3m.github.io/blog/filejacking-initial-access-with-file-system-api
https://github.com/Print3M/FileJacking-PoC
Delete Shadow Copies Using The IOCTL_VOLSNAP_DELETE_SNAPSHOT IOCTL
NUL0x4C provides a capability we can expect to be leveraged in ransomware operations..
This branch completely avoids using any COM/VSS API, and instead, completely relies on IOCTL codes to query and delete all existing Shadow Copies
https://github.com/NUL0x4C/IOCTL_VOLSNAP_DELETE_SNAPSHOT
https://github.com/NUL0x4C/IOCTL_VOLSNAP_DELETE_SNAPSHOT/tree/IOCTL_VOLSNAP_QUERY_NAMES_OF_SNAPSHOTS
malefic
From China and seen in use in the wild
IoM implant, C2 Framework and Infrastructure
Starting with v0.1.1, we can eliminate the need for installation scripts and compilation environments. With just the server and client binaries, you can use IoM anywhere, eliminating the complexities of installing an environment or compiling Rust.
https://github.com/chainreactors/malefic
https://wiki.chainreactors.red/blog/2025/07/09/IoM_v0.1.1/
Exploitation
What is being exploited..
TrendMicro exploitation
Trend Micro Apex One™ (On-Premise) Management Console Command Injection RCE Vulnerabilities
Trend Micro notified..
Trend Micro has observed as least one instance of an attempt to actively exploit one of these vulnerabilities in the wild.
https://success.trendmicro.com/en-US/solution/KA-0020652
Alert Regarding Multiple OS Command Injection Vulnerabilities in Trend Micro Multiple Endpoint Security Products for Enterprises
JPCERT also issued this alert
On August 6, 2025, Trend Micro has released the information regarding vulnerabilities (CVE-2025-54948, CVE-2025-54987) in the management console of multiple endpoint security products for enterprises.
If these vulnerabilities are exploited, an unauthenticated attacker may execute arbitrary code. Trend Micro Incorporated has reported that attacks exploiting CVE-2025-54948 have been observed in the wild.
Since the vulnerabilities are already being exploited in the wild, the users of the affected products are recommended to update the affected system to the latest version as soon as possible. Please refer to the information provided by Trend Micro.
https://www.jpcert.or.jp/english/at/2025/at250016.html
SonicWall exploitation
SonicWall clarified the situation as the week went on..
We now have high confidence that the recent SSLVPN activity is not connected to a zero-day vulnerability. Instead, there is a significant correlation with threat activity related to CVE-2024-40766, which was previously disclosed and documented in our public advisory SNWLID-2024-0015.
July 2025 Uptick in Akira Ransomware Activity Targeting SonicWall SSL VPN
ArcticWolf called the zero-day originally,,,
The initial access methods have not yet been definitively confirmed in this campaign. While the existence of a zero-day vulnerability was initially deemed to be highly plausible by Arctic Wolf, SonicWall’s updated product notice suggests the possible exploitation of CVE-2024-40766, a previously disclosed vulnerability from August 2024.
Huntress then joined the pile in/on..
The Huntress SOC continues to see organizations impacted by threat actors targeting SonicWall seventh-generation firewall appliances. As of August 6, we've seen eight additional incidents (at least 28 overall) that stem from this cluster of threat activity.
https://www.huntress.com/blog/exploitation-of-sonicwall-vpn
GRITREP: Observed Malicious Driver Use Associated with Akira SonicWall Campaign
Jason Baker provides some details of the Windows drivers used in the campaign.
we have detected the repeated use of two Windows drivers by Akira affiliates. These drivers have almost certainly been used to facilitate AV/EDR evasion or disablement through a Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver (BYOVD) exploitation chain.
The first driver,
rwdrv.sys, is a legitimate driver for ThrottleStop. This Windows-based performance tuning and monitoring utility is primarily designed for Intel CPUs. It is often used to override CPU throttling mechanisms, improve performance, and monitor processor behavior in real time. We have observed Akira affiliates registering this driver as a service and we assess that this driver is used to gain kernel-level access to the impacted device.The second driver,
hlpdrv.sys, is similarly registered as a service. When executed, it modifies the DisableAntiSpyware settings of Windows Defender within\REGISTRY\MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\DisableAntiSpyware. The malware accomplishes this via execution of regedit.exe.
https://www.guidepointsecurity.com/blog/gritrep-akira-sonicwall/
Exploiting Retbleed in the real world
Matteo Rizzo and Andy Nguyen shows exploitation is at times still indistinguishable from magic when performed by the highly capable..
We focused specifically on AMD Zen 2 processors and successfully demonstrated arbitrary memory read access from a sandboxed, unprivileged process.
…
The exploit strategy involves breaking virtual and physical KASLR using microarchitectural side channels, and creating ideal disclosure gadgets through speculative Return Oriented Programming (ROP). We achieved data leakage at approximately 13 KB/s with high accuracy. This is sufficient to list running processes and VMs on the host machine and leak sensitive data from them in a targeted fashion (for example, cryptographic keys). The exploit also works from inside VMs, allowing the leakage of host machine data. Mitigations are expensive, impacting performance significantly.
https://bughunters.google.com/blog/6243730100977664/exploiting-retbleed-in-the-real-world
Tooling and Techniques
Low level tooling and techniques for attack and defence researchers…
YARAAST - YARA Abstract Syntax Tree
Marc R. provides this work aid which will support Yara optimisations.
A powerful Python library and CLI tool for parsing, analyzing, and manipulating YARA rules through Abstract Syntax Tree (AST) representations.
https://github.com/seifreed/yaraast
BamboozlEDR
Olaf Hartong provides a work aid which will support detection engineering to ensure coverage exists.
A comprehensive ETW (Event Tracing for Windows) event generation tool designed for testing and research purposes. BamboozlEDR features a TUI interface and can generate realistic security events across multiple Windows ETW providers to test EDR detection capabilities, log analysis systems, and security monitoring solutions.
https://github.com/olafhartong/BamboozlEDR
User-mode accessors
Microsoft publishes..
User-mode accessors (UMA) are a set of DDIs designed to safely access and manipulate user-mode memory from kernel-mode code. These DDIs address common security vulnerabilities and programming errors that can occur when kernel-mode drivers access user-mode memory.
Kernel-mode code that accesses/manipulates user-mode memory will soon be required to use UMA.
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/drivers/kernel/user-mode-accessors
Footnotes
Some other small (and not so small) bits and bobs which might be of interest.
Annual, quarterly and monthly reports
Cost of a data breach report 2025 - not sure why AI hyper focus
Trust but Verify: An Assessment of Vulnerability Tagging Services
Weapons of Information Warfare - Ukraine Government
The Discriminative Power of Cross-layer RTTs in Fingerprinting Proxy Traffic
Artificial intelligence
Books
Events
BlackHat Las Vegas - slides in part linked from schedule
Finally finally the NCSC’s podcast series.
Unless stated otherwise, linked or referenced content does not necessarily represent the views of the NCSC and reference to third parties or content on their websites should not be taken as endorsement of any kind by the NCSC. The NCSC has no control over the content of third party websites and consequently accepts no responsibility for your use of them.
This newsletter is subject to the NCSC website terms and conditions which can be found at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/terms-and-conditions and you can find out more about how will treat your personal information in our privacy notice at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/privacy-statement.