CTO at NCSC Summary: week ending August 17th
"AI Cyber Challenge marks pivotal inflection point for cyber defense.."
Welcome to the weekly highlights and analysis of the blueteamsec Lemmy (and my wider reading). Not everything makes it in, but the best bits do.
Operationally this week nothing overly of note…
In the high-level this week:
CyberFirst Bursary expression of interest - NCSC announce - “CyberFirst offers students a path into the UK’s most exciting and future-proof tech careers – whether you’re just finishing A Levels (or equivalent) or already at university.
With the CyberFirst Bursary, you’ll receive:
£4,000 per year financial assistance
8-week summer placements (receive at least £2,000 per placement) with leading tech employers
Hands-on training, building real-world experience and confidence”
Secure by Design: Two Years of Building a More Resilient MOD - Ministry of Defence UK reflects - “The success of Secure by Design depends on a collective effort. We urge all industry partners to embrace this approach, actively collaborating with MoD delivery teams, consulting the Secure by Design Guidance, and integrating security into their core processes. By working together, we can significantly strengthen our national cyber defences and safeguard the UK's future.”
Adoption of cyber insurance by UK small and medium sized enterprises - Department for Science, Innovation and Technology publishes - “This study explores small and medium sized enterprises’ (SMEs) perceptions of cyber insurance, their adoption decisions, its role in risk management, and market gaps requiring potential government intervention. Using a mixed-methods research approach combining literature review, interviews, and a survey, it offers a thorough analysis of key challenges and opportunities.”
Emerging technologies and their effect on cyber security - Department of Science Innovation and Technology publishes - “Through a comprehensive review of the literature and real-world case studies, this study identifies and highlights key vulnerabilities arising from these technological pairings.”
Commercial offensive cyber capabilities - Department for Science, Innovation and Technology and Feryal Clark MP publishes - “This research looks at how the commercial offensive cyber sector is integrating emerging technologies into their commercial offerings and what the implications of this integration are.”
Securing converged technologies: insights from subject matter experts -Department of Science Innovation and Technology publishes - “Based on research with 20 subject matter experts primarily from the cyber security sector, this report presents a series of findings on the challenges of identifying technology convergences for cyber security, how technology convergence operates across broader technology ecologies, and how engagement with a range of actors in order to build expert communities is essential to addressing and mitigating the impact of technology convergence for cyber security.”
CDS formally releases declassified versions of Joint Doctrines for Cyberspace Operations & Amphibious Operations - Ministry of Defence India declassifies - “The Joint Doctrine for Cyberspace Operations outlines a unified approach to defend national cyberspace interests, integrating offensive and defensive cyber capabilities and enabling synchronised operations across the three Services. It emphasises threat-informed planning, resilience building, real-time intelligence integration and development of joint cyber capabilities.”
Cyber Associates Network - NHS England establishes - “NHS England have established a free network of cyber security expertise across public-sector health and care”
Appeals Court Upholds FCC Data Breach Rules for Hacked Telecoms - Bloomberg Law reports - ”A federal appeals court delivered a victory to the Federal Communications Commission on Wednesday by upholding new and controversial data breach reporting requirements for telecommunications companies targeted in cyberattacks.”
Poland foiled cyberattack on big city's water supply, deputy PM says - Reuters reports - “In an interview with news portal Onet on Thursday, Deputy Prime Minister Krzysztof Gawkowski, who is also digital affairs minister, did not specify who was behind the attack or which city was targeted.”
Leak Reveals the Workaday Lives of North Korean IT Scammers - WIRED reports - ”Multiple screenshots of spreadsheets in the data obtained by SttyK show a cluster of IT workers that appear to be split into 12 groups—each with around a dozen members—and an overall “master boss.” The spreadsheets are methodologically put together to track jobs and budgets: They have summary and analysis tabs that drill down into the data for each group. Rows and columns are neatly filled out; they appear to be updated and maintained regularly.”
The Rules of the Road in Cyberspace, 10 Years Later - Allison Pytlak, Christina Rupp, Eugene EG Tan, Louise Marie Hurel, Talita Dias and Valentin Weber think tank - “As states exploit the fine lines between crisis and conflict, the strategic imperative remains: without shared understandings – however limited – about what constitutes responsible behaviour in cyberspace, the risk of escalation will only grow.”
The Intellectual Dishonesty and Moral Poverty of “Shields Up” - Joe Slowik opines - “The dislocation between physical and cyber security postures in state defensive decision making is confounding in many ways. While the cyber problem may be “hard” for a variety of technical and attributive reasons, the dereliction of duty of state authorities in pushing back against criminal and external entities operating with malicious purpose in this domain is astounding.”
Calibrated Signals: How Middle Powers Are Rewriting the Rules of Cyber Attribution in the Indo-Pacific - The Diplomat opines - “Across the Indo-Pacific, a new cyber doctrine is emerging among middle powers. As regional cyber threats mount and great power tensions deepen, countries such as Singapore, Samoa, and others are beginning to articulate strategies that assert digital sovereignty while presenting strategic autonomy. They are opting for attribution that is technically precise but diplomatically restrained, a form of sovereign signaling that eschews overt confrontationalism while subtly affirming their place in the digital order.”
Significant Service Provider Examination Program - Office of Inspector General outlines - “RMS stated that they consider quantitative factors to determine which service providers pose the greatest risk to banks. These factors include metrics such as the number of banking customers the service provider serves, the value of the assets held by client banks, the volume of payments processed, and other key business line metrics. RMS stated that they prioritize examining service providers who interact with the most banks and banks who have the most assets. This helps manage risk because a cyber incident at a large technology service provider has the potential to cause contagion within the financial sector, potentially having widespread impact.”
“Rules on preventative and criminal procedural (source) telecommunications surveillance and criminal procedural remote searches are constitutional for the most part - Federal Constitutional Court of Germany rules - “Source telecommunications surveillance for the investigation of criminal acts which only carry a maximum sentence of imprisonment of three years or less is not proportionate in the strict sense and was therefore declared void by the Senate.”
Quantum mechanics, classical backbone: DARPA’s QuANET advances practical quantum networking - DARPA announce - “On one link, messages were encoded onto squeezed light, which is a quantum state of light that can enhance precision for certain measurements. Researchers transmitted encoded data, including images of the DARPA logo, a QuANET event graphic, and an ascii cat. The initial transmission took five minutes, but through real-time optimization, subsequent attempts reduced the time to a never-before-achieved 0.7 milliseconds, or a bit rate of 6.8 Mbps – enough to stream high-definition video.”
Reporting on/from China
Researchers identify Chinese cybercriminal working for North Korean threat group - NK News reports - “Cybersecurity researchers say they have identified an operative working for the DPRK threat group Kimsuky who is Chinese, potentially marking the first known case of direct foreign participation in Pyongyang’s state-backed cybercrime.”
Thais Caught with Smishing SMS Blaster Say Chinese Boss Paid $75 per Day - CommsRisk reports - “One of the arrested men told the police that they had been recruited via Telegram messages from a Chinese man who paid them THB2,500 (USD75) a day. Both men admitted the SMS blaster had been driven around on three separate occasions, the earliest of which was August 2 of this year. A spokesperson for AIS stated the device they were using had an effective range of 1-2km and was capable of sending over 20,000 SMS messages a day.”
Taiwan cyberattacks ‘below average’ but widespread: Beijing political advisor - South China Morning Post reports - Zhou Hongyi, chairman of cybersecurity company Qihoo 360 and a member of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference, China’s top political advisory body, said in an interview with Hong Kong-based Phoenix TV that aired on Wednesday that Taiwanese hackers operated at a “below global-average level”.
Digital siege puts Taiwan’s resilience to the test - Australian Strategic Policy Institute asserts - “The campaign extends well beyond conventional cyber espionage. Beijing has significantly expanded its use of information warfare. According to the National Security Bureau, over 2.15 million disinformation incidents targeting Taiwan were documented in 2024, a nearly twofold increase from the previous year.”
SMIC says more Chinese chip players 'perfectly' replacing foreign rivals - Nikkei Asia reports - “Zhao said some of its Chinese customers, particularly in power-related semiconductors, previously only ordered about 2,000 8-inch wafers a month from SMIC. Within just two years, that monthly figure had surged tenfold to 20,000 wafers.”
From Shanghai to the Shore: The Silent Threat in Global Shipping - US Coast Guard present - the team that found the cellular modems.
AI
AI Cyber Challenge marks pivotal inflection point for cyber defense - DARPA and ARPA-H announce and draw to a close - “In total, competitors’ systems discovered 54 unique synthetic vulnerabilities in the Final Competition’s 70 challenges. Of those, they patched 43…In the Final Competition, teams also discovered 18 real, non-synthetic vulnerabilities that are being responsibly disclosed to open source project maintainers. Of these, six were in C codebases—including one vulnerability that was discovered and patched in parallel by maintainers—and 12 were in Java codebases. Teams also provided 11 patches for real, non-synthetic vulnerabilities.”
Buttercup is now open-source! - Trail of Bits detail..
Exploring Traces: Agent trajectory walkthroughs from interesting examples - Theori explain..
When LLMs autonomously attack - Carnegie Mellon teases - “Rather than requiring the LLM to execute raw shell commands—often a limiting factor in prior studies—this system provides the LLM with higher-level decision-making capabilities while delegating low-level tasks to a combination of LLM and non-LLM agents.” - we await the paper / detail here but a lot of claims which will need analysis..
This is the prior academic work from January - On the Feasibility of Using LLMs to Autonomously Execute Multi-host Network Attacks
Month of AI Vulns - Johann Rehberger publishes - a vulnerability a day in AI systems demonstrating that sadly that previous cycles are repeating.
NIST Releases Control Overlays for Securing AI Systems Concept Paper - NIST publishes - “The concept paper outlines proposed AI use cases for the control overlays to manage cybersecurity risks in the use and development of AI systems, and next steps. The use cases address generative AI, predictive AI, single and multi-agent AI systems, and controls for AI developers.”
Automate security reviews with Claude Code - Anthropic announce - we await performance measurement - “checks for common vulnerability patterns including:
SQL injection risks
Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities
Authentication and authorization flaws
Insecure data handling
Dependency vulnerabilities”
No Increase in GPU, the First Token Latency Decreases by 50% | New Practices in LLM Service Load Balancing - Alibaba Cloud announce - “the Higress AI gateway provides load balancing algorithms geared toward LLM services in a plug-in form, including global least connections load balancing, prefix matching load balancing, and GPU-aware load balancing. This can enhance system throughput, reduce response delays, and achieve fairer and more efficient task scheduling without increasing hardware costs.”
ASTRA: Autonomous Spatial-Temporal Red-teaming for AI Software Assistants - Purdue University researches - “We present ASTRA, an automated agent system designed to systematically uncover safety flaws in AI-driven code generation and security guidance systems.”
Gartner Hype Cycle Identifies Top AI Innovations in 2025 - Gartner opines - “Among the AI innovations Gartner expects will reach mainstream adoption within the next 5 years, multimodal AI and AI trust, risk and security management (TRiSM) have been identified as dominating the Peak of Inflated Expectations”
Cyber proliferation
Prefiguring Responsibility: The Pall Mall Process and Cyber Intrusion Capabilities - Andrew Dwyer opines - “With the conclusion of the UN OEWG on cyber in June 2025, there are clearly limitations to what can be achieved in the international community at large. This is where the narrower scope of the Pall Mall Process could be a more successful approach to limiting the proliferation of cyber intrusion capabilities and building desirable markets for them.”
Bounty Hunting
Justice Department Announces Coordinated Disruption Actions Against BlackSuit (Royal) Ransomware Operations - US Department of Justice announce - “The Justice Department announced today coordinated actions against the BlackSuit (Royal) Ransomware group which included the takedown of four servers and nine domains on July 24, 2025.”
ICE Washington, D.C. leads international takedown of BlackSuit ransomware infrastructure - US Immigration and Customs Enforcement announce - “ICE’s Homeland Security Investigations, in close coordination with U.S. and international law enforcement partners, has successfully dismantled critical infrastructure used by BlackSuit ransomware, a major cybercriminal operation and successor to Royal ransomware, responsible for attacks on essential services around the world. The operation resulted in the seizures of servers, domains and digital assets used to deploy ransomware, extort victims, and launder proceeds.”
No reflections this week but I will be at BSides Bournemouth tomorrow.
Not getting this via email? Subscribe:
Think someone else would benefit? Share:
All attribution is by others and not the UK Government unless specifically stated as such, please see the legal text at the end.
Have a lovely Friday…
Ollie
Cyber threat intelligence
Who is doing what to whom and how allegedly.
Reporting on Russia
Curly COMrades: A New Threat Actor Targeting Geopolitical Hotbeds
Victor Vrabie details a campaign which is allegedly Russian in origination. It shows a degree of persistent intent and is noteworthy for regional targeting as well as some of the technical tradecraft on show.
This research from Bitdefender Labs details a cluster of malicious activity we've been tracking since mid-2024. It uncovers a new threat actor group we’ve named Curly COMrades, operating to support Russian interests, that's been targeting critical organizations in countries facing significant geopolitical shifts.
The group's primary objective is to maintain long-term access to target networks and steal valid credentials. This allows them to move around the network, collect data, and send it out. They repeatedly attempted to extract the NTDS database from domain controllers, the primary repository for user password hashes and authentication data in a Windows network. Additionally, they attempted to dump LSASS memory from specific systems to recover active user credentials, potentially plain-text passwords, from machines where users were logged on.
Update WinRAR tools now: RomCom and others exploiting zero-day vulnerability
Anton Cherepanov, Peter Strýček and Damien Schaeffer detail the exploitation of this vulnerability by an operation which is allegedly Russian in origin. The fact this vulnerability was exploited as a zero-day and the sectoral targeting is of note.
If you use WinRAR or other affected components such as the Windows versions of its command line utilities, UnRAR.dll, or the portable UnRAR source code, upgrade immediately to the latest version.
On July 18th, 2025, ESET researchers discovered a previously unknown zero-day vulnerability in WinRAR being exploited in the wild.
Analysis of the exploit led to the discovery of the vulnerability, now assigned CVE-2025-8088: a path traversal vulnerability, made possible with the use of alternate data streams. After immediate notification, WinRAR released a patched version on July 30th, 2025.
The vulnerability allows hiding malicious files in an archive, which are silently deployed when extracting.
Successful exploitation attempts delivered various backdoors used by the RomCom group, specifically a SnipBot variant, RustyClaw, and Mythic agent.
This campaign targeted financial, manufacturing, defense, and logistics companies in Europe and Canada.
Reporting on China
Few and Far Between: During China’s Red Hacker Era, Patriotic Hacktivism Was Widespread—Talent Was Not
Eugenio Benincasa continues to build on their analysis of the origins of a national capability which has developed over nearly 30 years..
This piece dives deeper into that history and examines how these hacker groups, despite their size, relied on a small, tightly knit circle of technically proficient individuals. It highlights the distinction between core members and registered users, the range of roles within the core teams, and their internal structures.
..
Despite their importance, the number of highly skilled hackers within red hacker groups was likely small. In some cases, the lack of enough technical talent proved a challenge to the group’s ability to function—at times even threatening its survival. In 2004, HUC’s leader Lin Yong (林勇, lion) acknowledged the group's lack of enough technical talent in his farewell message:
“To be truthful, the Honker Union of China has been surviving in name only… Talking about the technical side, there have been only three people providing technical support for the Honker Union of China, bkbll (online name), uhhuhy (online name), and myself.”
nattothoughts.substack.com/p/few-and-far-between-during-chinas
UNC3886 Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures: Full Technical Breakdown
Sıla Özeren Hacıoğlu provides a breakdown / write up of this alleged Chinese threat actor. Given recent attribution of some of their intrusions it summarises in open source what is known.
UNC3886 is a China-linked cyber espionage group targeting critical infrastructure in Asia, Europe, and North America. In 2025, Singapore formally attributed attacks to the group, highlighting its focus on sectors like energy, telecom, healthcare, and transportation.
Known for exploiting zero-days in Fortinet, VMware, and Juniper systems, UNC3886 deploys rootkits, maintains persistence, and evades detection using encrypted channels, renamed utilities, and non-standard protocols.
Initial access via Fortinet and VMware zero-day vulnerabilities
Persistence using TinyShell, REPTILE, and kernel-level rootkits
Command and Control through encrypted channels and non-standard ports
Target focus: strategic infrastructure and unmonitored environments (e.g., hypervisors, routers)
Ongoing campaigns observed in 2025, including overlaps with the “Fire Ant” espionage operation
Reporting on North Korea
APT Down: The North Korea Files
Saber / cyb0rg writes up an apparent leak against this alleged North Korean threat actor. A look behind the curtain which may be useful to some research groups.
The dump includes many of Kimsuky's backdoors and their tools as well as the internal documentation. It shows a glimpse how openly "Kimsuky" cooperates with other Chinese APTs and shares their tools and techniques. Some of these tools may already be known to the community: You have seen their scans and found their server side artifacts and implants. Now you shall also see their clients, documentation, passwords, source code, and command files...
https://drive.proton.me/urls/ZQ1235FY7C#P0khjXI2uEtS
Reporting on Iran
Handala Hacker Exposed: Iran International Identifies Intelligence Ministry Operative Behind Cyber Attack
Iran international identify the individuals they alleged behind some of the alleged Iranian cyber attacks.
Tonight's investigation by Iran International identifies Ali Bermoode, a 27-year-old from Tabriz, as an admin of Handala's channels—an amateur hacker whose father works for the Martyrs Foundation and who has been serving Iran's cyber police since he was 16.
The investigation goes deeper, connecting Bermoode to his Intelligence Ministry handler Morteza Aftabifar, and ultimately to Yahya Hosseini Panjaki, the Deputy Director of Domestic Security at Iran's Intelligence Ministry.
https://blog.narimangharib.com/posts/2025%2F08%2F1755123023755?lang=en
Reporting on Other Actors
CrossC2 Expanding Cobalt Strike Beacon to Cross-Platform Attacks
Yuma Masubuchi details the use of a specific implant framework by an an apparent criminal threat group. The fact that Linux is being targeted in this manner is of note coupled with the fact this implant specifically.
From September to December 2024, JPCERT/CC has confirmed incidents involving CrossC2, the extension tool to create Cobalt Strike Beacon for Linux OS. The attacker employed CrossC2 as well as other tools such as PsExec, Plink, and Cobalt Strike in attempts to penetrate AD. Further investigation revealed that the attacker used custom malware (hereafter referred to as "ReadNimeLoader") as a loader for Cobalt Strike.
..
Despite architectural differences, confirmed identical characteristics suggest that this attacker and the attack campaign have a potential connection to BlackBasta.
https://blogs.jpcert.or.jp/en/2025/08/crossc2.html
Scammers mass-mailing the Efimer Trojan to steal crypto
Artem Ushkov and Vladimir Gursky detail a campaign which is noteworthy for the fact that WordPress sites are being compromised in order to distribute some of the payloads. That and Tor being used as the command and control infrastructure..
Efimer is spreading through compromised WordPress sites, malicious torrents, and email.
It communicates with its command-and-control server via the Tor network.
Efimer expands its capabilities through additional scripts. These scripts enable attackers to brute-force passwords for WordPress sites and harvest email addresses for future malicious email campaigns.
https://securelist.com/efimer-trojan/117148/
Shedding Light on PoisonSeed’s Phishing Kit
Efstratios Lontzetidis provides some insight into this phishing kit which attempts to downgrade the methods of authentication used. The lesson here is only use phishing resistent authentication mechanisms.
NVISO identified and analyzed the MFA-resistant phishing kit employed by the threat actor PoisonSeed, which is loosely aligned with Scattered Spider and CryptoChameleon. This kit is still active as of the time of reporting.
PoisonSeed uses this phishing kit to acquire credentials from individuals and organizations, leveraging them for email infrastructure purposes such as sending emails and acquiring email lists to expand the scope of cryptocurrency-related spam.
The domains hosting this phishing kit impersonate login services from prominent CRM and bulk email companies like Google, SendGrid, Mailchimp, and likely others, targeting individuals’ credentials.
PoisonSeed employs spear-phishing emails embedding malicious links, which redirect victims to their phishing kit.
https://blog.nviso.eu/2025/08/12/shedding-light-on-poisonseeds-phishing-kit/
New Ransomware Charon Uses Earth Baxia APT Techniques to Target Enterprises
Jacob Santos, Ted Lee, Ahmed Kamal and Don Ovid Ladores evidence what the contemporary criminal threat is employing in places. Whilst the techniques might have originated in some APT groups, it didn’t always and has been documented extensively by various commercial red teamers and threat intelligence outfits.
Trend™ Research uncovered a campaign that makes use of Charon, a new ransomware family, and advanced APT-style techniques, including DLL sideloading, process injection, and anti-EDR capabilities, to target organizations with customized ransom demands.
https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/research/25/h/new-ransomware-charon.html
Discovery
How we find and understand the latent compromises within our environments.
Detection Engineering Framework
Kunal Hatode, Frank Hassenrueck and Matrix Chau provide a framework which some may find interesting..
A comprehensive framework for Security Operations Center (SOC) use case development, detection engineering, implementation, and management.
This framework is designed to help security teams develop, implement, and maintain effective SOC use cases and detection rules. Whether you're building a new SOC or enhancing existing capabilities, this repository provides the guidance you need to be better at it.
https://github.com/Ke0xes/Detection-Engineering-Framework
Practicing Detection-as-Code – Validation
Stamatis Chatzimangou walks through the next phase of employing detection-as-code in the real world.
In this part, we focus on implementing validation checks to improve consistency and ensure a minimum level of quality within the detection repository. Setting up validation pipelines is a key step, as it helps enforce the defined standards, reduce errors, and ensure that detections are reliable and consistent. We’ll break the validation process into several smaller scripts and pipelines that you can refer to when building your own validation workflows. This approach also helps make the content of this blog post easier to digest.
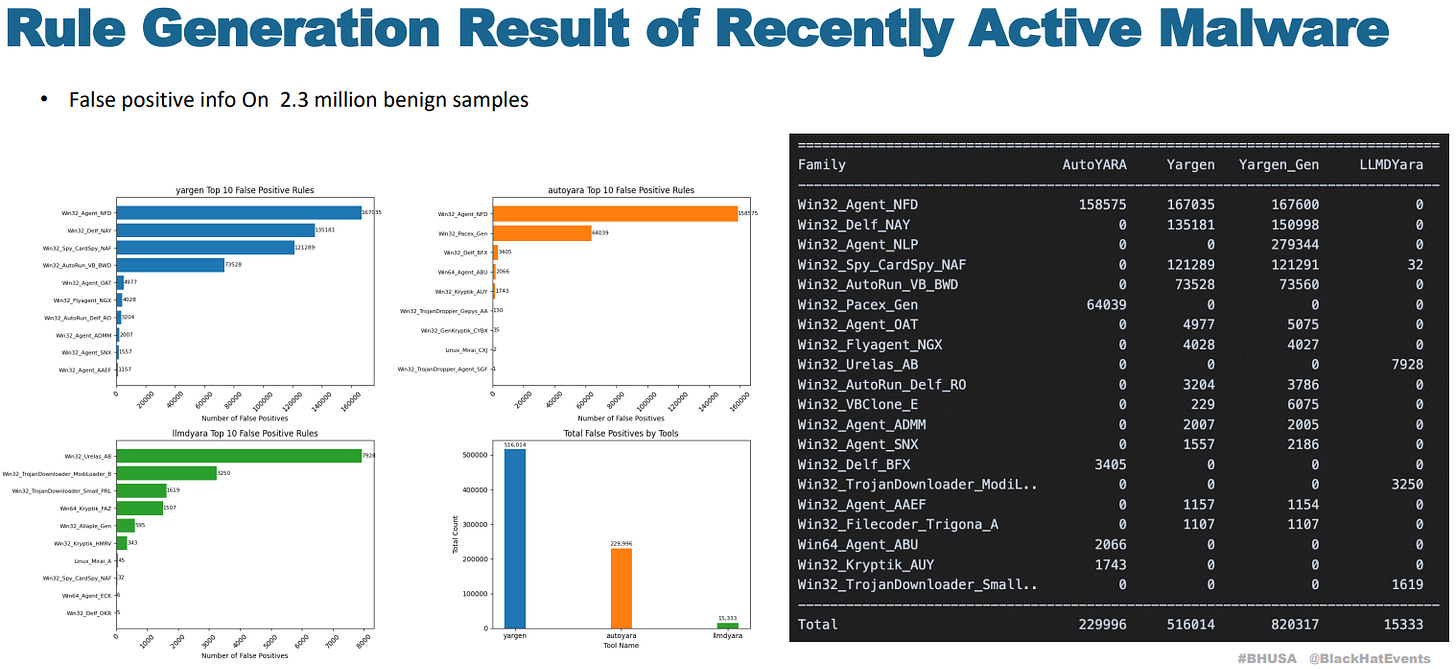
LLMDYara
Xiaochen Wang, Yiping Liu, Xiaoman Wang and Cong Cheng show an end-to-end approach which some comparatively impressive false positive results.
LLMs-Driven Automated YARA Rules Generation with Explainable File Features and DNAHash
Defence
How we proactively defend our environments.
Foundations for OT Cybersecurity
CISA release an Asset Inventory Guidance for Owners and Operators which is a very good start.
This guidance was developed to provide operational technology (OT) owners and operators across all critical infrastructure sectors with a systematic approach for creating and maintaining an OT asset inventory and supplemental taxonomy—essential for identifying and securing critical assets, reducing the risk of cybersecurity incidents, and ensuring the continuity of the organization's mission and services. By following the outlined process, organizations can enhance their overall security posture, improve maintenance and reliability, and ensure the safety and resilience of their OT environments. This guidance was created by CISA in partnership with:
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
U.S. National Security Agency
U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation
Australian Signals Directorate’s Australian Cyber Security Centre
Canadian Centre for Cyber Security
Germany’s Federal Office for Information Security
Netherlands’ National Cyber Security Centre
New Zealand’s National Cyber Security Centre
Secure Future Initiative (SFI) patterns and practices
Joy Chik and Ann Johnson release these patterns and practices to help organisations address these specific scenarios in the Microsoft eco-system..
We are launching the first wave of eight pattern and practice articles that help solve the most asked-for, urgent, and complex challenges faced by security practitioners today:
Phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication
Eliminate identity lateral movement
Remove legacy systems that risk security
Standardize secure development pipelines
Complete production infrastructure inventory
Rapid anomaly detection and response
Security log retention standards
Accelerate vulnerability mitigation
Sanctum EDR
flux details the journey so far in developing (and open sourcing) their own EDR.
Sanctum is an experimental proof-of-concept EDR, designed to detect modern malware techniques, above and beyond the capabilities of antivirus.
https://fluxsec.red/sanctum-edr-intro
https://github.com/0xflux/Sanctum
Stardust Chollima APT Adversary Simulation
Abdulrehman Ali release his next adversary simulation for that Rocky training montage..
This is a simulation of attack by (Stardust Chollima) APT group targeting Chilean interbank network, The attack campaign was active in December 2018, have used PowerRatankba, a PowerShell-based malware variant that closely resembles the original Ratankba implant. The Redbanc corporate network was infected with a version of the PowerRatankba that was not detected by anti-malware. The way attackers delivered the malware, according to Flashpoint a trusted Redbanc IT professional clicked to apply to a job opening found on social media (linkedin).
https://medium.com/@S3N4T0R/stardust-chollima-apt-adversary-simulation-d5c115a89ab9
A High-level Framework for Accelerating Cyber Deception Experimentation
Brian Singer, Yusuf Saquib, Lujo Bauer and Vyas Sekar released this back in June which will be of interest to some who are looking to build evidence bases around cyber deception efficacy.
we design four key modules for Perry:
an action planner that translates high-level actions into low-level implementations,
an observability module to translate low-level telemetry into high-level observations,
an environment state service that enables environment agnostic strategies, and
an attack graph service to reason about how attackers could explore an environment.
We illustrate that Perry's abstractions reduce the implementation effort of exploring a wide variety of deception defenses, attackers, and environments. We demonstrate the value of Perry by emulating 55 unique deception what-if scenarios and illustrate how these experiments enable operators to shed light on subtle tradeoffs.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.20770
Fingerprint-aware TLS reverse proxy
Adel Ka releases this proxy which will have a variety of defensive use cases.
Finch is a lightweight reverse proxy written in Go. It inspects TLS handshakes and HTTP requests to extract JA3, JA4, JA4H, and Akamai HTTP/2 fingerprints, then evaluates them—alongside the rest of the request metadata—against flexible, hot‑reloadable rules written in HCL. On a per‑request basis, Finch can:
allow legitimate traffic
deny unwanted traffic
route clients to alternate upstreams
deceive attackers with on‑the‑fly, LLM‑generated responses via Galah
tarpit scanners with slow drip responses
https://github.com/0x4D31/finch
SpecLFB: Eliminating Cache Side Channels in Speculative Executions
Xiaoyu Cheng , Fei Tong , Hongyu Wang , Zhe Zhou , Fang Jiang and Yuxing Mao show the potential value of open architectures in developing and experimenting with microarchitectural improvements against long standing issues. Will be interesting to see if this hits a mainline ISA and then production..
To further reduce processor performance overhead, SpecLFB narrows down the protection scope of unsafe speculative loads and determines the time at which they can be deprotected as early as possible. SpecLFB has been implemented in the open-source RISC-V core, SonicBOOM, as well as in Gem5. For the enhanced SonicBOOM, its register-transfer-level (RTL) code is generated, and an FPGA hardware prototype burned with the core and running a Linux-kernel-based operating system is developed. Based on the evaluations in terms of security guarantee, performance overhead, and hardware resource overhead through RTL simulation, FPGA prototype experiment, and Gem5 simulation, it shows that SpecLFB effectively defends against attacks. It leads to a hardware resource overhead of only 0.6% and the performance overhead of only 1.85% and 3.20% in the FPGA prototype experiment and Gem5 simulation, respectively.
https://www.usenix.org/system/files/sec24summer-prepub-556-cheng-xiaoyu.pdf
Incident Writeups & Disclosures
How they got in and what they did.
Nothing overly of note this week
Vulnerability
Our attack surface.
Chosen Plaintext Attack on AMD SEV-SNP
Benedict Schlüter, Christoph Wech and Shweta Shinde detail an attack against confidential compute which evidences one more we have a way to go to realise in reality.
Heracles makes three observations: the hypervisor can move encrypted guest pages in DRAM using 3 APIs; when it moves the guest pages to a new DRAM address, pages are re-encrypted; re-encryption is deterministic. By re-encrypting guest data at precisely chosen DRAM locations, we create an oracle allowing us to leak guest memory at block granularity. We build 4 primitives that leverage victims' access patterns to amplify Heracles' impact to not only leak data at block but at byte granularity. In our case studies, we leak kernel memory, crypto keys, and user passwords, as well as demonstrate web session hijacking
https://heracles-attack.github.io/
Breaking Into Your Network? Zer0 Effort
Gavin Holt details what they have discovered in terms of zero trust solution vulnerabilities. Given the scale at which some of these products have been deployed they raise a few eyebrows..
Netskope – Authentication Bypass in IdP Enrolment Mode
Full authentication bypass and user impersonation vulnerability when a non-revocable “OrgKey” value is known.
Netskope – Cross-tenant Authentication Bypass
Full authentication bypass and user impersonation vulnerability when a non-revocable “OrgKey” value is known, alongside any enrolment key. This key does not need to be associated with the same tenant as the OrgKey.
Netskope – Local Privilege Escalation via Rogue Server (CVE-2025-0309)
Local privilege escalation to SYSTEM by coercing the Netskope client to communicate with a rogue server.
Zscaler – SAML Authentication Bypass (CVE-2025-54982)
Full authentication bypass, as Zscaler failed to validate that SAML assertions were correctly signed.
Check Point – Hard-coded SFTP key (CVE-2025-3831)
Access to an SFTP server containing client logs for multiple tenants, including files with JWT material that could allow authentication against the Harmony SASE service.
https://blog.amberwolf.com/blog/2025/august/breaking-into-your-network-zer0-effort/
WinRAR 7.13 Final released
WinRAR release the patch the vulnerability covered under Threat Intelligence above.
Critical vulnerability CVE-2025-8088. Directory traversal vulnerability affecting the Windows versions of WinRAR, UnRAR, and associated components. The vulnerability allows specially crafted archives to bypass the user-specified extraction path and write files to unintended locations on the file system. This issue is distinct from the previously fixed vulnerability in version 7.12 and required immediate action.
https://www.win-rar.com/singlenewsview.html
Offense
Attack capability, techniques and trade-craft.
AWS WAF Solver
Kian shows applying contemporary AI can cut through some captchas.
This project provides a Golang & Python-based solver for the AWS WAF challenge. It supports both the type "token" / "Invisible" and type "Captcha" using Gemini
https://github.com/xKiian/awswaf
Remote DLL Injection with Timer-based Shellcode Execution
Andrea Bocchetti shows how this capability work which will be useful to detection engineers to ensure they have coverage for.
Remote DLL Injection with Timer-based Shellcode Execution is a technique that leverages the Windows thread pool to execute shellcode. Using the classic DLL injection with CreateThreadpoolTimer to run shellcode in-memory using legit system threads, stealthy, and likely to slip past modern defenses
This approach introduces a stealthy execution using Timer-based Shellcode Execution
https://github.com/andreisss/Remote-DLL-Injection-with-Timer-based-Shellcode-Execution
Dumping with Shadow Snapshot Method via WMI (No Code Execution)
Peter Gabaldon shows a technique and integrates into impact that teams will definitely want to ensure they have detection coverage for.
As a reminder of the workflow of this technique:
A Shadow Snapshot is created remotely via WMI. Create method of class Win32_ShadowCopy
Then, via SMB, the Shadow Snapshot is accesed using a previous version Token (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/openspecs/windows_protocols/ms-smb/bffc70f9-b16a-453b-939a-0b6d3c9263af). Shadow Snapshots are listed using SMB via SCTL_SRV_ENUMERATE_SNAPSHOTS
Then, SAM, SYSTEM, SECURITY (and if specfified via -use-remoteSSWMI-NTDS NTDS.dit) are download. Without a Shadow Snapshot this disk access attempt would be denied.
Then locally they are parsed and dumped.
Finally, the Shadow Snapshot is deleted. Call to DeleteInstance
https://github.com/fortra/impacket/pull/2021
Shade BIOS
Kazuki Matsuo releases the a capability that organisations will want to be mindful has now proliferated given the low levels of observability and potential detectability.
We propose the concept "pure-BIOS malware", which operates completely independent from OS-level security and performs malbehaviors without device dependence at runtime. Then, we will introduce Shade BIOS, which made this possible. Shade BIOS operates like an attacker-exclusive OS by running BIOS environment, which would normally lose its functionality after OS boot, in the shadow of OS at runtime.
In this talk, we dive into the technical details of Shade BIOS. Moreover, considering the latest trends in BIOS security, such as SMM deprivileging, we will take a broad perspective on BIOS and examine the optimal entity for pure-BIOS malware. As a starting point for detecting pure-BIOS malware, we will also demonstrate a practical method for detecting Shade BIOS.
ModuleLoaderPkg: DXE module that loads & executes DXE modules from a USB stick
ShadeBiosPkg: Main Shade BIOS package
VarPrintPkg: Library that allows printing debug messages or statuses to the UEFI variables
https://github.com/FFRI/ShadeBIOS/
BeaconatorC2
Mike Manrod and co releases this capability which detection engineering teams will want to ensure they are able to detect.
BeaconatorC2 is a framework for red teaming and adversarial emulation, providing a full-featured management interface, along with a catalog of beacons and a clear schema to add more beacons over time.
https://github.com/CroodSolutions/BeaconatorC2
Exploitation
What is being exploited..
Citrix vulnerability (Update 13-08-2025)
NCSC Netherlands highlights that this vulnerability was exploited earlier than first thought.
Based on forensic analyses of data from the affected organizations, the NCSC has indications that the vulnerabilities in Citrix NetScaler ADC were first exploited in early May.
Tooling and Techniques
Low level tooling and techniques for attack and defence researchers…
Relational Hoare Logic for Realistically Modelled Machine Code
Denis Mazzucato, Abdalrhman Mohamed, Juneyoung Lee, Clark Barrett, Jim Grundy, John Harrison and Corina S. Pasareanu show that relational verification can be applied to assembly. Useful for some low level code / embedded / media codec use cases.
In this work, we introduce a Hoare-style logic that provides low-level, expressive relational verification. We demonstrate our approach on the s2n-bignum library, proving both constant-time discipline and equivalence between optimized and verification-friendly routines. Formalized in HOL Light, our results confirm the real-world applicability of relational verification in large assembly codebases.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.14348
First steps for ASI (ASI is fast again)
Brendan Jackman detail how he has addressed performance improvements in Address Space Isolation which is intended to mitigate speculative execution attacks. The post provides insights into both the solution and where Google use it.
The goal of this prototype is to increase confidence that ASI is viable as a broad solution for CPU vulnerabilities. (If the community still has to develop and maintain new mitigations for every individual vuln, because ASI only works for certain use-cases, then ASI isn't super attractive given its complexity burden).
The biggest gap for establishing that confidence was that Google's deployment still only uses ASI for KVM workloads, not bare-metal processes. And indeed the page cache turned out to be a massive issue that Google just hasn't run up against yet internally.
This is achieved in this prototype by a mechanism that I've called the "ephmap". The ephmap is a special region of the kernel address space that is local to the mm (much like the "proclocal" idea from 2019 [2]). Users of the ephmap API can allocate a subregion of this, and provide pages that get mapped into their subregion. These subregions are CPU-local. This means that it's cheap to tear these mappings down, so they can be removed immediately after use (eph = "ephemeral"), eliminating the need for complex/costly tracking data structures.
https://lore.kernel.org/lkml/20250812173109.295750-1-jackmanb@google.com/T/
Windows 11 24H2 Runtime PatchGuard Bypass
Wane provides a proof-of-concept which we should expect will be patched. The whitepaper is extensive in its analysis and shows various bypass opportunities.
kurasagiis full POC of PatchGuard bypass for Windows 24H2, Build 26100.4351.
https://github.com/NeoMaster831/kurasagi
https://github.com/NeoMaster831/kurasagi/blob/product/Win11_PG_1-1.pdf
Footnotes
Some other small (and not so small) bits and bobs which might be of interest.
Annual, quarterly and monthly reports
2025年中网络安全漏洞威胁态势研究报告 - 2025 Cybersecurity Vulnerability Threat Landscape Research Report - from China
Cybercrime in Australia 2024 - “This is the second report in the Cybercrime in Australia series, which describes cybercrime victimisation, help-seeking and harms among Australian computer users.”
2025 State of the Internet: Digging into Residential Proxy Infrastructure
Noise-Coded Illumination for Forensic and Photometric Video Analysis
Evaluating Software Supply Chain Security in Research Software
Artificial intelligence
When AIOps Become "AI Oops": Subverting LLM-driven IT Operations via Telemetry Manipulation
Is Chain-of-Thought Reasoning of LLMs a Mirage? A Data Distribution Lens
Embedding Atlas - “Embedding Atlas is a tool that provides interactive visualizations for large embeddings. It allows you to visualize, cross-filter, and search embeddings and metadata.”
Books
Nothing overly of note this week
Events
Call for Submissions on “Digital Twins” - Harvard Data Science Review by January 15th, 2026
Finally finally the NCSC’s podcast series.
Unless stated otherwise, linked or referenced content does not necessarily represent the views of the NCSC and reference to third parties or content on their websites should not be taken as endorsement of any kind by the NCSC. The NCSC has no control over the content of third party websites and consequently accepts no responsibility for your use of them.
This newsletter is subject to the NCSC website terms and conditions which can be found at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/terms-and-conditions and you can find out more about how will treat your personal information in our privacy notice at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/privacy-statement.