CTO at NCSC Summary: week ending January 12th
Stack overflows being exploited in edge devices in 2025..
Welcome to the weekly highlights and analysis of the blueteamsec subreddit (and my wider reading). Not everything makes it in, but the best bits do.
Operationally this week we released an advisory on Active exploitation of vulnerability affecting Ivanti Connect Secure. Which is a stack based overflow.. in 2025 ..
In the high-level this week:
Driving Cyber Resilience in the Supply Chain – Call for action - UK Ministry of Defence publishes (well in December they did) - “Irrespective of the nature of your business, building resilience and good security practice across the end-to-end supply chain to mitigate this risk is non-negotiable and a critical requirement for all contracts with the Ministry of Defence”
New Australian Cyber Security Centre head appointed - Aussie government announces - “Ms Stephanie Crowe has today been appointed as the new Head of the Australian Signals Directorate (ASD) Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC).”
White House Launches "U.S. Cyber Trust Mark", Providing American Consumers an Easy Label to See if Connected Devices are Cybersecure - The White House announces - “Voluntary cybersecurity labeling program for wireless interconnected smart products, administered by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), will help Americans make more informed decisions about the cybersecurity of products”
White House Rushes to Finish Cyber Order After China Hacks - Bloomberg reports - “Among the measures, it directs the government to implement “strong identity authentication and encryption” across communications, according to an undated draft of the order seen by Bloomberg News. In the December Treasury hack, intruders accessed unclassified documents stored locally on laptops and desktop computers. Encrypting information sent by email and worked on in the cloud could help safeguard it from hackers who successfully access systems but then cannot open specific documents.”
Ukrainian Intel Strikes Russian Transport Service With Cyberattack on Budanov’s Birthday - Kyiv Post reports - “The attack led to the destruction of 78 servers, the disabling of 211 workstations, and the erasure of all backups, according to sources within HUR.”
OECD Policy Framework on Digital Security - OECD publishes - “Charts the economic and social dimension of cybersecurity, highlights the OECD approach to digital security policy and equips policymakers to use OECD digital security Recommendations in developing better policies.”
Myanmar enforces cybersecurity law effective January 1 - The Nation reports - “In addition, if an expatriate Myanmar citizen commits a crime punishable under the cyber law, it will be prosecuted under the cyber law.”
Myanmar cyber law worries foreign businesses over VPNs - Nikkei Asia reports - “Myanmar's military government has enacted a law that represses information on the internet and imposes penalties involving virtual private networks without authorization, complicating how businesses engage in daily operations.”
FCC chief urges auction to fund 'Rip and Replace' program - FCC outlines - “The recently passed National Defense Authorization Act provides essential funding for the Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Reimbursement (or “Rip and Replace”) Program by giving the Commission authority to auction AWS-3 spectrum licenses in its inventory.”
Israel unveils domestically built quantum computer - Asia Pacific Defence Reporter reports - “The 20-qubit quantum computer was developed under the leadership of the Israel Innovation Authority, Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), Hebrew University, and the university’s technology transfer company, Yissum.”
Reporting on/from China
READOUT: Secretary of the Treasury Janet L. Yellen’s Meeting with Vice Premier He Lifeng of the People’s Republic of China - US Department of the Treasury releases - “Secretary Yellen also expressed serious concern about malicious cyber activity by PRC state-sponsored actors and its impact on the bilateral relationship.”
How Chinese Hackers Graduated From Clumsy Corporate Thieves to Military Weapons - Wall Street Journal publishes - “Some national security officials involved in the investigation said they believe the telecom hack is so severe, and the networks so compromised, that the U.S. may never be able to say with certainty that the Chinese hackers have been fully rooted out”
China’s No 2 chip foundry Hua Hong names former Intel veteran as new president - South China Morning Post reports - “Bai has over 30 years of semiconductor fabrication experience and previously held executive positions at various chipmakers, including Intel”
Chinese state-owned AI firm hires ex-IBM executive as technology chief - South China Morning Post reports - “Xie previously served as CTO at IBM Greater China Group, vice-president at IBM China Systems Lab, and the director of the IBM China Research Lab. A Tsinghua University graduate, he worked at IBM for nearly three decades.”
AI
Japan and U.S. to start joint AI cyberattack research - Nikkei Asia reports - “TOKYO -- Japan and the U.S. will partner on research into cyberattacks that exploit artificial intelligence, Nikkei has learned, looking to combine advanced American technology with Tokyo's data on incidents outside English-speaking countries.”
Evaluating Large Language Models' Capability to Launch Fully Automated Spear Phishing Campaigns: Validated on Human Subjects - Harvard Kennedy School et al publish - “fully AI-automated emails 54% (clickthrough), and AI emails utilizing a human-in-the-loop (56% click-through). Thus, the AI-automated attacks performed on par with human experts” - from November but interesting nevertheless…
Cyber proliferation
Israeli Hackers Flock to Barcelona as Spyware Industry Shifts - Haaretz reports - "There are roughly six such groups of Israelis who are the elite in the field – and half of them have moved to Spain," says an industry executive.”
Bounty Hunting
Treasury Sanctions Technology Company for Support to Malicious Cyber Group - US Department of the Treasury announces - “the Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) sanctioned Integrity Technology Group, Incorporated (Integrity Tech), a Beijing-based cybersecurity company, for its role in multiple computer intrusion incidents against U.S. victims.”
89% of executives plan to expand cyber insurance for technological vulnerabilities - Reinsurance News reports - “The survey also found that 79% of companies are implementing AI in their risk management processes, though many executives express concerns about AI-related risks, such as deep fakes, with over 50% reporting that their companies have been impacted.” - note this was 500 companies..
Reflections this week are on one side we have stack based overflows being exploited in edge security devices in 2025..
.. on the other side we have memory safe languages, CHERI and a myriad of other mitigations which are available.
Think someone else would benefit? Share:
All attribution is by others and not the UK Government unless specifically stated as such, please see the legal text at the end.
Have a lovely Saturday…
Ollie
Cyber threat intelligence
Who is doing what to whom and how allegedly.
Reporting on Russia
Tracking Deployment of Russian Surveillance Technologies in Central Asia and Latin America
Insikt Group detail where Russia is exporting this technology..
Several countries in Central Asia –– Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Uzbekistan –– and in Latin America –– Cuba and Nicaragua –– almost certainly base their digital surveillance capabilities on Russia System for Operative Investigative Activities SORM, indicating that Russian surveillance technology has proliferated in Russias near abroad and among its allies. Russias largest SORM technology providers –– most notably, Citadel, Norsi-Trans, and Protei –– export to and participate in regional trade expositions in Africa, Latin America, and the Middle East, further indicating continued efforts to expand globally.
Governments in Central Asia –– Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Uzbekistan –– and in Latin America –– Cuba and Nicaragua –– have purchased surveillance solutions from Russian SORM providers, significantly expanding their capacity to conduct digital surveillance.
Russian SORM providers such as Protei market their products toward governments in Africa, Latin America, and the Middle East, and participate in regional trade shows –– signaling their desire to expand the market for Russian surveillance technology.
The presence of SORM-based surveillance systems in a country almost certainly indicates government capability to intercept telecommunications and internet traffic without notifying service providers, denoting a heightened level of state surveillance risk.
Each of the countries analyzed in this report is assessed to have high or very high state surveillance risk, has historically conducted intrusive domestic surveillance with limited oversight, and is likely to monitor foreign travelers of interest.
In light of these risks, companies seeking to establish physical operations or conduct business travel in markets where government surveillance capabilities are based on SORM should take steps to secure online communications and limit exposure of sensitive data, including using encrypted messaging applications and VPNs.
The provision of SORM hardware and software to foreign governments by Russian companies, particularly those with close ties to Russian security services, likely entails a degree of access to these systems by Russian intelligence. Thus, exports from Russian SORM providers likely both expand Russias influence and enhance Moscows intelligence collection capabilities globally.
https://go.recordedfuture.com/hubfs/reports/ta-ru-2025-0107.pdf
Reporting on China
Cyber attacks using MirrorFace
Japanese National Police Agency release this alert on attacks they attribute to China. In part initial access appears to have used phishing..
The National Police Agency and the National Center of Incident Readiness and Strategy for Cybersecurity have assessed that a cyber attack campaign against organizations, businesses and individuals in Japan from around 2019 to the present has been carried out by a cyber attack group called "MirrorFace" (also known as "Earth Kasha").
..
In addition, based on an analysis of the targets, methods, and attack infrastructure of the attacks that emerged in investigations by the National Police Agency Kanto Regional Police Bureau Cyber Special Investigation Unit, the Tokyo Metropolitan Police Department, and other prefectural police departments, it has been determined that the MirrorFace attack campaign is an organized cyber attack suspected to be linked to China, with the primary objective of stealing information related to Japan's security and advanced technology.
EAGERBEE, with updated and novel components, targets the Middle East
Saurabh Sharma and Vasily Berdnikov detail this alleged Chinese intrusion which utilised ProxyLogon (CVE-2021-26855) for its initial access.
This memory-resident architecture enhances its stealth capabilities, helping it evade detection by traditional endpoint security solutions. EAGERBEE also obscures its command shell activities by injecting malicious code into legitimate processes, such as dllhost.exe, and executing it within the context of explorer.exe or the targeted user’s session. These tactics allow the malware to seamlessly integrate with normal system operations, making it significantly more challenging to identify and analyze.
In the East Asian EAGERBEE attacks, the organizations were penetrated via the ProxyLogon vulnerability. ProxyLogon remains a popular exploit method among attackers to gain unauthorized access to Exchange servers. Promptly patching this vulnerability is crucial to securing your network perimeter.
Because of the consistent creation of services on the same day via the same webshell to execute the EAGERBEE backdoor and the CoughingDown Core Module, and the C2 domain overlap between the EAGERBEE backdoor and the CoughingDown Core Module, we assess with medium confidence that the EAGERBEE backdoor is related to the CoughingDown threat group.
However, we have been unable to determine the initial infection vector or identify the group responsible for deploying the EAGERBEE backdoor in the Middle East.
https://securelist.com/eagerbee-backdoor/115175/
Chinese State-Sponsored RedDelta Targeted Taiwan, Mongolia, and Southeast Asia with Adapted PlugX Infection Chain
Insikt Group detail a comprehensive set of campaigns by this alleged Chinese actor. Initial access appears to be phishing..
Between July 2023 and December 2024, Insikt Group observed the Chinese state-sponsored group RedDelta targeting Mongolia, Taiwan, Myanmar, Vietnam, and Cambodia with an adapted infection chain to distribute its customized PlugX backdoor. The group used lure documents themed around the 2024 Taiwanese presidential candidate Terry Gou, the Vietnamese National Holiday, flood protection in Mongolia, and meeting invitations, including an Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) meeting. RedDelta likely compromised the Mongolian Ministry of Defense in August 2024 and the Communist Party of Vietnam in November 2024. The group conducted spearphishing targeting the Vietnamese Ministry of Public Security, but Insikt Group observed no evidence of successful compromise. From September to December 2024, RedDelta likely targeted victims in Malaysia, Japan, the United States, Ethiopia, Brazil, Australia, and India.
Ivanti Connect Secure VPN Targeted in New Zero-Day Exploitation
John Wolfram, Josh Murchie, Matt Lin, Daniel Ainsworth, Robert Wallace, Dimiter Andonov, Dhanesh Kizhakkinan and Jacob Thompson detail exploitation which they allege in Chinese in origin..
Mandiant observed the deployment of the previously observed SPAWN ecosystem of malware (which includes the SPAWNANT installer, SPAWNMOLE tunneler and the SPAWNSNAIL SSH backdoor).
The deployment of the SPAWN ecosystem of malware following the targeting of Ivanti Secure Connect appliances has been attributed to UNC5337, a cluster of activity assessed with moderate confidence to be part of UNC5221, which is further described in the Attribution section.
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/ivanti-connect-secure-vpn-zero-day
Reporting on North Korea
Hangro: Investigating North Korean VPN Infrastructure Part 1
Nick details how it works.. which is best described as scrappy..
In a post from a now-deleted user on the webdev subreddit, someone asked about how to acquire a .kp TLD. While there were a few decent responses, the original poster shared an update: they successfully obtained a domain but noted that a VPN is required to access the website. This raised intriguing questions about VPN usage in North Korea.
Reporting on Iran
Nothing this week..
Reporting on Other Actors
Beware of foreign APT organizations poisoning GitHub and attacking domestic security practitioners and designated large enterprises
Chinese reporting on alleged Vietnamese activity using Microsoft developer tooling as the initial access vector..
In this attack, the attacker used the method of delivering malicious .suo files to Visual Studio projects for the first time. When the victim compiled the Visual Studio project, the Trojan was automatically executed. The attack method was novel and covert.
In recent incidents, "Ocean Lotus" has launched targeted attacks on different industries and groups in the country, and will also target designated large technology companies. The first attack will take place from mid-September to early October 2024. The Weibo Intelligence Bureau has captured multiple suspicious assets and Trojan files.
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ih36z93y6BazatjeoGjp1A
Jingle Shells: How Virtual Offices Enable a Facade of Legitimacy
S2 Research Team publishes insight into the business plumbing that means that organisations and infrastructure may not be what it appears.
Virtual office services are increasingly leveraged to establish shell companies, sometimes with multiple entities registered at the same address, creating an appearance of legitimacy while obscuring the true nature of operations.
Some hosting providers, including those registered in jurisdictions like the UK, operate infrastructure in regions with less regulatory oversight, such as Mauritius and Seychelles, which can make it easier to circumvent stricter compliance requirements.
The combination of leased IPv4 space, limited "know your customer" (KYC) processes, and weak regulatory frameworks may inadvertently enable the creation of hosting environments that support activities such as phishing and malware command-and-control (C2) servers.
https://www.team-cymru.com/post/how-virtual-offices-enable-a-facade-of-legitimacy
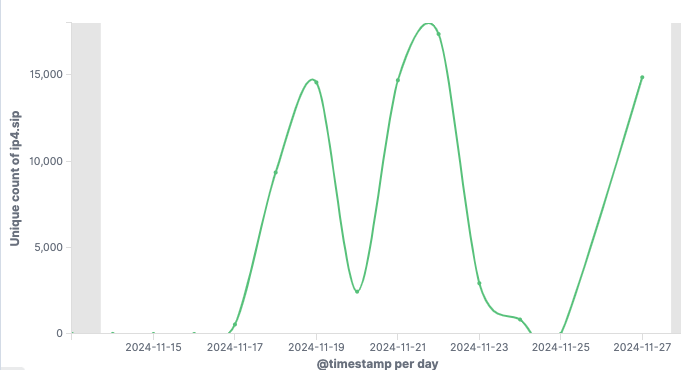
Gayfemboy: A Botnet Deliver Through a Four-Faith Industrial Router 0-day Exploit.
Wang Hao, Alex.Turing and Acey9 detail how what appears to be a rather basic operation has been successful in building a botnet..
February 12, 2024: XLab first discovered Gayfemboy samples, packed with a standard UPX shell.
April 15, 2024: The UPX magic number was modified to
YTS\x99, and the bot began using thegayfemboyregistration packet.Early June 2024: The UPX magic number was changed to
1wom. The bot code became relatively stable, with only occasional additions of new C2 domains.Late August 2024: Samples hardcoded six C2 domains, with the last three remaining unregistered.
November 9, 2024: Gayfemboy was observed exploiting a 0-day vulnerability in Four-Faith industrial routers to deliver its samples. The samples were executed with the parameter
faith2.November 17, 2024: We registered several unregistered domains found in Gayfemboy samples to observe infected devices and measure the botnet’s scale.
November 23, 2024: Gayfemboy’s operators detected our registration of their C2 domains and began periodically launching DDoS attacks against the domains we registered.
December 27, 2024: VulnCheck publicly disclosed the 0-day vulnerability information for Four-Faith industrial routers.
https://blog.xlab.qianxin.com/gayfemboy-en/
Discovery
How we find and understand the latent compromises within our environments.
GetTracelogProviderSecurity.ps1
Olaf Hartong publishes a small script which enumerate registered ETWTrace logging providers and their DACLs
gist.github.com/olafhartong/f4f438ae2143ad9f72f3dc60136a9066
Defence
How we proactively defend our environments.
Using CHERI capabilities instead of trusting 3rd party code
Phil Day shows off some of the hyper powerful features in the CHERIoT platform and specifically capabilities and how they can be used to provide library isolation.
When getting started with CHERI it’s easy to think of capabilities as just a better form of pointer that the compiler will set up and manage on your behalf. And of course there are a lot of memory safety benefits that come for free from that, but the real value is unlocked when you start to manipulate capabilities directly to capture intent.
So by explicitly using the extra controls that CHERIoT provides we can eliminate any trust relationship between our code and some third party module and its compilation environment. The CHERI processor will guarantee that the MQTT library can only use the pointers we supply in the way we intend it to, even if the library is implemented to make use of compiler escape hatches such as “
unsafe”. And that’s a significant step forwards in creating safe and reliable systems.
https://cheriot.org/rtos/cheri/2025/01/08/capabilities-not-trust-third-party.html
A just culture guide for information governance and cyber security
NHS England publishes this guide..
This guidance supports organisations to understand and embed a just culture in their information governance (IG) and cyber security risk management work, taking a compassionate approach to and learning from any data incidents.
It is for leaders and cyber security and IG professionals in NHS organisations and independent providers, arm’s length bodies and suppliers to the health and adult social care sectors. These include executive board members, data protection officers (DPOs), senior information risk owners (SIROs), Caldicott Guardians and leaders in social care.
Project Quarantine
Mike Fiedler publishes its planned mitigation against the myriad of malicious typo-squatting Python packages etc.
Earlier this year, I wrote briefly about new functionality added to PyPI, the ability to quarantine projects. This feature allows PyPI administrators to mark a project as potentially harmful, and prevent it from being easily installed by users to prevent further harm.
In this post I'll discuss the implementation, and further improvements to come.
https://blog.pypi.org/posts/2024-12-30-quarantine/
A Tour of WebAuthn
Adam Langley publishes a comprehensive overview which is a must read for those dealing with this technology.
https://www.imperialviolet.org/tourofwebauthn/tourofwebauthn.pdf
Incident Writeups & Disclosures
How they got in and what they did.
Hackers Claim Massive Breach of Location Data Giant, Threaten to Leak Data
Gravy Analytics has been one of the most important companies in the location data industry for years, collating smartphone location data from around the world selling some to the U.S. government. Hackers say they stole a mountain of data.
https://www.404media.co/hackers-claim-massive-breach-of-location-data-giant-threaten-to-leak-data/
Vulnerability
Our attack surface.
WorstFit: Unveiling Hidden Transformers in Windows ANSI!
Orange Tsai details a vulnerability class which I suspect I unknowingly used about 25 years ago to convert Cyrillic (from memory) pipe characters to | for use on penetration test..
The research unveils a new attack surface in Windows by exploiting Best-Fit, an internal charset conversion feature. Through our work, we successfully transformed this feature into several practical attacks, including Path Traversal, Argument Injection, and even RCE, affecting numerous well-known applications!
https://devco.re/blog/2025/01/09/worstfit-unveiling-hidden-transformers-in-windows-ansi/
KernelSnitch: Side-Channel Attacks on Kernel Data Structures
Lukas Maar, Jonas Juffinger, Thomas Steinbauer, Daniel Gruss and Stefan Mangard detail a set of techniques which will be useful in certain niche use cases.
In three case studies, we show that KernelSnitch allows unprivileged and isolated attackers to leak sensitive information from the kernel and activities in other processes. First, we demonstrate covert channels with transmission rates up to 580 kbit/s. Second, we perform a kernel heap pointer leak in less than 65 s by exploiting the specific indexing that Linux is using in hash tables. Third, we demonstrate a website fingerprinting attack, achieving an F1 score of more than 89 %, showing that activity in other user programs can be observed using KernelSnitch. Finally, we discuss mitigations for our hardware-agnostic attacks.
https://lukasmaar.github.io/papers/ndss25-kernelsnitch.pdf
Hat Trick: AWS introduced same RCE vulnerability three times in four years
Giraffe Security detail how regressions and variations can be painful..
Now, in December 2024, I happened to visit Amazon’s Neuron SDK private package index again, and I observed that they had expanded their set of packages quite a bit and had introduced many new ones. Out of curiosity, I checked whether they had claimed all these new packages in PyPi, and stumbled upon packages that were available and I was able to claim under my own PyPi account. This means that they have still not properly addressed the problem by getting rid of the “extra-index-url” in their documentation, 2+ years after my report in 2022, and they still do not have a foolproof system to claim package names on PyPi.
https://giraffesecurity.dev/posts/amazon-hat-trick/
Offense
Attack capability, techniques and trade-craft.
I’m watching you! How to spy Windows users via MS UIA
Michael Zhmailo shows how accessibility frameworks can be misused by adversaries. In reality this is not a security boundary - the complexity arises when trying to - interestingly it potentially has implications for information protection solutions..
there is a Windows User Automation framework that allows you to work with any Windows graphical elements.
They handle all the GUI changes we are interested in: data input, text copying, data modification. Among other things, I've added handlers under different processes and even domains in the browser so you can get more familiar with the framework!
I added an example of using patterns (one of the UIA components) on the example of KeePass looting.
https://cicada-8.medium.com/im-watching-you-how-to-spy-windows-users-via-ms-uia-c9acd30f94c4
https://github.com/CICADA8-Research/Spyndicapped
Cobalt Strike Beacon Open Source Implementation
El Javi Luki provides a capability which is a couple of years old. I am including because of the value and need to be able to detect to ensure coverage.
Please note that this project is not a reverse-engineered version of the Cobalt Strike Beacon but a ground-up open-source implementation.
https://github.com/ElJaviLuki/CobaltStrike_OpenBeacon
Exploitation
What is being exploited..
Ivanti Connect Secure VPN Targeted in New Zero-Day Exploitation
John Wolfram, Josh Murchie, Matt Lin, Daniel Ainsworth, Robert Wallace, Dimiter Andonov, Dhanesh Kizhakkinan and Jacob Thompson detail exploitation which they allege in Chinese in origin..
Mandiant observed the deployment of the previously observed SPAWN ecosystem of malware (which includes the SPAWNANT installer, SPAWNMOLE tunneler and the SPAWNSNAIL SSH backdoor).
The deployment of the SPAWN ecosystem of malware following the targeting of Ivanti Secure Connect appliances has been attributed to UNC5337, a cluster of activity assessed with moderate confidence to be part of UNC5221, which is further described in the Attribution section.
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/ivanti-connect-secure-vpn-zero-day
Backdooring Your Backdoors - Another $20 Domain, More Governments
Benjamin Harris and Aliz Hammond exploit expired domains to obtain contact from various webshells resulting in understanding the level of latent compromise.
Put simply - we have been hijacking backdoors (that were reliant on now abandoned infrastructure and/or expired domains) that themselves existed inside backdoors, and have since been watching the results flood in. This hijacking allowed us to track compromised hosts as they ‘reported in’, and theoretically gave us the power to commandeer and control these compromised hosts.
..
Friends - we registered 40+ domains and began spinning up infrastructure.
..
Over 4000 unique and live backdoors later (the number continues to grow), we decided this research would never be finished, and it would be interesting to share the results in their current state.
https://labs.watchtowr.com/more-governments-backdoors-in-your-backdoors/
Tooling and Techniques
Low level tooling and techniques for attack and defence researchers…
Copycat
Magnus Groß gives a capability that memory forensics teams will want to ensure they can detect..
This library allows you to overwrite system calls of arbitrary binaries in an intuitive way.
..
Internally
copycatuses a modern Seccomp Notifier implementation to reliably intercept system calls. This is more elegant and much faster than usualptrace-based implementations. However due to this relatively new Linux Kernel feature,copycatonly works on Linux 5.9 or higher.
https://github.com/vimpostor/copycat
Footnotes
Some other small (and not so small) bits and bobs which might be of interest.
Aggregate reporting
The Cyber Sessions: Fail to plan, plan to fail by NHS England Transformation
Artificial intelligence
Books
Nothing this week
Events
Program Agenda: 2025 FIRST Cyber Threat Intelligence Conference, April 21st, Berlin
Video of the week is Systematization of Knowledge: Quantifying Cyber Risk by Daniel W. Woods and Rainer Böhme from a few years back..
Unless stated otherwise, linked or referenced content does not necessarily represent the views of the NCSC and reference to third parties or content on their websites should not be taken as endorsement of any kind by the NCSC. The NCSC has no control over the content of third party websites and consequently accepts no responsibility for your use of them.
This newsletter is subject to the NCSC website terms and conditions which can be found at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/terms-and-conditions and you can find out more about how will treat your personal information in our privacy notice at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/privacy-statement.



Ollie, your White House links are 404s. Here is the Federal Register version m8: https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2025/01/17/2025-01470/strengthening-and-promoting-innovation-in-the-nations-cybersecurity