CTO at NCSC Summary: week ending January 21st
Ivanti Connect Secure VPN and Citrix NetScaler exploitation etc.. is the focus of the week..
Welcome to the weekly highlights and analysis of the blueteamsec subreddit (and my wider reading). Not everything makes it in, but the best bits do.
Operationally this week it is all around the exploitation of security appliances, which once again evidence that security products do not always equal secure products..
In the high-level this week:
Landing at the NCSC (glad I brought my towel) - by moi at NCSC UK, more in the reflections…
NCSC UK launched Cyber League which builds on Industry 100 - come help protect the nation
Membership of Cyber League is voluntary and we welcome new members. To participate in Cyber League, an organisation must:
have a substantial UK connection
be part of the cyber security or threat intelligence industry
Up to three individuals in an organisation can join the Cyber League community, providing they have the relevant cyber experience and knowledge.
UK-Ukraine Agreement on Security Co-operation - The Participants will work together on intelligence and security co-operation to enable Ukraine to detect, deter and disrupt Russian conventional aggression, espionage and hybrid warfare, including through greater cyber resilience, with cyber advice and industry support to secure IT infrastructure from cyber-attack, while supporting the modernisation and reform of Ukraine’s security and intelligence architecture, including on cyber and information security issues.
US Federal Cybersecurity Research And Development Strategic Plan - wonderful bit of work..
Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2024 by the World Economic Forum - The concerns about disruption are not unfounded when considering that 29% of leaders stated that their organization had experienced a material impact from a cyberattack in the past 12 months.
Systemic Risk Survey Results - 2023 H2 by the Bank of England - Cyber attack and geopolitical risk remain the most frequently cited perceived sources of risk to the financial system among financial market participants. The proportion of respondents citing cyber risk is at its highest level recorded in the survey.
Impact of the Russia–Ukraine War on National Cyber Planning: A Survey of Ten Countries - Cyber security can only be achieved by proactive measures informed by the principles of ‘active defence’ and ‘defence in depth’.
Cyber Diplomacy: State's Efforts Aim to Support U.S. Interests and Elevate Priorities - interesting insight on how they got their talent - State used special hiring authorities, such as Direct Hire Authority, as well as special programs, such as the Foreign Affairs Information Technology Fellowship Program to meet mission priorities. As mentioned above, CDP is exploring additional special hiring mechanisms to expedite the process and working to develop partnerships with industry, academia, and other agencies to create a talent pipeline.
CISA ready to take CDM program into the world of OT - In the Office of Management and Budget’s 2024 Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) guidance, agencies must establish an enterprise-wide inventory of their agency’s covered IoT assets by the end of fiscal 2024. These OT systems include everything from industrial control systems to building management systems to fire control systems to physical access control mechanisms.
Thousands of pension holders to sue Capita over ‘Russia-linked’ hack - It is the first such litigation following last year’s cyber attack. The law firm acting for the claimants estimated the case could be worth up to £5m. Capita has said it does not believe there is “any valid basis” for bringing a claim against it.
19 Individuals Worldwide Charged In Transnational Cybercrime Investigation Of The xDedic Marketplace - xDedic offered more than 700,000 compromised servers for sale, including at least 150,000 in the United States and at least 8,000 in Florida
Defending Democracy
Taiwan bombarded with cyberattacks ahead of election - Google Cloud’s cyber threat intelligence firm Mandiant warned Tuesday of a “substantial volume of espionage operations” by China against Taiwan’s government, technology and critical infrastructure, according to a statement from Ben Read, the company’s head of cyber espionage analysis. “While this type of targeting has occurred for years, the volume over the past few months has been notable.”
Slew of deepfake video adverts of Sunak on Facebook raises alarm over AI risk to (UK) election - More than 100 deepfake video advertisements impersonating Rishi Sunak were paid to be promoted on Facebook in the last month alone, according to research that has raised alarm about the risk AI poses before the general election - the research.
Free Cybersecurity Support for your NGO - nice initiative here.
Reporting on/from China
Cybersecurity Guidance on Chinese-Manufactured UAS for Critical Infrastructure Owners and Operators - by CISA - The People’s Republic of China (PRC) has enacted laws that provide the government with expanded legal grounds for accessing and controlling data held by firms in China. The use of Chinese-manufactured UAS in critical infrastructure operations risks exposing sensitive information to PRC authorities. This guidance outlines the potential vulnerabilities to networks and sensitive information when operated without the proper cybersecurity protocols and the potential consequences that could result.
China's military and government acquire Nvidia chips despite U.S. ban by Reuters - Buying or selling high-end U.S. chips is not illegal in China and the publicly available tender documents show dozens of Chinese entities have bought and taken receipt of Nvidia semiconductors since restrictions were imposed.
Artificial intelligence
Generative AI first call for evidence: The lawful basis for web scraping to train generative AI models - from the UK’s Information Commissioners Office
Draft S.3205 - Federal Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Act of 2023 - This bill directs federal agencies to use the Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Framework developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) regarding the use of artificial intelligence (AI).
NIST Identifies Types of Cyberattacks That Manipulate Behavior of AI Systems - Their work, titled Adversarial Machine Learning: A Taxonomy and Terminology of Attacks and Mitigations (NIST.AI.100-2), is part of NIST’s broader effort to support the development of trustworthy AI, and it can help put NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework into practice.
The Australian Government’s interim response to safe and responsible AI consultation - The consultation received over 500 submissions. Over 20% of submissions were from individuals, showing that citizens care about safe and responsible AI. We also heard from 345 virtual town hall attendees and over 200 roundtable attendees.
AI agents help explain other AI systems - a novel approach that uses AI models to conduct experiments on other systems and explain their behavior. Their method uses agents built from pretrained language models to produce intuitive explanations of computations inside trained networks.
Hallucinating Law: Legal Mistakes with Large Language Models are Pervasive - First, we found that performance deteriorates when dealing with more complex tasks that require a nuanced understanding of legal issues or interpretation of legal texts. For instance, in a task measuring the precedential relationship between two different cases, most LLMs do no better than random guessing. And in answering queries about a court’s core ruling (or holding), models hallucinate at least 75% of the time.
Cyber proliferation
Nothing this week…
The reflections this week are in the shiny new blog I wrote on the NCSC website titled Landing at the NCSC (glad I brought my towel) where I outline my external priorities for which the headlines are:
Cyber as a science, data as an enabler
Imposing cost on our adversaries
Addressing levels of technical security debt
An end to cyber security as a ‘premium feature’
Market signalling and convening
Preparing for ‘when’, not 'if'
Beyond that, look at the quality of research around AI in footnotes section. The vulnerabilities being found are a good reminder..
Enjoying this? Don’t get via e-mail? Subscribe:
Think someone else would benefit? Share:
All attribution is by others and not the UK Government, please see the legal text at the end.
Have a lovely Friday
Ollie
Cyber threat intelligence
Who is doing what to whom and how.
Reporting on Russia
Russian threat group COLDRIVER expands its targeting of Western officials to include the use of malware
Wesley Shields outlines an alleged campaign which relies on PDFs using a press ‘op ed’ lure which is “encrypted”. The interesting aspect is they build a relationship over email and then get the target to download and run a binary… a takeaway here might be as the technical controls become more effective the human is path of least resistance..
COLDRIVER continues its focus on credential phishing against Ukraine, NATO countries, academic institutions and NGOs. In order to gain the trust of targets, COLDRIVER often utilizes impersonation accounts, pretending to be an expert in a particular field or somehow affiliated with the target. The impersonation account is then used to establish a rapport with the target, increasing the likelihood of the phishing campaign's success, and eventually sends a phishing link or document containing a link. Recently published information on COLDRIVER highlights the group's evolving tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs), to improve its detection evasion capabilities.
Recently, TAG has observed COLDRIVER continue this evolution by going beyond phishing for credentials, to delivering malware via campaigns using PDFs as lure documents. TAG has disrupted the following campaign by adding all known domains and hashes to Safe Browsing blocklists.
https://blog.google/threat-analysis-group/google-tag-coldriver-russian-phishing-malware/
Cyber spies Sticky Werewolf came out of New Year's hibernation
Reporting on cyber activity against Russia which is always interesting. Darktrack RAT has an interesting history including being advertised in 2015 on Facebook.
The phishing message with the subject “About providing information” asked for certified copies of documents “as requested” and a link to download a malicious file. As part of the attack, the attackers once again used the Darktrack RAT remote access Trojan .
Remcos RAT communication model analysis and offensive and defensive technology confrontation
Chinese reporting on a commercial implant used by alleged Russian-nexus actors and others. This is a deep technical analysis which will be of use..
"Хакер" из Вороново попался на заказе в 347 рублей
Reporting of an arrest in Russia of an individual allegedly selling capability to aligned consumers.
A 35-year-old man was detained in Voronovo. Suspected of producing malicious software that allows access to user accounts - It has been previously established that the customers were from the CIS countries and China
Clearing the Fog of War A Critical Analysis of Recent Energy Sector Attacks in Denmark and Ukraine
Further reporting on the energy sector attacks from last year which had an OT flavour Also of note is performance assessment of Living off the Land (LotL). Although I am note sure we would expect it to be quicker, but instead harder to detect.
Evidence suggests that the two waves of attacks on Danish infrastructure reported by SektorCERT were unrelated. It also suggests that the second wave was simply part of a mass exploitation campaign against unpatched firewalls, not part of a targeted attack by Sandworm or another state-sponsored actor.
Our data reveals that the campaign described as the “second wave” of attacks on Denmark, started before, and continued after, the period reported by SektorCERT, targeting firewalls indiscriminately in a very similar manner, only changing staging servers periodically. We see a prevalence of exploitation attempts in Europe, where nearly 80% of publicly identifiable and potentially vulnerable firewalls are located.
There is little evidence that OT attacks using ‘living off the land’ (LotL) techniques are faster than approaches using custom malware. However, LotL techniques provide a stealth benefit to attackers and demonstrate that they continue to deploy new OT-oriented TTPs rather than rely on existing capabilities alone. There is also one previously undiscussed advantage to LotL techniques: enabling attackers to abstract away from legacy and proprietary OT protocols that lack open-source implementations or extensive available documentation.
https://www.forescout.com/resources/clearing-the-fog-of-war/
Analyzing APT28’s OCEANMAP Backdoor & Exploring its C2 Server Artifacts
Neeraj provides a technical analysis of a Russian implant framework that was attributed by the Ukrainian Government. Of note is the strong opportunity for detection on the persistence technique. Startup items feels like the early 2000s called..
Furthermore, the OCEANMAP maintains persistence on the infected machine by creating an Internet Shortcut (.URL file) titled “EdgeContext.url” in the StartUp Folder, with the URL parameter containing the file path to the OCEANMAP binary.
Reporting on China
Volt Typhoon Compromises 30% of Cisco RV320/325 Devices in 37 Days
Dr. Robert Ames details this alleged Chinese activity. Speed and scale are of note with regard the alleged covert infrastructure.
What emerged was a network of covert infrastructure operating in Europe, North America, and Asia Pacific that appears to be composed of compromised routers and other network edge devices. Our data indicates that predominantly Cisco RV320/325 devices were impacted in the last 37 days. Cisco RV’s are network edge devices. It appears that, in keeping with previous reports, Volt Typhoon may aim to use these compromised devices to transfer stolen data or connect to target organizations’ networks.
https://securityscorecard.com/blog/threat-intelligence-research-volt-typhoon/
Reporting on North Korea
Comprehensive Report on North Korean Hackers, Phishing Groups, and Money Laundering in 2023
Analysis of crypto campaigns which were allegedly undertaken by North Korea. Of note if the fact their money laundering tradecraft is evolving..
During this ‘Dark 101 Days’ period, a total of five platforms were breached, with the stolen amount exceeding $300 million.
According to our analysis, the money laundering methods of the Lazarus Group have been evolving over time. New laundering techniques emerge periodically, and the timeline of these changes in laundering methods is outlined in the following table
Reporting on Iran
New TTPs observed in Mint Sandstorm campaign targeting high-profile individuals at universities and research orgs
Alleged Iranian activity going after Universities, which they have been known to do in open source. Of note here is the continued ability to develop new implants..
Since November 2023, Microsoft has observed a distinct subset of Mint Sandstorm (PHOSPHORUS) targeting high-profile individuals working on Middle Eastern affairs at universities and research organizations in Belgium, France, Gaza, Israel, the United Kingdom, and the United States. In this campaign, Mint Sandstorm used bespoke phishing lures in an attempt to socially engineer targets into downloading malicious files. In a handful of cases, Microsoft observed new post-intrusion tradecraft including the use of a new, custom backdoor called MediaPl.
Reporting on Other Actors
WorkersDevBackdoor Delivered via Malvertising
Of note in this reporting is both the use of Malvertising as well the demographic of those being targeted i.e. network administrators.
In November 2023, [we] detected WorkersDevBackdoor malware impacting a customer in business services industry. This malware spreads through malicious online ads, tricking users into downloading it by mimicking legitimate software. Once installed, it secretly collects sensitive information and provides backdoor access to the infected system.
The initial infection vector was a drive-by download via a Google Search advertisement. The service can be used to distribute malware to targets within an ideal group, such as network administrators without knowledge of their email address (something that would be required for malware delivered via email).
https://www.esentire.com/blog/workersdevbackdoor-delivered-via-malvertising
New variant of Shiz virus emerges with multiple countermeasures to steal information
Chinese reporting on an implant which has a degree of evasion capability.
The Shiz virus mainly targets foreign user groups. After being activated, it can steal sensitive information on the user's computer and perform other malicious operations. Not only that, when the victim visits the anti-virus software website, it will also be hijacked to Google's website, causing great interference to the user.
Means to fight against anti-virus software; then, malicious modules are injected into the system process for execution, and malicious operations such as data theft, screenshots, and DNS hijacking are performed.
After the virus is started, it is loaded by the outermost Loader. There are many obfuscation methods in the outermost Loader. It confuses the analysis of security personnel by executing a large amount of garbage code, and it also makes meaningless calls to unpopular APIs
Flying Under the Radar: Abusing GitHub for Malicious Infrastructure
Data as to how common this type of technique is in practice. Thankfully the vendor is mature so we should also expect the counter to this use will increase.
GitHub is frequently abused across all malware categories and by all types of threat actors, offering benefits like detection evasion, reduced operational overhead, and lower costs. The 4 primary infrastructure schemes for GitHub abuse are payload delivery, DDR, full C2, and exfiltration.
Payload delivery stands out as the most prevalent infrastructure scheme, mainly due to its ease of implementation and alignment with GitHub's “legitimate” use case. Yet, it poses a risk to threat actors of unintended exposure, potentially revealing operational insights into development capabilities and tempo, targets, and attack vectors, as seen in some notable operational security failures.
The use of GitHub for DDR is common and comes in various forms. This is driven by the minimal risk of data removal, which is exacerbated by the challenges faced by platform operators like GitHub in discerning malicious intent behind posted addresses or strings without further context.
Full C2 implementations in GitHub are relatively uncommon and are predominantly linked to APT activity thus far. This may be due to functional constraints imposed by GitHub's services, concerns about potential exposure of threat operations, and implementation challenges.
https://go.recordedfuture.com/hubfs/reports/cta-2024-0111.pdf
Bigpanzi Exposed: The Hidden Cyber Threat Behind Your Set-Top Box
This botnet is of a notable size as is the infection mechanisms being used.
we noted approximately 170,000 daily active bots, predominantly in Brazil.
How does such a large-scale botnet infect devices? Currently, we know that Bigpanzi targets Android and eCos platforms, employing the following three methods to infect user devices:
Pirated movie & TV apps (Android)
Backdoored generic OTA firmware (Android)
Backdoored "SmartUpTool" firmware (eCos)
https://blog.xlab.qianxin.com/bigpanzi-exposed-hidden-cyber-threat-behind-your-stb/
Discovery
How we find and understand the latent compromises within our environments.
Detecting Office365 Attacker-in-the-Middle attempts in Azure
Neat use of canaries here to detect AitM phishing..
We’ll be using a canary URL, which will get triggered behind the scenes and allow us to check the originating website the user is trying to authenticate to. This canary URL will be loaded alongside the official Microsoft authentication web page.
https://ironpeak.be/blog/azure-detecting-aitm-attacks/
Defence
How we proactively defend our environments.
misp-airgap: Scripts to deploy and update MISP in air-gapped environments
A work aid by the team of Niclas Dauster and Alexandre Dulaunoy which will be of use to those running OT and other air gapped environments.
Key Features
Automated setup and configuration of MISP in a secure, isolated environment.
Containerized approach using LXD for easy management and isolation.
Support for both interactive and non-interactive installation modes.
Comprehensive validation and security checks, ensuring secure deployment.
Modular setup allowing for easy updates and maintenance.
https://github.com/MISP/misp-airgap
Incident Writeups
How they got in and what they did.
Nothing this week
Vulnerability
Our attack surface.
It’s 2024 and Over 178,000 SonicWall Firewalls are Publicly Exploitable
Jon Williams gives a sense of scale as to the remaining exposure from just a couple of vulnerabilities.
we scanned SonicWall firewalls with management interfaces exposed to the internet and found that 76% (178,637 of 233,984) are vulnerable to one or both issues.
https://bishopfox.com/blog/its-2024-and-over-178-000-sonicwall-firewalls-are-publicly-exploitable
GitLab Critical Security Release: Account Takeover via password reset without user interactions
Stuff of nightmares..
An issue has been discovered in GitLab CE/EE affecting all versions from 16.1 prior to 16.1.6, 16.2 prior to 16.2.9, 16.3 prior to 16.3.7, 16.4 prior to 16.4.5, 16.5 prior to 16.5.6, 16.6 prior to 16.6.4, and 16.7 prior to 16.7.2 in which user account password reset emails could be delivered to an unverified email address.
Malicious model deployed in HF repo to reversed RCE and worm
Peng Zhou, a researcher from China, found this now fixed vulnerability. It serves as a good warning of the challenges as models (which are comprised of a mixture of code/data) are flung around from sources we might not trust.
The Hugging Face (HF) repo enables the remote users to fetch RagRetriever models from the hub by simply running the official demo function code
RagRetriever.from_pretrained(). However, this demo function parses the remote config.json at first and can be misled by"index_name"and"index_path"to implicitly redirect the victim users to load pickle files from the other repos specified by"index_path", hence suffering deserialization attacks. In this vulnerable condition, the attackers have two repos, one is a frontend one to phish the victims to run the demo code RagRetriever.from_pretrained(frontend), and the other is a backend repo that holds the real attacking pickle file. The frontend repo redirects the victim users to load the backend one by setting{"index_path":backend}in its config.json. As the victim users are likely not aware of the existence of the backend repo, they just find the frontend repo safe enough, meaning the complete bypass of HF' pickle scanning.
https://huntr.com/bounties/423611ee-7a2a-442a-babb-3ed2f8385c16/
ASLRn’t: How memory alignment broke library ASLR on Linux
Justin Miller highlights why functional tests for security features is critical. This break happned over a year ago…
As it turns out, on recent Ubuntu, Arch, Fedora, and likely other distro’s releases, with kernel versions >=5.18, library ASLR is literally broken for 32-bit libraries of at least 2MB in size, on certain filesystems. Also, ASLR’s entropy on 64-bit libraries that are at least 2MB is significantly reduced, 28 bits -> 19 bits, on certain filesystems.
https://zolutal.github.io/aslrnt/
Hunting down the HVCI bug in UEFI
Satoshi walks us through this vulnerability which is both deep as is it devasting. The sooner these roots of trust get re-written in Rust etc the better.
This post details the story and technical details of the non-secure Hypervisor-Protected Code Integrity (HVCI) configuration vulnerability disclosed and fixed with the January 9th update on Windows. This vulnerability, CVE-2024-21305, allowed arbitrary kernel-mode code execution, effectively bypassing HVCI within the root partition.
https://tandasat.github.io/blog/2024/01/15/CVE-2024-21305.html
LeftoverLocals: Listening to LLM responses through leaked GPU local memory
Tyler Sorensen and Heidy Khlaaf bring us evidence of some the technical debt we are already carrying in ML/AI usage.
We are disclosing LeftoverLocals: a vulnerability that allows recovery of data from GPU local memory created by another process on Apple, Qualcomm, AMD, and Imagination GPUs. LeftoverLocals impacts the security posture of GPU applications as a whole, with particular significance to LLMs and ML models run on impacted GPU platforms. By recovering local memory—an optimized GPU memory region—we were able to build a PoC where an attacker can listen into another user’s interactive LLM session (e.g., llama.cpp) across process or container boundaries, as shown below:
Android-based PAX POS vulnerabilities (Part 1)
Adam Kliś and Hubert Jasudowicz detail various local attacks against Point of Sale (POS) devices which could enable a variety of criminal activity.
[We] decided to reverse engineer POS devices made by the worldwide known company PAX Technology, as they are being rapidly deployed in Poland. In this article, we present technical details of 6 vulnerabilities, which were assigned CVEs.
https://blog.stmcyber.com/pax-pos-cves-2023/
Offense
Attack capability, techniques and trade-craft.
OMGCICD - Attacking GitLab CI/CD via Shared Runners
Denis Andzakovic serves a warning on how the automation and complexity of modern development pipelines continues to be challenge to secure.
On the attacker side of things, we’ve only looked at extracting credentials used for deployments. After compromising a shared runner there are a whole myriad of other attacks that are possible, including transparently backdooring software with malicious code as the pipeline is executing.
https://pulsesecurity.co.nz/articles/OMGCICD-gitlab
VBA: having fun with macros, overwritten pointers & R/W/X memory
Imperfect but challenging technique..
This idea has tons of drawbacks. Although I have a reliable way to find the pointer to hijack, if I execute other stuff previously in the same process (e.g. a few innocent macros that do a lot of activity) sometimes (5%) the pointer I abuse is misplaced and I overwrite other that has no effect or it crashes the process.
https://adepts.of0x.cc/vba-hijack-pointers-rwa/
BobTheSmuggler
Expect malicious use in 3..2..
Leverages HTML Smuggling Attack and allows you to create HTML files with embedded 7z/zip archives. The tool would compress your binary (EXE/DLL) into 7z/zip file format, then XOR encrypt the archive and then hides inside PNG/GIF image file format (Image Polyglots). The JavaScript embedded within the HTML will download the PNG/GIF file and store it in the cache. Following this, the JavaScript will extract the data embedded in the PNG/GIF, assemble it, perform XOR decryption, and then store it as an in-memory blob.
https://github.com/TheCyb3rAlpha/BobTheSmuggler
CanaryTokenScanner
Iodn provides an offensive capability to try and detect the presence of Canaries.
a script designed to proactively identify Canary Tokens within Microsoft office documents (docx, xlsx, pptx).
https://github.com/0xNslabs/CanaryTokenScanner
Exploitation
What is being exploited.
NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway Security Bulletin for CVE-2023-6548 and CVE-2023-6549
Under active exploitation..
Exploits of these CVEs on unmitigated appliances have been observed.
Cutting Edge: Suspected APT Targets Ivanti Connect Secure VPN in New Zero-Day Exploitation
Continued reporting on these vulnerability including all the details. We know this has now been used to deploy coin miners.
https://www.mandiant.com/resources/blog/suspected-apt-targets-ivanti-zero-day
https://www.volexity.com/blog/2024/01/15/ivanti-connect-secure-vpn-exploitation-goes-global/
https://attackerkb.com/topics/AdUh6by52K/cve-2023-46805/rapid7-analysis
Thousands of Sites with Popup Builder Compromised by Balada Injector
Denis Sinegubko evidences the pace and scale criminals are operating at using rather trivial web vulnerabilities - also the detection tradecraft of using PublicWWW is of note.
on December 13th, the Balada Injector campaign started infecting websites with older versions of the Popup Builder. The attack used a freshly registered (December 13) domain. At the current time of writing PublicWWW detects the injection on over 6,200 sites
Tooling and Techniques
Low level tooling and techniques for attack and defence researchers…
Hook the CoreAnalytics sendEvent function to uncover event subscriptions
Nice macOS technique here which will be useful to researchers.
This script attempts to instrument the `sendEvent:event:` method of the ESCoreAnalytics class.
Download this script
Target: You're targeting `endpointsecurityd`, so grab its PID: `sudo launchctl list | grep endpointsecurityd`
To run: `sudo frida -p $PID -l es_coreanalytics_event_subs.js`
gist.github.com/Brandon7CC/14cd97458629ca045774cb767d476e59
llvm yx callobfuscator
Interesting capability out of Spain here which we can expect to see adoption in maliicous use cases.
LLVM plugin to transparently apply stack spoofing and indirect syscalls to Windows x64 native calls at compile time.
https://github.com/janoglezcampos/llvm-yx-callobfuscator
gef: GEF (GDB Enhanced Features)
Work aid here which should lead to greater productivity.
GEF(pronounced ʤɛf - "Jeff") is a set of commands for x86/64, ARM, MIPS, PowerPC and SPARC to assist exploit developers and reverse-engineers when using old school GDB. It provides additional features to GDB using the Python API to assist during the process of dynamic analysis and exploit development. Application developers will also benefit from it, as GEF lifts a great part of regular GDB obscurity, avoiding repeating traditional commands, or bringing out the relevant information from the debugging runtime.
raddebugger: A native, user-mode, multi-process, graphical debugger
New debuggers are like buses..
The RAD Debugger is a native, user-mode, multi-process, graphical debugger. It currently only supports local-machine Windows x64 debugging with PDBs, with plans to expand and port in the future. In the future we'll expand to also support native Linux debugging and DWARF debug info.
https://github.com/EpicGames/raddebugger
Footnotes
Some other small (and not so small) bits and bobs which might be of interest.
Aggregate reporting
FBI 2023 Year in Review - FBI-led operations dismantled 18 criminal cyber operations—and disrupted another 285—in the fiscal year that ended September 30. More than $200 million in assets were seized or forfeited in operations that netted 202 arrests and 139 convictions. The figures themselves, however, don't fully illustrate the breadth of the cyber takedowns, which occurred nearly every month of the past year and revealed tens of thousands of victims worldwide.
The pervasive informality of the international cybersecurity regime: Geopolitics, non-state actors and diplomacy - Drawing on recent scholarship that explains the emergence of informality in global governance, the article calls for greater attention to be paid to the substantive outcomes of informal institutions to understand their stickiness in regimes.
Secure, Governable Chips - some aspirational work, efficacy and practicality of which is worthy of debate.
Artificial intelligence
Benchmarking and Defending Against Indirect Prompt Injection Attacks on Large Language Models
LeftoverLocals: Listening to LLM responses through leaked GPU local memory
Sleeper Agents: Training Deceptive LLMs that Persist Through Safety Training
A Comprehensive Survey of Hallucination Mitigation Techniques in Large Language Models
Books
Events
Nothing this week
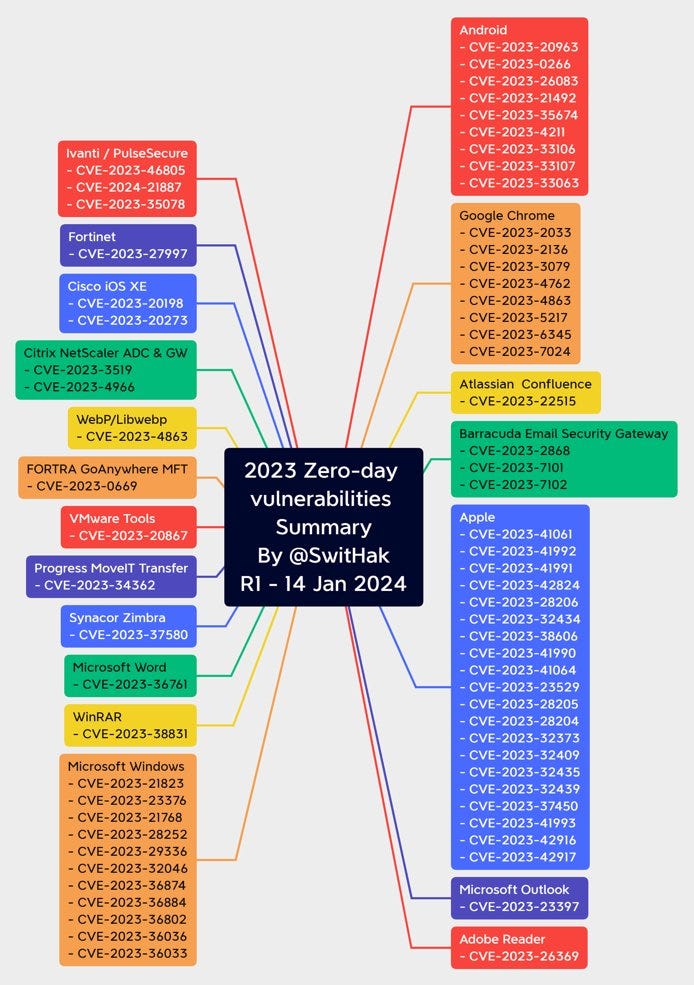
Graphic of the week..
Unless stated otherwise, linked or referenced content does not necessarily represent the views of the NCSC and reference to third parties or content on their websites should not be taken as endorsement of any kind by the NCSC. The NCSC has no control over the content of third party websites and consequently accepts no responsibility for your use of them.
This newsletter is subject to the NCSC website terms and conditions which can be found at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/terms-and-conditions and you can find out more about how will treat your personal information in our privacy notice at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/privacy-statement.





Very insightful report, aside from the CanaryTokenScanner from Iodn, which is a plagiarized version of the @lupovis repository, same code at 4 days interval.