CTO at NCSC Summary: week ending January 26th
More edge device vulnerabilities and exploitation...
Welcome to the weekly highlights and analysis of the blueteamsec subreddit (and my wider reading). Not everything makes it in, but the best bits do.
Operationally this week more edge device vulnerabilities and exploitation... Our guidance to vendors will now be out early February for telemetry and forensics..
In the high-level this week:
ACD 2.0 exploration into attack surface management completed - UK’s National Cyber Security Centre publishes - high-level overview of the scale - detailed report will be released February - “In total we ran 35 product trials (including some organisations trialling multiple products), for an average of 25-30 days per product per customer, resulting in around 900 days’ worth of combined trial time.”
"Bulletproof" hosting providers - Australian Signals Direcotrate’s ACSC publishes this explainer - “BPH providers configure their networks and system architecture to make it harder to identify their customers. For example, they frequently change the internet facing identifiers associated with the customer’s activity – such as their assigned IP addresses and domain name”
Guidelines 01/2025 on Pseudonymisation - European Data Protection Board publishes - “Controllers should establish and precisely define the risks they intend to address with pseudonymisation. The intended reduction of those risks constitutes the objective of pseudonymisation within the concrete processing activity. Controllers should shape pseudonymisation in a way that guarantees that it is effective in reaching this objective.”
Position paper on Interplay between data protection and competition law - European Data Protection Board publishes - “Promoting cooperation between personal data protection and competition authorities can be useful to protect individuals and increase their choice. In fact, as companies’ business models evolve, personal data and the rules applicable to its processing are becoming increasingly central. It is therefore essential to consider ways of promoting coherence among separate but interacting areas of regulation, bearing in mind the risks from their incoherent application at individual and societal levels.”
When the police asked the crew of the Eagle S about the anchor, the answer raised suspicions of intentionality - Yle reports - “The general director of the investigation, Chief Inspector Risto Lohi, says the police are now investigating whether the crew should have noticed and reacted to the fact that the anchor was hanging outside the ship for almost a hundred kilometers.d.”
FLOSS (Free/Libre Open Source Software) - Strategic Position - Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik publishes - “Adaptability and software diversity as well as the use of open standards provide a basis for IT security. However, security is a process. In order to maintain IT security, those responsible must know the system well, maintain it regularly and quickly fix security gaps. The use of FLOSS does not in itself guarantee a secure system. However, it does offer significant strategic advantages in this process.”
Reporting on/from China
Salt Typhoon: the Other Shoe Has Dropped, but Consternation Continues - Natto Thoughts thinks- “However, without intrusion details and with sparse publicly available information about the company, It is not easy to pinpoint the connections. Nevertheless, the Natto Team’s preliminary research discovered that Sichuan Juxinhe is likely a front company of China’s Ministry of State Security (MSS)”
Inside China's 'hacking capital' that has ignited global cyber security alarms - ITV reports - “It turns out that Chengdu's universities were the first in China to offer degrees in cyber security. For the past two decades its elite institutions have been producing thousands of graduates that have gone on to start companies and developed the espionage skills which have become so prized by the Chinese Communist government.”
Petrodollar to Digital Yuan - Asia Society Policy Institute analyses - “Three powerful forces are converging to drive this change: China's strategic push to reduce its dollar vulnerability as the world's largest oil importer, the Gulf states' pressing need for economic transformation through massive investment in technology and infrastructure, and breakthrough innovations in digital payment technologies initiated by China that make alternatives to the dollar-led global payments not just possible but potentially more efficient than traditional systems.”
AI
Trump revokes Biden executive order on addressing AI risks - Reuters reports - “U.S. President Donald Trump on Monday revoked a 2023 executive order signed by Joe Biden that sought to reduce the risks that artificial intelligence poses to consumers, workers and national security.”
How GhostGPT Empowers Cybercriminals with Uncensored AI - Abnormal asserts - “GhostGPT is a chatbot specifically designed to cater to cybercriminals. It likely uses a wrapper to connect to a jailbroken version of ChatGPT or an open-source large language model (LLM), effectively removing any ethical safeguards.” - Jail Breaking as a Service has alleged arrives..
Cyber proliferation
Pegasus spyware in Bangladesh's political domain - The Financial Express reports - “If Bangladesh is to truly thrive as a democracy, then it needs to ensure its methods of guaranteeing security do not trample on the very freedoms it promises to uphold. Legal and Ethical Implications: The use of Pegasus, without stringent legal oversight and ethical boundaries, creates a deep threat to individual freedoms and the rule of law”
Bounty Hunting
Treasury Targets IT Worker Network Generating Revenue for DPRK Weapons Programs - US Department of Treasury targets - “Today, the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) is sanctioning two individuals and four entities for generating illicit revenue for the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) government.”
MGAs under close scrutiny from reinsurers - The Insurer reports - Aon commented in its Reinsurance Market Dynamics report on the 1 January 2025 renewals that one factor during discussions was that reinsurers are mindful of conditions in the underlying market. “Cyber insurance pricing experienced a steep decline since Q1 2022 due to a softening market and improved cyber security controls,” the report said.
No reflections this week..
Think someone else would benefit? Share:
All attribution is by others and not the UK Government unless specifically stated as such, please see the legal text at the end.
Have a lovely Saturday…
Ollie
Cyber threat intelligence
Who is doing what to whom and how allegedly.
Reporting on Russia
Nothing of note this week
Reporting on China
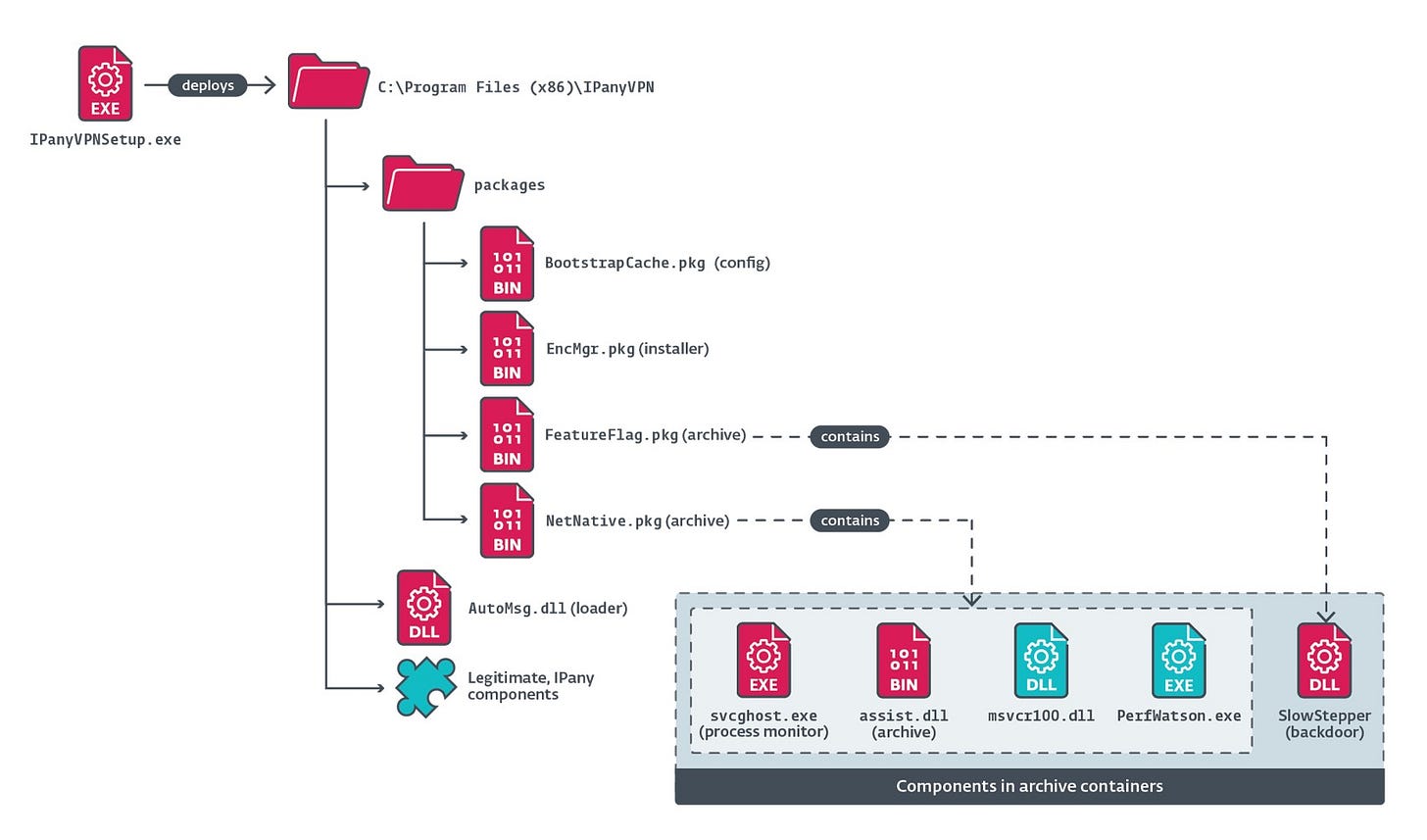
PlushDaemon compromises supply chain of Korean VPN service
Facundo Muñoz details this alleged Chinese operation, note the use of supply chains for initial access.
PlushDaemon is a China-aligned threat group, engaged in cyberespionage operations.
PlushDaemon’s main initial access vector is hijacking legitimate updates of Chinese applications, but we have also uncovered a supply-chain attack against a South Korean VPN developer.
We believe PlushDaemon is the exclusive user of several implants, including SlowStepper for Windows.
SlowStepper has a large toolkit composed of around 30 modules, programmed in C++, Python, and Go.
Reporting on North Korea
Kimsuky APT attack discovered using Facebook and MS Management Console
Genians details this alleged social engineering campaign. Note the use of Facebook messenger as an approach platform.
Disguised as a public official in the North Korean human rights field, looking for targets on Facebook
After approaching each person individually through Facebook Messenger, start a casual conversation with a greeting.
Sharing malicious URL link addresses pretending to be specific document files
MSC-based threat monitoring via OneDrive cloud service
Identification of ReconShark-like malware from Kimsuky group
Beware of Contacts through LinkedIn: They Target Your Organization’s Property, Not Yours
朝長 秀誠 (Shusei Tomonaga) details various alleged North Korean campaigns we have covered numerous times but with the Japanese perspective.
3 operations identified in Japan previously and associated with Lazarus attack group. Attackers who attempt to contact their target through LinkedIn have the following characteristics. If you are contacted by an unknown individual with any of these characteristics, you should be alerted.
Requests you to change the communication tool from LinkedIn to something else
Attempts to make you download and execute files
Persistently checks whether you have executed sent (downloaded) files and about your system environment
Attackers often use English in attacks through LinkedIn, while most targeted emails are written in Japanese (Some cases with Japanese text have been confirmed)
Pretends to be a recruiter and post expensive fees
https://blogs.jpcert.or.jp/en/2025/01/initial_attack_vector.html
An exploratory analysis of the DPRK cyber threat landscape using publicly available reports
Jeonggak Lyu, Ahyun Song, Euiseong Seo & Gibum Kim take a literature based review which hints are both the potential scale but also the challenge of Rosetta stones (or lack there of).
This approach identified 160 distinct code names for these actors. Additionally, the threat actors were categorized into seven widely recognized groups in the threat intelligence industry. Furthermore, 154 notable incidents attributed to these actors were extracted and documented.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10207-025-00980-x
North Korean IT Workers Conducting Data Extortion
FBI alert which outlines some observed behaviours..
After being discovered on company networks, North Korean IT workers have extorted victims by holding stolen proprietary data and code hostage until the companies meet ransom demands. In some instances, North Korean IT workers have publicly released victim companies' proprietary code.
North Korean IT workers have copied company code repositories, such as GitHub, to their own user profiles and personal cloud accounts. While not uncommon among software developers, this activity represents a large-scale risk of theft of company code.
North Korean IT workers could attempt to harvest sensitive company credentials and session cookies to initiate work sessions from non-company devices and for further compromise opportunities.
https://www.ic3.gov/PSA/2025/PSA250123
Reporting on Iran
Nothing of note this week
Reporting on Other Actors
Targeted supply chain attack against Chrome browser extensions
Quentin Bourgue and Sekoia TDR hint that this campaign is bigger than initially thought..
The spearphishing emails targeting Chrome extension developers, successfully compromising dozens of them since mid-November 2024.
The compromise of approximately a dozen Chrome extensions since early December 2024, allegedly infecting hundreds of thousands of extensions’ users.
Sekoia analysts assess with high confidence that during 2023 and 2024, the threat actor conducted additional campaigns targeting Chrome extensions, using similar techniques, along with additional ones. The section below provides an analysis of the most recent campaign, which was active until 30 December 2024.
https://blog.sekoia.io/targeted-supply-chain-attack-against-chrome-browser-extensions/
Discovery
How we find and understand the latent compromises within our environments.
The J-Magic Show: Magic Packets and Where to find them
Black Lotus Labs detail this unattributed campaign..
. This backdoor is opened by a passive agent that continuously monitors for a “magic packet,” sent by the attacker in TCP traffic. We have dubbed this campaign J-magic, it is a recent operation with the earliest sample uploaded to VirusTotal in September 2023. At present, we are unable to determine the initial access method, however once in place it installs the agent – a variant of cd00r – which passively scans for five different predefined parameters before activating. If any of these parameters or “magic packets” are received, the agent sends back a secondary challenge. Once that challenge is complete, J-magic establishes a reverse shell on the local file system, allowing the operators to control the device, steal data, or deploy malicious software.
…
Our telemetry indicates the J-magic campaign was active from mid-2023 until at least mid-2024; in that time, we observed targets in the semiconductor, energy, manufacturing, and IT verticals among others.
https://blog.lumen.com/the-j-magic-show-magic-packets-and-where-to-find-them/
Hunting Infostealers: A Practical Approach
Israeli National Cyber Directorate publishes this work aid to help discover any latent breaches..
a practical methodology for identifying, investigating, and mitigating the impact of infostealers within your environment. The focus will be on real-world tools and techniques, emphasizing actionable steps that can be taken by security professionals at any level.
https://www.gov.il/BlobFolder/reports/alert_1848/he/ALERT-CERT-IL-W-1848.pdf
Baitroute
Utku Sen provides some further use cases in cyber deception..
A web honeypot project that serves realistic, vulnerable-looking endpoints to detect vulnerability scans and mislead attackers by providing false positive results. It can be imported as a library into your project and is ready to use with its rules. Go, Python and Javascript implementations are available.
https://github.com/utkusen/baitroute
Automating Malicious Infrastructure Discovery With Graph Neural Networks
Nabeel Mohamed, Keerthiraj Nagaraj, Billy Melicher, Shehroze Farooqi, Alex Starov, Brady Stout and Robert Davis show an applied use of GNNs to discovery..
This article describes the benefits of automated pivoting and uses three case studies to show how we can discover new indicators. Using a network crawler leveraging relationships among domains, we discovered network artifacts around known indicators and trained a graph neural network (GNN) to detect additional malicious domains.
These three case studies show that defenders can proactively discover attack infrastructure by continuously monitoring a threat actor's evolving indicators. The three case studies covered in this article are:
A postal services phishing campaign
A credit card skimmer campaign
A financial services phishing campaign
https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/graph-neural-networks/
Defence
How we proactively defend our environments.
Data Safety Levels Framework: The foundation of how we look at data in Block
John Rogers, Dino Dai Zovi, and Gelareh Taban outline what Secure by Design might look like at a data level.
In this post, we introduce the Data Safety Levels (DSL) Framework that we initially built for Cash App and have since extended across the rest of our diverse product ecosystem, including Square and TIDAL. The DSL framework forms the foundation of the way we understand data. It acknowledges the complexities of data by recognizing that data:
Exists as part of a larger set, with sensitivity being an emergent property of the set rather than individual elements.
Is contextual, requiring us to consider context when determining its management and usage policies.
This framework has created a strong foundation for us to build guidelines and policies on top of which allow us to better show not just our compliance with our regulatory requirements but also our commitment to customer trust.
..
Data Classification Rubrics
Data Safety Guidelines
Automation and Manual Processes
Access and Usage Controls
https://code.cash.app/dsl-framework
Preventing unintended encryption of Amazon S3 objects
Steve de Vera and Jennifer Paz provide mitigations to a campaign technique which has been observed in the wild whilst highlighting the response is multifaceted.
We recommend that customers implement these four security best practices to protect against the unauthorized use of SSE-C:
Implement short-term credentials
Implement data recovery procedures
Monitor AWS resources for unexpected access patterns
Block the use of SSE-C unless required by an application
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/preventing-unintended-encryption-of-amazon-s3-objects/
How to correctly use access tokens and ID tokens in your client application
Adam Matthews and James Casey detail a product change in response to exposure..
In this post, we’ll explore the differences between the different types of security tokens that are provided by the Microsoft Identity Platform. We will compare access tokens and ID tokens, showing how and where you should use them in your application. We will highlight why access tokens should be treated as opaque by client applications and outline best practices around access token usage, helping you avoid common pitfalls.
Starting October 2024, we have been gradually enabling encrypted access tokens for more Microsoft-owned APIs.
https://devblogs.microsoft.com/identity/access-tokens-and-id-tokens/
DataCon2024 problem solving report WriteUp—Software supply chain security track
From China and further examples of their use of internal competition to make strides in cyber defence. The number of teams and players is notable.
On November 28, 2024, the DataCon2024 big data security analysis competition came to an end. The competition has five major tracks: AI security, software supply chain security, network infrastructure security, network black product analysis and vulnerability analysis. In the fierce competition among 706 teams and 1,556 professional players, the "SecureNexusLab Supply Chain Security" team from the Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences took first place in the overall score and won the software supply chain security track championship .
Incident Writeups & Disclosures
How they got in and what they did.
Vulnerability
Our attack surface.
Fediverse CVE feed by searching CVE data
A feed which will be of use to some..
https://fedisecfeeds.github.io/
CVE-2025-23006: Pre-authentication deserialization of untrusted data vulnerability
Deserialization bites (or bytes?)..
Pre-authentication deserialization of untrusted data vulnerability has been identified in the SMA1000 Appliance Management Console (AMC) and Central Management Console (CMC), which in specific conditions could potentially enable a remote unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary OS commands.
IMPORTANT: SonicWall PSIRT has been notified of possible active exploitation of the referenced vulnerability by threat actors. We strongly advises users of the SMA1000 product to upgrade to the hotfix release version to address the vulnerability.
https://psirt.global.sonicwall.com/vuln-detail/SNWLID-2025-0002
CVE-2025-23013: Yubico PAM Module Vulnerability
Interesting vulnerability here which depending on how the module is deployed may live on for a while..
This vulnerability, under specific configurations, can allow attackers to bypass authentication mechanisms on macOS and Linux systems, leading to severe security implications. The flaw can potentially facilitate local privilege escalation or bypass second-factor authentication, posing a critical risk to systems employing YubiKey for multifactor authentication (MFA).
CVE-2025-21298: Outlook RTF Vulnerability Trigger
Miloš provides a trigger for this memory corruption vulnerability, will be interesting to see if it gets fully weaponized.
In the repo is an rtf file which reproduces the vulnerability. I tested by opening the file in MS Word but you can also test it with other applications that parse RTF data (e.g. Outlook). Exploitation through other formats which embed OLE objects may be possible,
https://github.com/ynwarcs/CVE-2025-21298
Uncovering Security Vulnerabilities in Intel Trust Domain Extensions
Upasana Mandal, Shubhi Shukla, Nimish Mishra, Sarani Bhattacharya, Paritosh Saxena and Debdeep Mukhopadhyay show the quality coming out of India with this research but also highlight the side channel challenges in confidential compute.
Intel Trust Domain Extensions (TDX) has emerged as a crucial technology aimed at strengthening the isolation and security guarantees of virtual machines, especially as the demand for secure computation is growing largely. Despite the protections offered by TDX, in this work, we dig deep into the security claims and uncover an intricate observation in TDX. These findings undermine TDX's core security guarantees by breaching the isolation between the Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) and Trust Domains (TDs). In this work for the first time, we show through a series of experiments that these performance counters can also be exploited by the VMM to differentiate between activities of an idle and active TD. The root cause of this leakage is core contention. This occurs when the VMM itself, or a process executed by the VMM, runs on the same core as the TD. Due to resource contention on the core, the effects of the TD's computations become observable in the performance monitors collected by the VMM. This finding underscore the critical need for enhanced protections to bridge these gaps within these advanced virtualized environments.
https://eprint.iacr.org/2025/079
Offense
Attack capability, techniques and trade-craft.
Entra Connect Attacker Tradecraft: Part 2
hotnops provides the technique but also the detection route so ⭐ to them..
·Now that we know how to add credentials to an on-premises user, lets pose a question:
“Given access to a sync account in Domain A, can we add credentials to a user in another domain within the same Entra tenant?”
This is a bit of a tall order assuming we have very few privileges in Entra itself. Remember from Part 1 that the only thing we can sync down, by default, is the msDS-KeyCredentialLink property. In order to understand how to take advantage of this, we need to learn some more fundamentals of the Entra sync engine and how the rules work.
..
Detection of this misconfiguration/attack may be difficult but there are some solid signals that something is off. If any users in the Entra connector space have a metaverse projection with a “cloudFiltered” attribute set to “true”, then something is wrong.
https://posts.specterops.io/entra-connect-attacker-tradecraft-part-2-672df0147abc
Exploitation
What is being exploited..
Threat Actors Chained Vulnerabilities in Ivanti Cloud Service Applications
CISA and FBI release an advisory which is notable due to the use of chained vulnerabilities..
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) are releasing this joint Cybersecurity Advisory in response to exploitation in September 2024 of vulnerabilities in Ivanti Cloud Service Appliances (CSA): CVE-2024-8963, an administrative bypass vulnerability; CVE2024-9379, a SQL injection vulnerability; and CVE-2024-8190 and CVE-2024-9380, remote code execution vulnerabilities. According to CISA and trusted third-party incident response data, threat actors chained the listed vulnerabilities to gain initial access, conduct remote code execution (RCE), obtain credentials, and implant webshells on victim networks
https://www.ic3.gov/CSA/2025/250122.pdf
Zyxel vulnerability exploited by “Helldown” ransomware group
Ylabs highlights the threat actor has a degree of operational security consideration..
During the campaign of cyberattacks that targeted Zyxel devices, cybercriminals have always chosen their geolocation appropriately to be in the same country as the attacked infrastructures, using VPN services.
https://labs.yarix.com/2025/01/zyxel-vulnerability-exploited-by-helldown-ransomware-group/
Tooling and Techniques
Low level tooling and techniques for attack and defence researchers…
nt-load-order Part 1
Colin Finck shows how to get started..
WinDbg'ing our way into the Windows bootloader
To figure that out, we need to go deeper and debug the actual bootloader and not just the kernel. And we’re lucky: Although WinDbg has been created to debug the Windows kernel, the bootloader also comes with a WinDbg stub and can be debugged likewise.
https://colinfinck.de/posts/nt-load-order-part-1/
WinVisor
x86matthew is back and now working for the light side for the force..
A hypervisor- based emulator for Windows x64 user- mode executables
https://www.elastic.co/security-labs/winvisor-hypervisor-based-emulator
Footnotes
Some other small (and not so small) bits and bobs which might be of interest.
Aggregate reporting
Huione: the company behind the largest ever illicit online marketplace has launched a stablecoin
Regulatory Horizons Council: the Governance of Engineering Biology
Proxy Wars in Cyberspace - Integrated Operations of Hacktivists
Artificial intelligence
Books
Nothing this week
Events
JSAC2025 – Tokyo, January 21-22, 2025 - content now published
RE//verse - Feb 24th to 25th, 2025
Cybernetic Culture - Consumption, Security & Society in the Digital Age - April 11th, 2025
Unless stated otherwise, linked or referenced content does not necessarily represent the views of the NCSC and reference to third parties or content on their websites should not be taken as endorsement of any kind by the NCSC. The NCSC has no control over the content of third party websites and consequently accepts no responsibility for your use of them.
This newsletter is subject to the NCSC website terms and conditions which can be found at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/terms-and-conditions and you can find out more about how will treat your personal information in our privacy notice at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/privacy-statement.