CTO at NCSC Summary: week ending July 28th
A new UK Cyber Security and Resilience Bill is go...
Welcome to the weekly highlights and analysis of the blueteamsec subreddit (and my wider reading). Not everything makes it in, but the best bits do.
Operationally this week the likely most noteworthy aspect is the industrial control system reporting. That and an alleged North Korean who got a job with a US firm and upon receiving their laptop deployed malware..
In the high-level this week:
New legislation will help counter the cyber threat to our essential services - NCSC UK - Jonathan Ellison - “The announcement of the Cyber Security and Resilience Bill is a landmark moment in tackling the growing threat to the UK's critical systems.”
NCSC and partners issue warning over North Korean state-sponsored cyber campaign to steal military and nuclear secrets - NCSC UK - “The National Cyber Security Centre – a part of GCHQ – has issued a new advisory today (Thursday) alongside partners in the United States and the Republic of Korea which reveals how a cyber threat group known as Andariel has been compromising organisations around the world to steal sensitive and classified technical information and intellectual property data. “
If you have knowledge, let others light their candles in it. - NCSC UK - Ralph B - Why sharing lessons learned from cyber security incidents and ‘near misses’ will help everyone to improve
Consultation: Global Titles and Mobile Network Security - UK’s Ofcom consults - We are therefore proposing to strengthen our existing rules and introduce new rules to tackle misuse of Global Titles, in particular by:
banning leasing of Global Titles to third parties by operators that hold UK mobile numbers;
banning the creation of Global Titles from sub-allocated numbers by third parties;
strengthening our rules to prohibit the misuse of Global Titles by operators that hold UK mobile numbers; and
strengthening our rules to prohibit the creation of Global Titles from numbers not allocated for use.
Chairmen Green, Garbarino Request Public Testimony From Crowdstrike CEO Following Global IT Outage - US House Committee on Homeland Security requests - “We write in response to the global information technology (IT) outage, which has been attributed to a “defect” in a CrowdStrike software update that impacted Microsoft Windows. While we appreciate CrowdStrike’s response and coordination with stakeholders, we cannot ignore the magnitude of this incident, which some have claimed is the largest IT outage in history.”
NCA infiltrates world's most prolific DDoS-for-hire service - UK National Crime Agency reports - “It comes after the PSNI arrested one of the site’s suspected controllers earlier this month. The NCA took over the site and disabled its functionality, replacing the domain with a splash page, warning users that their data has been collected by law enforcement.”
French Government runs 'disinfection operation' against PlugX - Tribunal Judiciaire de Paris press releases - “The disinfection operation was launched on July 18, and will continue for several months. A few hours after the start of the process, around a hundred victims have already benefited from this disinfection, mainly in France, but also in Malta, Portugal, Croatia, Slovakia and Austria.”
Russia’s Cyber Campaign Shifts to Ukraine’s Frontlines - Dan Black researches - “The harsher reality is that Russia’s intelligence services have adapted their posture in cyberspace to the demands of a long war. Mounting evidence, stretching back to the months preceding Ukraine’s counteroffensive in 2023, indicates that multiple Russian cyber units have shifted their sights away from strategic civilian targets toward soldiers’ computers and mobiles endpoints in order to enable tactical military objectives on Ukraine’s frontlines. This change in operational focus has been cross-cutting, with Russian military intelligence (GRU) and the domestic security service (FSB) – long renowned for rivalry and mistrust – unifying their earlier disjointed cyber efforts and systematising a series of tradecraft adaptations intended to increase their military effectiveness.”
Cyber is our fastest growing national security threat: O’Neil - Australian Financial Review reports - “Home Affairs Minister Clare O’Neil says banks, telcos and technology providers need to do more to help small business and consumers fight off growing cybercrime, pledging landmark new legislation will better protect the Australian economy from rising threats.”
United States Cyber Force A Defense Imperative - Dr. Erica Lonergan and RADM (Ret.) Mark Montgomery - March 2024 - an analysis - “CYBERCOM’s budget request is approximately $2.9 billion, while DoD’s total Cyberspace Activities Budget request for the services is $13.5 billion.”
Ctrl Alt Army - US Army podcasts - Hosted by Dr. Michael Sulmeyer, principal cyber advisor to the secretary of the Army, this podcast series features informal conversations with senior Army leaders about cyber issues.
Reporting on/from China
Matrix Cup: Cultivating Top Hacking Talent, Keeping Close Hold on Results - Eugenio Benincasa and Natto Thoughts analyze - “the Matrix Cup brings together China’s highly influential actors from academia and the private sector, featuring various types of challenges and offering substantial monetary rewards. With higher award payouts than any other domestic or international hacking competitions, the Matrix Cup boasts prize amounts of US$ 2.75 million that surpass even Pwn2Own's US$1.1 million (2024) and the Tianfu Cup's US$1.4 million (2023).”
China details expanded law on state secrets, eyeing data security - Reuters reports - “China revealed details this week of a revised state secrets law that changes curbs on government officials' handling of confidential information, banning those entrusted with state secrets from going abroad without approval.”
What do investment banks think of the Chinese Communist Party’s long-overdue third plenum? - South China Morning Post reports - “Offering little in the way of details, the communique outlined China’s broad reform package over the medium and longer term, focusing on technology innovation, the new-quality productive force, risk control and supply-chain security.”
Chinese official calls for ‘proactive’ stimulus to distribute growth across economy - Financial Times reports - “President Xi Jinping is encouraging investment in high-technology manufacturing as China seeks to compete with the US amid mounting geopolitical tensions.”
China Puts Power of State Behind AI—and Risks Strangling It - The Wall Street Journal reports - “A nationwide government campaign is helping to promote the technology widely: China now leads the world in the adoption of generative AI, according to a recent survey of industry leaders by American software company SAS and market research agency Coleman Parkes.”
Artificial intelligence
Artificial Intelligence: 'call for views' on the cyber security of AI closes soon - NCSC UK - “Businesses, academia and international partners invited to respond to the UK government's ‘call for views’ on the security of AI.”
OECD launches pilot to monitor application of G7 code of conduct on advanced AI development - The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) press releases - “The draft reporting framework was designed with input from leading AI developers across G7 countries and supported by the G7 under the Italian Presidency. It includes a set of questions based on the Code of Conduct’s 11 Actions.”
AI Innovations Explored: Insights into AI Applications in Financial Services and Housing - US House Committee on Financial Services reports -
The Committee should continue to consider how to reform data privacy laws given the importance of data, especially consumer data, to AI.
Aussie tech company uploads ChatGPT to people’s brains - The Australian Business Review hyperboles - “Synchron’s BCI is implanted into the blood vessel on the surface of the motor cortex of the brain via the jugular vein via a “minimally invasive” procedure, unlike Neurolink. Dr Oxley compared it to installing a stent versus open-heart surgery.”
related The protection of mental privacy in the area of neuroscience - Societal, legal and ethical challenges - European Parliament thinktanks - “Advances in (neuro)technological development have led to an increase in the use and accessibility of neurotechnologies (NT), allowing brain activity to be recorded, analysed and manipulated by neurotechnological devices. While they were originally used only for clinical purposes, they are becoming more and more attractive for healthy populations willing to enhance their cognitive or physical abilities.”
Cyber proliferation
Spyware targeted MEP critical of Hungary - Politico reports - “One of Hungary's most outspoken critics in the European Parliament said he was targeted by spyware, just two weeks before the European elections in June. German Green lawmaker Daniel Freund said he narrowly averted a cyberattack via his Parliament email.”
Protecting users and reaffirming our commitment to combatting cyber mercenaries - Microsoft asserts - “In this new amicus brief, we highlight two important points: First, the proliferation of commercial spyware developed by cyber mercenaries is a significant national security threat. Second, the US Government has a strong interest in protecting American tech companies from being exploited. “
Israel tried to frustrate US lawsuit over Pegasus spyware, leak suggests - Guardian reports - “Documents suggest the seizures were part of an unusual legal manoeuvre created by Israel to block the disclosure of information about Pegasus, which the government believed would cause “serious diplomatic and security damage” to the country.”
Bounty Hunting
North Korean Government Hacker Charged for Involvement in Ransomware Attacks Targeting U.S. Hospitals and Health Care Providers - US Department of Justice press releases - “Hacking Group Known as “Andariel” Used Ransom Proceeds to Fund Theft of Sensitive Information from Defense and Technology Organizations Worldwide, Including U.S. Government Agencies”
Two Foreign Nationals Plead Guilty to Participation in LockBit Ransomware Group - US Department of Justice press releases - “Two foreign nationals pleaded guilty today in Newark federal court to participating in the LockBit ransomware group – at various times the most prolific ransomware variant in the world – and to deploying LockBit attacks against victims in the United States and worldwide.”
Walsall teenager arrested in joint West Midlands Police and FBI operation - Regional Organised Crime Unit for the West Midlands press releases - “We have arrested a 17-year-old boy from Walsall in connection with a global cyber online crime group which has been targeting large organisations with ransomware and gaining access to computer networks.”
Three arrested for crimes of computer damage for terrorist purposes - Ministerio Del Interior reports - “The detainees would have voluntarily participated in carrying out denial of service attacks organized by the hacktivist group NoName057(16)”
Can lawyers lose wars by stifling cyber capabilities? - An Anonymous European Intelligence Official asserts - “Idealistic legalism is increasingly constraining our ability to manoeuvre and contest our adversaries in and through cyberspace. A balanced debate on any legal framework overseeing cyber capabilities is necessary, with as much thought to operational constraints as to any inevitable privacy impact.”
No reflections this week..
Think someone else would benefit? Share:
All attribution is by others and not the UK Government unless specifically stated as such, please see the legal text at the end.
Have a lovely Friday..
Ollie
Cyber threat intelligence
Who is doing what to whom and how allegedly.
Reporting on Russia
CERT-UA: Hackers attacked science & research facility using malicious macro in Word document
The Computer Emergency Response Team of Ukraine (CERT-UA) at SSSCIP reports on this alleged (moderate confidence) Russian threat actor and a recent operation. The tradecraft is rather basic which we have seen time and time again.
investigated the cyberattack of the cybercriminal group tracked as UAC-0063 on one of the Ukrainian research institutions, which occurred on July 8.
Attackers gained access to the facility's employee's email account, taking advantage of the organization's insufficient cybersecurity measures, and distributed a Word document containing a malicious macro to dozens of addressees.
Opening the document triggered the installation of HATVIBE and CHERRYSPY backdoor malware on the affected computers, which enabled hackers to gain unauthorized access to them.
With moderate confidence, CERT-UA associates this criminal activity with the APT28 group (UAC-0001), affiliated with the military intelligence of the Russian federation (GRU) .
Reporting on China
Daggerfly: Espionage Group Makes Major Update to Toolset
Symantec reports on this alleged Chinese threat actor who appears to have macOS capabilities. Equally concerning are the Solaris capabilities given the age of those systems and historically the CNI and other sensitive locations they will be running in.
Among the new additions to Daggerfly’s arsenal are a new malware family based on the group’s MgBot modular malware framework and a new version of the Macma macOS backdoor. While Macma is a previously documented threat, it had hitherto been of unknown authorship. However, Symantec’s Threat Hunter Team has now found evidence suggesting that it is developed by Daggerfly.
New findings provide a clearer picture of the capabilities and resources behind Daggerfly. The group can create versions of its tools targeting most major operating system platforms. In addition to the tools documented here, Symantec has seen evidence of the ability to Trojanize Android APKs, SMS interception tools, DNS request interception tools, and even malware families targeting Solaris OS. Daggerfly appears to be capable of responding to exposure by quickly updating its toolset to continue its espionage activities with minimal disruption.
Reporting on North Korea
North Korea Cyber Group Conducts Global Espionage Campaign to Advance Regime’s Military and Nuclear Programs
US Government, South Korea Government and UK Government assemble with this exposé on North Korean threat actor operations. The actual initial access tradecraft shows agility more than sophistication - i.e. at speed (and not so) exploitation of old-days..
The actors gain initial access through widespread exploitation of web servers through known vulnerabilities in software, such as Log4j, to deploy a web shell and gain access to sensitive information and applications for further exploitation. The actors then employ standard system discovery and enumeration techniques, establish persistence using Scheduled Tasks, and perform privilege escalation using common credential stealing tools such as Mimikatz. The actors deploy and leverage custom malware implants, remote access tools (RATs), and open source tooling for execution, lateral movement, and data exfiltration.
The actors also conduct phishing activity using malicious attachments, including Microsoft Windows Shortcut File (LNK) files or HTML Application (HTA) script files inside encrypted or unencrypted zip archives.
https://www.ic3.gov/Media/News/2024/240725.pdf
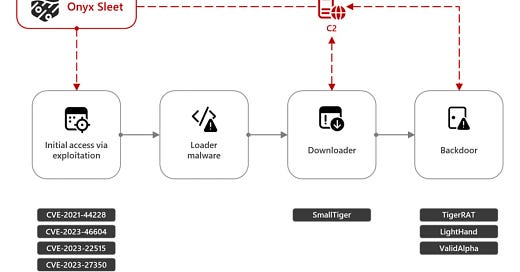
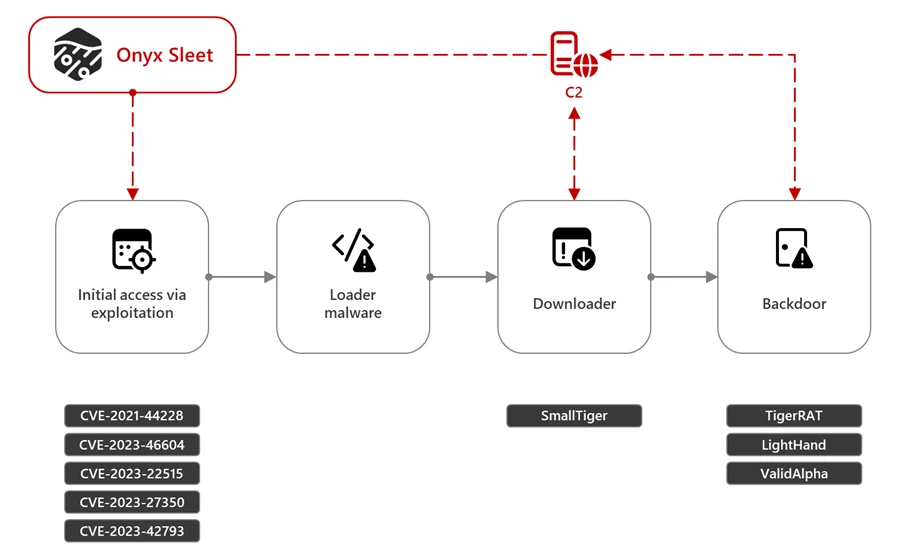
Onyx Sleet uses array of malware to gather intelligence for North Korea
Microsoft also reports on the same threat actor showing their tradecraft and victimology..
First observed by Microsoft in 2014, Onyx Sleet has conducted cyber espionage through numerous campaigns aimed at global targets with the goal of intelligence gathering. More recently, it has expanded its goals to include financial gain. This threat actor operates with an extensive set of custom tools and malware, and regularly evolves its toolset to add new functionality and to evade detection, while keeping a fairly uniform attack pattern.
..
In pursuit of its primary goal of intelligence collection, Onyx Sleet has focused on targeting entities in the defense and energy industries, predominately in India, South Korea, and the United States. Recent attacks include the targeting of South Korean educational institutions, construction companies, and manufacturing organizations in May 2024.
APT45: North Korea’s Digital Military Machine
Google also reports which provides further evidence of the for-profit element of their operations.
APT45 is a long-running, moderately sophisticated North Korean cyber operator that has carried out espionage campaigns as early as 2009.
APT45 has gradually expanded into financially-motivated operations, and the group’s suspected development and deployment of ransomware sets it apart from other North Korean operators.
APT45 and activity clusters suspected of being linked to the group are strongly associated with a distinct genealogy of malware families separate from peer North Korean operators like TEMP.Hermit and APT43.
Among the groups assessed to operate from the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), APT45 has been the most frequently observed targeting critical infrastructure.
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/apt45-north-korea-digital-military-machine
Reporting on Iran
Nothing this week
Reporting on Other Actors
HotPage: Story of a signed, vulnerable, ad-injecting [Windows] driver
Romain Dumont shows a process built on trust might actually be misused by those who are untrustworthy. A degree of sophistication here, or at least ability to follow a proces.
We found a reference to this company in the Windows Server Catalog, as shown in Figure 5. The company used various product categories when submitting its drivers for certification. Based on its name, it appears the company developed two network filtering programs: a netfilter component and the HotPage driver referred as adsafe or by its internal name KNewTalbeBase (Note the [Tt]albe typo, which also occurs elsewhere in the HotPage code).
https://www.welivesecurity.com/en/eset-research/hotpage-story-signed-vulnerable-ad-injecting-driver/
Impact of FrostyGoop ICS Malware on Connected OT Systems
Magpie, Carolyn Ahlers and Kyle O’Meara report on this unattributed incident. Given the locality of the event/victimlogy I suspect readers will have likely candidates however..
Dragos discovered FrostyGoop in April 2024. It can interact directly with ICS using Modbus, a standard ICS protocol across all industrial sectors and organizations worldwide. Additionally, the Cyber Security Situation Center (CSSC), a part of the Security Service of Ukraine (Служба безпеки України), shared details with Dragos about a disruptive cyber attack on a district energy company in Lviv, Ukraine, which resulted in a two-day loss of heating to customers
..
The investigation revealed that the adversaries possibly gained access to the victim network through an undetermined vulnerability in an externally facing Mikrotik router. The network assets, including the Mikrotik router, four management servers, and district heating system controllers, were not adequately segmented, facilitating the attack.
https://hub.dragos.com/hubfs/Reports/Dragos-FrostyGoop-ICS-Malware-Intel-Brief-0724_.pdf?hsLang=en
Brute Ratel C4 Badger Used to Load Latrodectus
Mohamed Talaat details a use of a commercial C2 framework in this criminal operation. Also the successor a long time adversary..
Latrodectus is a recently discovered malware loader that is suspected to be a potential successor to the IcedID malware. Security researchers believe that Latrodectus was developed by the same threat actor group responsible for IcedID, due to similarities in development and behavior. Like other malware loaders, Latrodectus is used to deploy additional, more sophisticated malware onto compromised systems.
https://any.run/cybersecurity-blog/brute-ratel-c4-analysis/
Discovery
How we find and understand the latent compromises within our environments.
The Responder Honeypot
C.J. May gives us a capability to detect the use of Responder within networks. Shows the value of reviewing the code/behaviour of adversarial tools used by many to develop detection tradecraft.
This application detects active instances of Responder by taking advantage of the fact that Responder will respond to any DNS query. Respotter uses LLMNR, mDNS, and NBNS protocols to search for a bogus hostname that does not exist (default: Loremipsumdolorsitamet). If any of the requests get a response back, then it means Responder is probably running on your network.
Respotter can send webhooks to Slack, Teams, or Discord. It also supports sending events to a syslog server to be ingested by a SIEM. Webhooks alerts are rate limited to 1 alert per IP per hour.
https://github.com/lawndoc/Respotter
Defence
How we proactively defend our environments.
5G Security Guide Version 3.0
Released 16 July 2024 by the GSM Association.
This has seen the introduction of security enhancements such as default mandatory encryption of network and privacy-sensitive information as well as another principles-based concepts and methodologies, including:
Use of mutual authentication – ensure that sender and receiver have an established trusted and secured relationship.
Assume Zero Trust design principles – operate on the basis of not automatically trusting anybody or anything inside or outside the network perimeter, while not automatically assuming encrypted traffic to be valid (see Section 8.9.1 for more details).
Do not assume transport links are secure – use encryption to ensure any compromised information is of no value to recipients.
This document discusses different aspects of 5G security identified by GSMA as requiring attention within appropriate bodies (e.g. 3GPP, IETF, ETSI, and GSMA).
Unfashionably secure: why we use isolated VMs
Marco Slaviero details their journey in secure by design..
Services for a single customer are contained within their own AWS EC2 instance. In other words, we run a VM per customer.
In some circles, this approach isn’t considered sexy. There are no containers, no serverless functions, no cloud databases, no hyperscale support, no message buses (well… there are but they exist on the instance only), no load balancers, no k8s clusters. Nothing here will earn us a speaking invite to CNCF events, or an architecture diagram full of AWS service icons, and we happily accept this trade off.
https://blog.thinkst.com/2024/07/unfashionably-secure-why-we-use-isolated-vms.html
Incident Writeups & Disclosures
How they got in and what they did.
CrowdStrike Preliminary Post Incident Review
They have started to report on the incident..
On Friday, July 19, 2024 at 04:09 UTC, as part of regular operations, CrowdStrike released a content configuration update for the Windows sensor to gather telemetry on possible novel threat techniques.
These updates are a regular part of the dynamic protection mechanisms of the Falcon platform. The problematic Rapid Response Content configuration update resulted in a Windows system crash.
Systems in scope include Windows hosts running sensor version 7.11 and above that were online between Friday, July 19, 2024 04:09 UTC and Friday, July 19, 2024 05:27 UTC and received the update. Mac and Linux hosts were not impacted.
The defect in the content update was reverted on Friday, July 19, 2024 at 05:27 UTC. Systems coming online after this time, or that did not connect during the window, were not impacted.
https://www.crowdstrike.com/falcon-content-update-remediation-and-guidance-hub/
How a North Korean Fake IT Worker Tried to Infiltrate Us
Stu Sjouwerman reminds the world why it needs insider risk programmes.
TLDR: KnowBe4 needed a software engineer for our internal IT AI team. We posted the job, received resumes, conducted interviews, performed background checks, verified references, and hired the person. We sent them their Mac workstation, and the moment it was received, it immediately started to load malware.
Our HR team conducted four video conference based interviews on separate occasions, confirming the individual matched the photo provided on their application. Additionally, a background check and all other standard pre-hiring checks were performed and came back clear due to the stolen identity being used. This was a real person using a valid but stolen US-based identity. The picture was AI "enhanced". .
https://blog.knowbe4.com/how-a-north-korean-fake-it-worker-tried-to-infiltrate-us
Domain Hijacking
Incident report for Squarespace which occurred when they assumed operation of the Google Domains.
There were a limited number of Domains customers who had their member accounts compromised, leading to unauthorized changes to their domain settings and DNS records. Squarespace suspended the affected accounts, which caused a temporary lockout to those logins while remediation efforts were taken to restore access and control. We worked directly with the affected customers to authenticate their identity and ensure the security of their domains.
https://status.squarespace.com/incidents/cw2wf55bps15
Vulnerability
Our attack surface.
View State, The unpatchable IIS forever day being actively exploited
Adrian Justice shows the risks stemming from a web server compromise on the long term security of applications hosted upon it.
I’ll be skipping the initial access phase of our “compromise” and using my physical access to the target to deploy any needed webshells etc.
To successfully exploit view state, we’ll need to acquire several values:
Validation keyThe validation key component of the IIS machine key for our target application
Validation algorithmThe validation algorithm in use
Target pathThe relative path to the webroot of the page we intend to target
App pathThe path of the application we are targeting
https://zeroed.tech/blog/viewstate-the-unpatchable-iis-forever-day-being-actively-exploited/
SAPwned: SAP AI vulnerabilities expose customers’ cloud environments and private AI artifacts
Hillai Ben-Sasson shows rapidly developed Software as a Service is likely as resilient as you would expect.
Specifically, the access we gained allowed us to:
Read and modify Docker images on SAP’s internal container registry
Read and modify SAP’s Docker images on Google Container Registry
Read and modify artifacts on SAP’s internal Artifactory server
Gain cluster administrator privileges on SAP AI Core’s Kubernetes cluster
Access customers’ cloud credentials and private AI artifacts
https://www.wiz.io/blog/sapwned-sap-ai-vulnerabilities-ai-security
Offense
Attack capability, techniques and trade-craft.
Thread Name-Calling - using Thread Name for offense
hasherezade creates some work for EDR vendors..
Process Injection is one of the important techniques in the attackers’ toolkit.
In the following write-up, Check Point Research (CPR) explains how the API for thread descriptions can be abused to bypass endpoint protection products.
We propose a new injection technique: Thread Name-Calling, and offer the advisory related to implementing protection.
https://research.checkpoint.com/2024/thread-name-calling-using-thread-name-for-offense/
dirDevil: Hiding Code and Content Within Folder Structures
Nyxgeek details a technique which should be easy enough to spot.
You can hide data in directory structures, and it will be more or less invisible without knowing how to decode it. It won't even show up as taking up space on disk. However, its real-world applications may be limited because it is the code execution itself which is often the difficulty with AV/EDR evasion.
https://trustedsec.com/blog/dirdevil-hiding-code-and-content-within-folder-structures
Benign Hunter
Brendan Ortiz releases a capability which EDR vendors will want to understand the implications of. Adversaries will use this to find APIs to get some unmonitored functionality/access. The game of whack-a-mole continues
this tool is a simple tool to try and identify which native API's are deemed benign by EDRs and are therefore not hooked.
https://github.com/Allevon412/BenignHunter
Exploitation
What is being exploited.
CVE-2024-38112: Void Banshee Targets Windows Users Through Zombie Internet Explorer in Zero-Day Attacks
Peter Girnus and Aliakbar Zahravi shows that criminal actors are increasingly capable. Although the use of e-mail and ZIPs etc.
In May, ZDI threat hunters under Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative discovered a vulnerability that the APT group Void Banshee had been exploiting in an updated Atlantida Stealer campaign. We promptly identified and reported this as a zero-day vulnerability to Microsoft.
The vulnerability CVE-2024-38112 (ZDI-CAN-24433) was used as a zero-day to access and execute files through the disabled Internet Explorer using MSHTML.
As part of Void Banshee's attack chain, CVE-2024-38112 is being used to infect victim machines with the Atlantida info-stealer, which focuses on pilfering system information and sensitive data (like passwords and cookies) from various applications.
Void Banshee lures in victims using zip archives containing malicious files disguised as book PDFs; these are disseminated in cloud-sharing websites, Discord servers, and online libraries, among others. Void Banshee's attacks are concentrated in North America, Europe, and Southeast Asia.
This zero-day attack is a prime example of how unsupported Windows relics are an overlooked attack surface that can still be exploited by threat actors to infect unsuspecting users with ransomware, backdoors, or as a conduit for other kinds of malware.
https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/research/24/g/CVE-2024-38112-void-banshee.html
Cursed tapes: Exploiting the EvilVideo vulnerability on Telegram for Android
Lukas Stefanko also evidence that the exploit commercial eco-system is rich with capability.
ESET researchers discovered a zero-day exploit that targets Telegram for Android, which appeared for sale for an unspecified price in an underground forum post from June 6th, 2024. Using the exploit to abuse a vulnerability that we named EvilVideo, attackers could share malicious Android payloads via Telegram channels, groups, and chat, and make them appear as multimedia files.
We were able to locate an example of the exploit, allowing us to analyze it further, and report it to Telegram on June 26th, 2024. On July 11th, they released an update that fixes the vulnerability in Telegram versions 10.14.5 and above.
Tooling and Techniques
Low level tooling and techniques for attack and defence researchers…
LIEF v0.15.0
Romain Thomas updates this tooling which will be useful in various analysis tasks.
LIEF is now providing additional features thanks to an extended version. Among those features, it provides support for DWARF and PDB debug formats as well as Objective-C metadata.
https://lief.re/blog/2024-07-21-lief-0.15-0/
Ghidra script that calls OpenAI to give meaning to decompiled functions
Charles Lomboni leverages the power of AI with a risk of hallucination..
AskJoe is a tool that utilizes OpenAI to assist researchers wanting to use Ghidra as their malware analysis tool. It was based on the Gepetto idea. With its capabilities, OpenAI highly simplifies the practice of reverse engineering, allowing researchers to better detect and mitigate threats.
https://github.com/securityjoes/AskJOE
BinaryNinja Shellcodehashes
Adam Prescott does the life and shift here..
Port of Mandiant ShellcodeHashes plugin from IDA to BinaryNinja
The IDA plugin
Searches in an IDB for known symbol hashes retrieved from a pre-calculated set stored in a sqlite db.
https://github.com/PwCUK-CTO/BinaryNinja_shellcodehashes
Footnotes
Some other small (and not so small) bits and bobs which might be of interest.
Aggregate reporting
Research Report: The strategic and symbolic value of digital technologies - “In a new report released today, ECCRI explores how states attach strategic value to digital technologies. Combining conceptual insights and practical applications, the report introduces and assesses a comprehensive framework designed to identify the strategic properties of critical and emerging technologies.”
Killing us with cyber incompetence - from 2019
Everything Matters in Programmable Packet Scheduling - a implementation of sorts is here - https://github.com/nsg-ethz/SP-PIFO?tab=readme-ov-file
Artificial intelligence
Nothing this week
Books
Events
JSAC 2025 CFP - being held in January 2025 in Tokyo
Unless stated otherwise, linked or referenced content does not necessarily represent the views of the NCSC and reference to third parties or content on their websites should not be taken as endorsement of any kind by the NCSC. The NCSC has no control over the content of third party websites and consequently accepts no responsibility for your use of them.
This newsletter is subject to the NCSC website terms and conditions which can be found at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/terms-and-conditions and you can find out more about how will treat your personal information in our privacy notice at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/privacy-statement.