CTO at NCSC Summary: week ending March 10th
'The Invisible $1.52 Trillion Problem - Software technical debt...
Welcome to the weekly highlights and analysis of the blueteamsec subreddit (and my wider reading). Not everything makes it in, but the best bits do.
Operationally this week the usual smoulder continues..
In the high-level this week:
Royal Navy combine with Japanese forces to battle cyber attacks - “Forty-one teams from 17 nations tested their cyber defence skills during the British Army’s Defence Cyber Marvel 3 exercise in Estonia, but with an international network plugging in from across three continents. The Royal Navy’s cyber operations specialists based in Portsmouth are usually on the front line across the world, protecting ships and bases from threats around the clock, but were deployed to Tokyo for this valuable exercise.”
President Biden Issues Executive Order to Protect Americans’ Sensitive Personal Data - The White House (not me) says “The President’s Executive Order focuses on Americans’ most personal and sensitive information, including genomic data, biometric data, personal health data, geolocation data, financial data, and certain kinds of personally identifiable information.”
Justice Department to Implement Groundbreaking Executive Order Addressing National Security Risks and Data Security - “Our adversaries are exploiting Americans’ sensitive personal data to threaten our national security,”
Citing National Security Concerns, Biden-Harris Administration Announces Inquiry into Connected Vehicles “the U.S. Department of Commerce issued an advance notice of proposed rulemaking (ANPRM) seeking public comment to inform the potential development of regulations to secure and safeguard the Information and Communications Technology and Services (ICTS) supply chain for connected vehicles (CVs).”
South Korean National Intelligence Service urges semiconductor industry to be cautious of 'spread of North Korean hacking - South Korean National Interface Service says “North Korean hacking organizations targeted companies whose servers were connected to the Internet and exposed vulnerabilities. The company's business servers, which are used to manage documents and other data, were targeted by hackers.”
Strategy for Cyber-Physical Resilience: Fortifying Our Critical Infrastructure for a Digital World - another White House release - “We must continue to ensure effective cyber defenses and, at the same time, acknowledge that we cannot make all our infrastructure impervious to every threat or hazard. Instead, we must make our cyber-physical infrastructure resilient. Fortifying the resiliency of our critical infrastructure will require a substantially deeper partnership between the public and private sectors to focus attention and to unleash deeper investment.”
Report on the cybersecurity and resiliency of the EU communications infrastructures and networks - “As regards strategic aspects, the report recommends to:
Assess resilience of international interconnections;
Assess criticality, resilience and redundancy of core Internet infrastructure, such as submarine cables;
Implement the recommendations related to suppliers in the second Progress Report on the EU Toolbox implementation;
Create transparency on the landscape of suppliers and managed service provider or managed security service provider used for fixed networks, fibre technology, submarine cables, satellite networks and other important ICT suppliers;
Involve the electronic communications sector in cyber exercises and operational collaboration;
Foster information sharing and improve situational awareness about threats for operators;
Provide funding support to operators for technical measures against cyber attacks in their networks;
Exchange good practices among national authorities about physical attacks on digital infrastructure;
Extend physical stress testing of critical infrastructure to include digital infrastructure.”
Cyber ransoms are too profitable. Let’s make paying illegal - Ciaran Martin’s view on the topic.
Senator Demands Overhaul of Telecom Security to Curb Abuses - “Foreign governments are abusing security flaws in mobile phone networks to secretly track Americans in the US and journalists and dissidents abroad, Senator Ron Wyden has warned.”
Schumer calls for emergency cash as major cyberattack drags on - “Senate Majority Leader Charles E. Schumer asked federal health officials Friday to provide up-front cash for New York hospitals and other health care providers, which are struggling as a result of a massive cyber attack that has downed multiple health care systems and in some cases has affected crucial operations at health facilities.”
Cyber defenses of 40 critical [Ukrainian] infrastructure facilities to be enhanced through cyber diagnostics - The diagnostics program includes:
Cybersecurity assessment based on the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
Identifying the target cybersecurity status
Guidance: high-level design, technical architecture specifications, cybersecurity operation models
Drawing up a roadmap for the guidance implementation
Implementation of the guidance
Follow-up cybersecurity assessment
The Global Dimension of Ukraine’s Cyber Defense: A conversation with Ambassador Nathaniel C. Fick and Director Jen Easterly - there is a video which is worth a watch.
MEPs back plans for an EU-wide digital wallet - “this new Digital Identity Wallet will allow citizens to identify and authenticate themselves online without having to resort to commercial providers - a practice that raises trust, security and privacy concerns.”
How to master Europe’s digital infrastructure needs? - “With this White Paper the Commission launches a broad consultation of Member States, civil society, industry, and academics, to collect their views on the scenarios outlined in this White Paper and provide them with an opportunity to contribute to the Commission’s future proposals in this domain”
Europe’s cyber rapid response teams should pivot to proactive missions - Binding Hook oped - “For now, multinational teams are better suited for proactive missions, which allow for longer planning timelines and often involve less sensitive political situations. National teams are much more effective at responding: they can work directly with the country in need, establishing more streamlined information sharing and liability protocols. “
The economic implications of services in the metaverse - from the Bank of International Settlements - For computer scientists, substantial work is to be done to understand technology choices and their impact on user outcomes, (cyber)security, scalability and more. For legal scholars, there is scope to consider how regulatory compliance, civil disputes, property rights and more will be arranged in a virtual world that goes beyond the boundaries of national jurisdictions. For sociologists and communications scholars, there are important questions about the societal processes and narratives that accompany such technology developments.
Defending Democracy
The Kremlin’s Efforts to Spread Deadly Disinformation in Africa - United States Department of State - “Today, the U.S. Department of State’s Global Engagement Center is exposing Russia’s intelligence services for providing material support and guidance to “African Initiative,” a new information agency focused on Africa-Russia relations that has spread disinformation regarding the United States and European countries”
Reporting on/from China
China Rules AI Firm Committed Copyright Infringement - Forbes reports “The first of its kind ruling places clear responsibility on the AI company, which the plaintiff argued reproduced copyrighted images unlawfully and without permission.”
Too late to act? Europe’s quest Policy Brief for cloud sovereignty - Netherlands Institute for International Relations reports - “Chinese companies are by definition excluded from hosting applications and data deemed sensitive, as the country is identified as running a structural, offensive cyber offensive against the Netherlands and Dutch interests.”
Hi-Tech, High Risk? Russo-Chinese Cooperation on Emerging Technologies - RUSI reports - “Extensive deployment of drones and advanced telecommunications equipment have been crucial on all fronts in Ukraine, from intelligence collection to airstrike campaigns. These technologies, though critical, require steady connectivity and geospatial support, making cooperation with China a potential solution to Moscow’s desire for a military breakthrough.”
Ex-Google engineer charged with stealing AI trade secrets while working with Chinese companies - Associated Press reports - “A former software engineer at Google has been charged with stealing artificial intelligence trade secrets from the company while secretly working with two companies based in China, the Justice Department said Wednesday.”
Artificial intelligence
We Hacked Google A.I. for $50,000 - punchline here is web vulnerabilities..
On the Societal Impact of Open Foundation Models - “Analyzing the benefits and risks of foundation models with widely available weights”
The Perilous Coming Age of AI Warfare - Foreign Affairs article “Widely deployed autonomous weapons integrated with other aspects of military AI could result in a new era of machine-driven warfare. Military AI applications can accelerate information processing and decision-making.”
AI and Product Safety Standards Under the EU AI Act - The EU’s AI Act marks a critical step toward regulating the fast-evolving field of artificial intelligence, setting a precedent for global digital regulation. However, its success hinges on the effective translation of its high-level safety requirements into precise, actionable standards by CEN and CENELEC. Comparisons with standards providing guidance for risk assessment and mitigation in established safety-critical sectors reveal the need for standards that are not only detailed and legally certain but also flexible enough to accommodate the unique characteristics of AI technologies.
Interoperable Europe act: Council adopts new law for more efficient digital public services across the EU - consistency with the provisions of the artificial intelligence act (AIA) and of the general data protection regulation (GDPR), with regard to the establishment of and participation to interoperability regulatory sandboxes
Explanatory memorandum on the updated OECD definition of an AI system - In November 2023, OECD member countries approved a revised version of the Organisation’s definition of an AI system.
Language models, when aided by information retrieval systems, can potentially produce forecasts as accurate as those created by competitive human forecasters. - On average, the system nears the crowd aggregate of competitive forecasters, and in some settings surpasses it. Our work suggests that using LMs to forecast the future could provide accurate predictions at scale and help to inform institutional decision making.
Cyber proliferation
Treasury Sanctions Members of the Intellexa Commercial Spyware Consortium US Treasury - “the Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) designated two individuals and five entities associated with the Intellexa Consortium for their role in developing, operating, and distributing commercial spyware technology used to target Americans, including U.S. government officials, journalists, and policy experts.”
Court orders maker of Pegasus spyware to hand over code to WhatsApp - “The decision by Judge Phyllis Hamilton is a major legal victory for WhatsApp, the Meta-owned communication app which has been embroiled in a lawsuit against NSO since 2019, when it alleged that the Israeli company’s spyware had been used against 1,400 WhatsApp users over a two-week period.” - a new way to burn capability, legal discovery - this is a lawfare exemplar
The Predator spyware ecosystem is not dead - Sekoia reports “we discovered domains related to three countries not included in our previous paper: Botswana, Mongolia and Sudan”
Media Freedom in Europe - 2024 report - key bit is the Safety of Journalists platform 2024 report: serious concern about the use of spyware against journalists, abusive lawsuits and journalists in exile
Bounty Hunting
Iranian National Charged for Multi-Year Hacking Campaign Targeting U.S. Defense Contractors and Private Sector Companies - US Justice Department - “According to court documents, from at least in or about 2016 through in or about April 2021, Alireza Shafie Nasab, 39, of Iran, and other co-conspirators were members of a hacking organization that participated in a coordinated multi-year campaign to conduct and attempt to conduct computer intrusions.”
Data processing: Europol and the Member State in which damage has occurred arising from unlawful data processing carried out in the context of cooperation between Europol and that Member State are to be jointly and severally liable for that damage - Judgment of the Court in Case C-755/21 P | Kočner v Europol
Futures of big tech in Europe - This policy brief uses a scenario approach to sketch the implications of Big Tech for Europe’s future by 2040.
Cyber threats impacting the safety and dignity of civilians in conflict - from the International Committee of the Red Cross - “we would like to draw your attention to one threat which is not yet reflected in the progress report. States have emphasized in the United Nations that the use of civilian ICT infrastructure, such as cloud computing or communication infrastructure, faces serious risks of disruption or destruction if it is used by the military in situations of armed conflict.”
The reflections this week come from the Wall Street Journal article The Invisible $1.52 Trillion Problem: Clunky Old Software Old code piles up and raises the risk of hacks and other breaches, even on new devices. Our compounding ‘technical debt’. The article has its roots in a 2022 report by the Consortium for Information & Software Quality™ which looks at the US. This is a topic James and I wrote on in the paper Software Security Austerity - Software security debt in modern software development a dizzying twelve years ago.
The WSJ article further quantifies the adverse impact of today’s market incentives. It is for this reason why at the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre we see that fixing the fundamentals of the market for technology and associated services is critical. Related to which there was also an interesting article titled Securing critical infrastructure in the US is not a policy problem, it’s a market problem.
All of this has led to an interesting discussion this week on how technical debt might be reflected on an organisation’s balance sheet as a way for boards to govern and be incentivised..
Think someone else would benefit? Share:
All attribution is by others and not the UK Government unless specifically stated as such, please see the legal text at the end.
Have a lovely Thursday
Ollie
Cyber threat intelligence
Who is doing what to whom and how.
Reporting on Russia
Russia-Ukraine war: pro-Russian hacktivist activity two years on
An analysis which asserts that year-on-year pro-Russian hacktivism is down. Interesting that hobby-hackers might go and do something else..
Whilst pro-Russian hacktivist activity has decreased compared to levels observed in 2023, these groups do still continue to claim attacks on Ukraine and its allies.
https://www.kelacyber.com/russia-ukraine-war-pro-russian-hacktivist-activity-two-years-on/
Getting Bored of Cyberwar: Exploring the Role of Low-level Cybercrime Actors in the Russia-Ukraine Conflict
Similar reporting, this time from Cambridge University and Anh V. Vu, Daniel R. Thomas, Ben Collier, Alice Hutchings, Richard Clayton and Ross Anderson attempt to quantify the impact of hobby-hackers on the war.
The role of the low-level cybercrime actors studied in this paper amounts to essentially trivial acts of solidarity and opportunistic competition. Their primary impact is probably to disseminate political propaganda, with little measurable evidence to suggest these actors are making any persistent contribution to the conflict, even in a major war between two nations with a long history of cyberwarfare. Their role and capacity in future nation-state conflicts should not be confounded with state hacking or political ‘hacktivism’. Our diverse, separately collected datasets all point to a narrative that notable attention was temporarily drawn to Russia and Ukraine rather than other countries. Neither the engagement on Hack Forums nor Telegram, or the outbreak of defacements and DDoS attacks, was long-lasting – presumably as participants just lost interest, despite their choice of targets being influenced by the war for a while
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2208.10629.pdf
Software, Ciphers, Secret Documents — DIU Cyber Specialists Hacked Russia’s Defence Ministry
Ukrainian government attributing one of their own offensive ops which will be note worthy for that vary reason. Let alone their claimed target..
The cyber specialists of the Defence Intelligence of Ukraine conducted another successful special operation against the aggressor state of Russia. As a result of the attack, it was managed to gain access to the servers of the Russian ministry of defence.
TA577 phishing campaign uses NTLMv2 handshakes to steal user credentials/hashes
An alleged Russian criminal actor appears they might be after password hashes according to Deutsche Telekom.. as long as you block SMB/WebDav outbound you should be fine..
TA577, are a Russia-based threat group that have been reported to deliver payloads including Qbot, IcedID, SystemBC, SmokeLoader, Ursnif, and Cobalt Strike in ongoing phishing campaigns since 2020.
This week, it was reported by Deutsche Telekom CERT that TA577 have been sending .HTML files to make outbound SMB connections to file:// URLs to retrieve a file in an attempt to capture NTLMv2 handshakes.
Reporting on China
A comprehensive analysis of I-Soon's commercial offering
The data leak that keeps on giving in the way Conti Leaks did for cybercrime. You have to wonder how many academic papers are in the works based on this data as well…
I-Soon’s commercial offering reveals that their main issue is processing collected data, not breaching their targets in the first place. Their products leverage deep learning to help them sort and classify stolen documents.
The company appears to have trouble sourcing malware and relies on generally crude methods (i.e., phishing). Yet they breached countless strategic targets worldwide in the last 10 years.
The leaks confirm analyst suspicions about the Chinese cybersecurity apparatus organization, particularly regarding vulnerability management and regional tasking spread across provinces.
Intelligence contractors such as I-Soon benefit from a large degree of operational autonomy and may proactively breach victims in the hopes that their clients will be interested in the collected data.
Contrary to initial reporting, I-Soon’s social media influence capabilities appear to be overblown and likely couldn’t noticeably impact the public debate.
https://harfanglab.io/en/insidethelab/isoon-leak-analysis/
Reporting on North Korea
Phishing by Appointment: Suspected North Korean Hackers Target Blockchain Community Via Telegram
Michael Rippey details a campaign allegedly by North Korea which seems to imply they might still be after financial instruments. The fact they are going after the start-up community in alternative financial tools space will be of note.
[We are] tracking an ongoing sophisticated phishing campaign targeting individuals in the Telegram groups focused on the blockchain and angel investing communities, specifically entrepreneurs. The tactics described below are strikingly similar to those previously attributed to the Lazarus Group, a North Korean state-sponsored threat actor. Communication begins with the actor posing as a representative of an investment company seeking business opportunities. As the conversation progresses, the victim is asked to download an Apple Script after ‘technical difficulties’ are encountered in setting up a meeting.
https://hunt.io/blog/suspected-north-korean-hackers-target-blockchain-community-via-telegram
Shadow Hunting: Analysis of APT37’s attack activities against South Korea using North Korean political topic
Chinese reporting on alleged North Korean activity, nothing overly of note beyond the lure topics being used.
The bait released in Sample 1 is a column published by a senior researcher at the Institute of National Security and Unification of South Korea, an adjunct professor at Dankook University’s Graduate School of Administrative Law, and the director of the Institute for 21st Century Strategy. The article discusses North Korea’s intensification of hostility and external infiltration. and espionage concerns.
Judging from the attack samples captured this time, the organization's core attack Trojan has not changed much from a year ago. It only improves the attack success rate by changing the bait file and Trojan loading method.
TODDLERSHARK: ScreenConnect Vulnerability Exploited to Deploy BABYSHARK Variant
Keith Wojcieszek, George Glass and Dave Truman show that North Korea was allegedly quick to get on the exploit train for this vulnerability. Their relative level of capability is semi noteworthy.
[We] discovered new malware resembling the VBScript based BABYSHARK malware that we've called TODDLERSHARK.
The malware was used in post-compromise activity following exploitation of a ScreenConnect application.
BABYSHARK has been associated, by several sources, with a threat actor Kroll tracks as KTA082 (Kimsuky).
The malware utilized legitimate Microsoft binary and alternate data streams and exhibited elements of polymorphic behavior.
Reporting on Iran
Nothing this week
Reporting on Other Actors
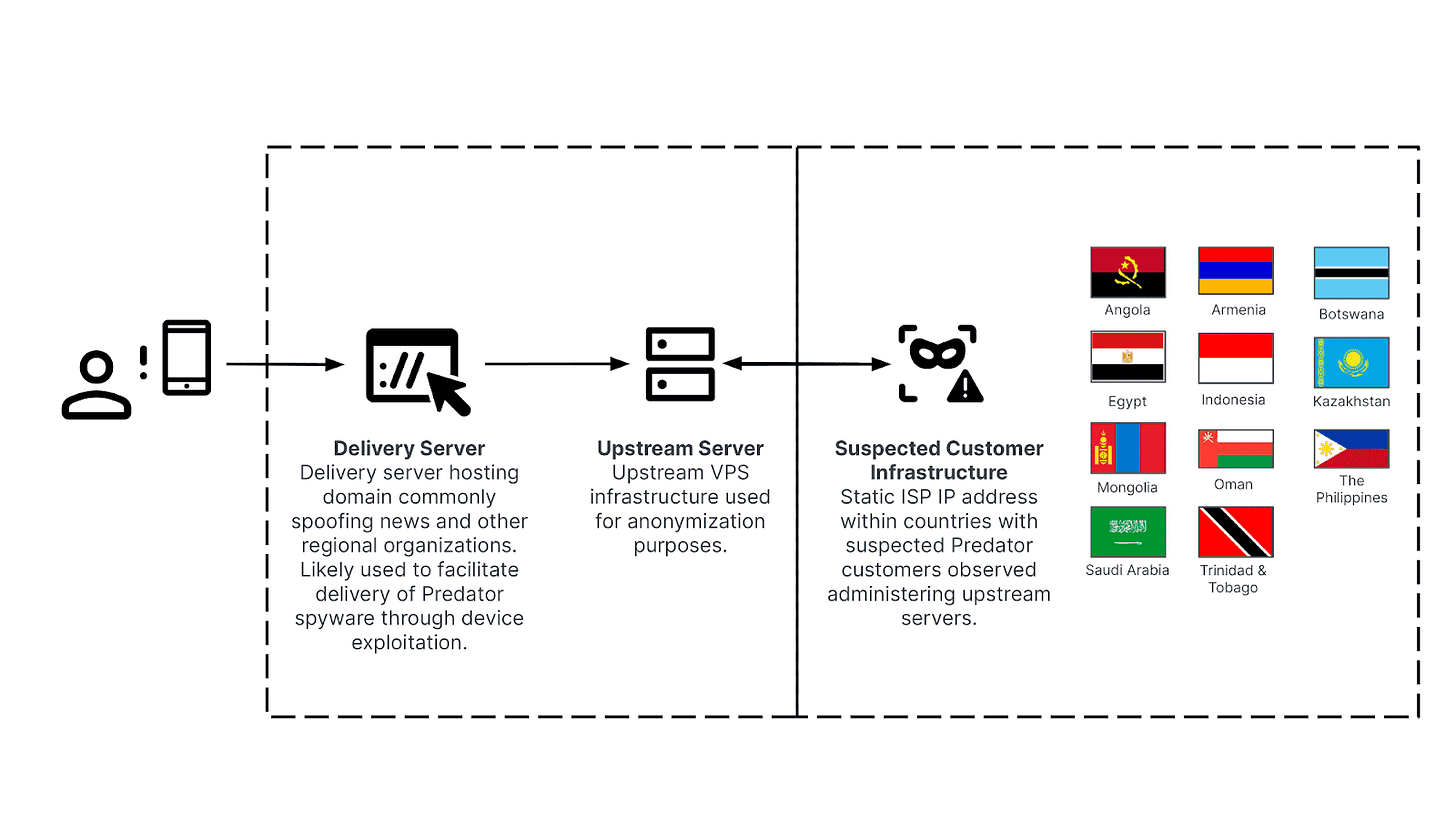
Predator Spyware Operators Rebuild Multi-Tier Infrastructure to Target Mobile Devices
Insikt Group® alleged the use of commercial spyware by a whole host of countries using fresh infrastructure. Those who can’t build buy it would appear..
In particular, we identified evidence of the likely continued use of Predator within at least eleven countries, specifically Angola, Armenia, Botswana, Egypt, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, Oman, the Philippines, Saudi Arabia, and Trinidad and Tobago. Before this, no Predator customers within Botswana and the Philippines had been identified
CryptoChameleon: New Phishing Tactics Exhibited in FCC-Targeted Attack
David Richardson and Savio Lau detail a campaign which is noteworthy for its attempt to hinder automatic discovery/analysis and then victimology. Other than that it all rather run-of-the-mill.
This phishing kit first asks the victim to complete a captcha using hCaptcha. This is a novel tactic that prevents automated analysis tools from crawling and identifying the phishing site. It may also give the illusion of credibility to the victim, as typically only legitimate sites use captcha.
Employees targeted at
Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
Binance
Coinbase
Cryptocurrency users at
Binance
Coinbase
Gemini
Kraken
ShakePay
Caleb & Brown
Trezor
https://www.lookout.com/threat-intelligence/article/cryptochameleon-fcc-phishing-kit
Over 100,000 Infected Repos Found on GitHub
Matan Giladi and Gil David detail a rather large campaign and thus notable which you could see might have the risk of being effective.
In this case, in order to maximize the chances of infection, the malicious actor is flooding GitHub with malicious repos, following these steps:
Cloning existing repos (for example: TwitterFollowBot, WhatsappBOT, discord-boost-tool, Twitch-Follow-Bot, and hundreds more).
Infecting them with malware loaders.
Uploading them back to GitHub with identical names.
Automatically forking each thousands of times.
Covertly promoting them across the web via forums, discord, etc.
https://apiiro.com/blog/malicious-code-campaign-github-repo-confusion-attack/
Spreading MSIX malware disguised as Notion installation file
South Korean reporting a suspect stealer operation which is of note due to the use of a valid code signing certificate to 'Consoneal Ltd' issued by SSL.com
Discovery
How we find and understand the latent compromises within our environments.
How To Hunt For UEFI Malware Using Velociraptor
Matthew Green does what he does best with this release…
Despite UEFI threats possessing intimidating capabilities, security practitioners can deploy some visibility with current tools for remote investigation. Forensically parsing disk and not relying on the Windows API, or reviewing other systemic indicators that may signal compromise, is a practical way to detect components of these threats.
https://www.rapid7.com/blog/post/2024/02/29/how-to-hunt-for-uefi-malware-using-velociraptor/
Hunting Cobalt Strike LNK Loaders
A work aid for those still dealing with Cobalt Strike at scale..
The idea of the tool is to allow the user to intuitively use multiple search filters at once. It is not perfect, as there is a quirk can can produce false negatives, and not all search parameters are supported; however, it should still be useful to quickly find malware with specific properties.
https://montysecurity.medium.com/hunting-cobalt-strike-lnk-loaders-f3c407a991c0
Detecting Manual AWS Actions: An Update!
Arkadiy Tetelman provides a detection edge with this release..
The primary 3 updates are:
A new trigger mechanism
An updated list of filtered IAM actions, and
Detecting session name bypasses
Detecting on manual actions continues to be one of my biggest “bang for your buck” alerts at every employer I’ve worked at - it’s a fanastic tool to enforce that infrastructure changes can only happen via pull requests against your infrastructure-as-code github repo (terraform in our case).
https://arkadiyt.com/2024/02/18/detecting-manual-aws-actions-an-update/
Get malware c2s from Cryptneturlcache
Konrads Klints provides a capability edge with this novel technique..
CryptnetUrlCache is a directory which contains cached certificate validation data - OCSP and CRLs for WinInet and WinHTTP library calls (most Windows native programs do it)
We can use the certificate serial number in OCSP requests and responses to retrieve the actual certificates from Certificate Transparency log database such as crt.sh. Subject Name and Subject Alternative Name will tell us what are the possible hostname values
This is useful when you want to examine where programs may have connected to
https://github.com/truekonrads/ocspcryptneturlcache
GTPDoor Network Detection
As described the implant in it's default state (without being re-keyed) will use a hardcoded key of
135798642, this leads to a basic detection method where we can use theGTP ECHO Request(type 1) to monitor for any packets containing this request, as well as any kind of responses that are of theGTP ECHO Response(type 2). If we use the xbits feature of Suricata we can actually monitor for the presence of this implant within a network environment.
https://github.com/sud0woodo/detect_gtpdoor
DefenderYara: Extracted Yara rules from Windows Defender mpavbase and mpasbase
Roadwy has industrialised this..
Extracted Yara rules from Windows Defender mpavbase and mpasbase
https://github.com/roadwy/DefenderYara/
Defence
How we proactively defend our environments.
NSA Releases Maturity Guidance for the Zero Trust Network and Environment Pillar
Our US partners gives Zero Trust a nudge on its evolution journey..
The CSI outlines the key capabilities of the network and environment pillar, including data flow mapping, macro and micro segmentation, and software defined networking.
Using WDAC to ingest missing MDE events and detect token stealing
Robbe Van den Daele bridges a detection gap which will be useful to those protecting windows environments.
In this blog post we went over how we can use WDAC to ingest missing DeviceImageLoad events in Defender, without having to ingest Windows Events or using Sysmon. By doing this, we can detect PRT token stealing on a device via BrowserCore.exe and detect exploitation of MicrosoftAccountTokenProvider.dll by following this one
https://hybridbrothers.com/using-wdac-to-ingest-missing-mde-events/
Protect your users from Device Code Flow abuse
Fabian Bader closes an interesting gap with conditional access here. Also serves a reminder of cloud security complexity in 2024.
Device Code Flow is a great feature. You are signed in on a machine that does not have any UI but need to connect to an Azure or Microsoft 365 resource? No problem, device code flow to the rescue. All major PowerShell cmdlets, the az tools and many other tools support this authentication flow.
But the device code flow itself also has a dark side. Device Code phishing for example tries to convince the user to enter the device code and their credentials and the resulting access and refresh token are then used to access resources, without having to worry about reauthentication. The user already provided MFA, no phishing website had to be used, just something like TokenTactics or TokenTacticsV2 in the backend.
If you wanted to protect your users from this kind of attack there are already two powerful access controls in Conditional Access:
Require device to be marked as compliant
Require Microsoft Entra hybrid joined device
https://cloudbrothers.info/protect-users-device-code-flow-abuse/
Investigating a possible Ivanti compromise
Michael Schrijver, Rang Salih & Patrick van Looy provide an end to end guide here, which given the recent challenges will have wide applicability.
The vulnerability tracked as CVE-2023-46805 is an authentication bypass vulnerability in the web component of Ivanti Connect Secure (9.x, 22.x) and Ivanti Policy Secure, which allows a remote attacker to access restricted resources by bypassing control checks.
The other vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-21887, is a command injection vulnerability in web components of Ivanti Connect Secure (9.x, 22.x) and Ivanti Policy Secure. It allows an authenticated administrator to send specially crafted requests and execute arbitrary commands on the appliance. What makes this vulnerability particularly concerning is its potential for exploitation over the internet, posing a direct threat to the security posture of the affected systems.
https://northwave-cybersecurity.com/whitepapers-articles/investigating-a-possible-ivanti-compromise
What You See is What You Get - Building a Verifiable Enclave Image
Richard Fan shows how to do it right with some engineering finesse…
I want to dive deep into achieving zero-trust between service providers and consumers on TEE, particularly AWS Nitro Enclaves.
Incident Writeups & Disclosures
How they got in and what they did.
Keep and eye on the SEC -https://www.board-cybersecurity.com/incidents/tracker/
ACEMAGIC Mini PC Virus Incident: Comprehensive Resolution and Future Security Measures
Yep…
NEW YORK- February 21, 2024 – ACEMAGIC, a leading provider of innovative mini PC solutions, has proactively addressed an isolated virus incident affecting a specific batch of mini PCs. The incident was identified through Windows Defender, detecting the presence of the Bladabindi and Redline malware families in the ENDEV folder. As a result, several consumers across the United States and Europe reported similar concerns, prompting a thorough investigation into the root causes and swift implementation of corrective measures.
Vulnerability
Our attack surface.
SolarWinds Security Event Manager
Patch…
was susceptible to Remote Code Execution Vulnerability - vulnerability allows an unauthenticated user to abuse SolarWinds’ service, resulting in remote code execution.
Progress OpenEdge Authentication Gateway and AdminServer
Patch this too…
When the OpenEdge Authentication Gateway (OEAG) is configured with an OpenEdge Domain that uses the OS local authentication provider to grant user-id and password logins authentication routines may lead to unauthorized access on attempted log
Scrutinizing the Scrutinizer
This one just goes to prove the old adage of security products aren’t always secure products..
Plixer Scrutinizer is a network monitoring and analysis appliance that collects, interprets, and contextualizes data from every digital exchange and transaction to deliver insightful network intelligence and security reports - multiple vulnerabilities pre-auth RCE
https://www.atredis.com/blog/2024/2/9/scrutinizing-the-scrutinizer
Additional Critical Security Issues Affecting TeamCity On-Premises (CVE-2024-27198 and CVE-2024-27199)
Vendor disclosure
Two additional critical security vulnerabilities have been identified in TeamCity On-Premises.
These critical security vulnerabilities have been assigned the CVE identifiers CVE-2024-27198 and CVE-2024-27199, and present the weaknesses CWE-288 and CWE-23.
The vulnerabilities may enable an unauthenticated attacker with HTTP(S) access to a TeamCity server to bypass authentication checks and gain administrative control of that TeamCity server.
Researcher counter view..
Offense
Attack capability, techniques and trade-craft.
Meet Silver SAML: Golden SAML in the Cloud
Tomer Nahum and Eric Woodruff outline a technique that anyone using SAML may want to pay attention too..
Golden SAML, an attack technique that exploits the SAML single sign-on protocol, was used as a post-breach exploit, compounding the devastating SolarWinds attack of 2020—one of the largest breaches of the 21st century.
[We] discovered a new application of Golden SAML—one that can be exploited even in organizations that have followed previous security recommendations meant to defend against Golden SAML.
The new attack technique, dubbed Silver SAML, enables the exploitation of SAML to launch attacks from an identity provider like Entra ID against applications configured to use it for authentication, such as Salesforce.
[We] rate this vulnerability as a MODERATE risk to organizations. Depending on the compromised system, should Silver SAML be used to gain unauthorized access to business-critical applications and systems, the risk is SEVERE.
https://www.semperis.com/blog/meet-silver-saml/
Nemesis: An offensive data enrichment pipeline
This is what industrial offensive tooling looks like in 2024.
Built on Kubernetes with scale in mind, our goal with Nemesis was to create a centralized data processing platform that ingests data produced during offensive security assessments.
Nemesis aims to automate a number of repetitive tasks operators encounter on engagements, empower operators’ analytic capabilities and collective knowledge, and create structured and unstructured data stores of as much operational data as possible to help guide future research and facilitate offensive data analysis.
https://github.com/SpecterOps/Nemesis
Disable Windows Defender (+ UAC Bypass, + Upgrade to SYSTEM)
DSAS-ИНЖЕКТ details the end-to-end of this technique. A good reason to have positive proof your EDRs are functional…
a method that is already known to many users, but has not been widely publicized to this day. We will talk about Privilege Tokens and manipulating them in order to disable Windows Defender.
https://blog.injectexp.dev/2024/02/28/disable-windows-defender-uac-bypass-upgrade-to-system/
BGGP4: A 420 Byte Self-Replicating UEFI App For x64
Netspooky continues to prove they are a god among mortals…
The challenge was to create the smallest self-replicating file that prints, returns, or displays the number 4. My entry is a 420 byte self-replicating UEFI app.
In this writeup, I will cover UEFI, the UEFI x64 ABI, writing UEFI applications in x86_64 assembly, Tianocore EDK2 image loader internals, QEMU automation, and binary golf strategies for UEFI PEs.
https://github.com/netspooky/golfclub/tree/master/uefi/bggp4
Keylogging in the Windows kernel with undocumented data structures
Sven Rath brings this capability to the fore which will also have some application in the defensive space.
Using the undocumented
gafAsyncKeyStatefunction we can parse keystrokes from a session without using any API calls besides reading memory
https://eversinc33.com/posts/kernel-mode-keylogging/
https://github.com/eversinc33/Banshee
Exploitation
What is being exploited.
CVE-2023-20078 technical analysis: Identifying and triggering a command injection vulnerability in Cisco IP phones
Todd Hastings reminds everyone why you should patch your desk phones..
At first glance, CVE-2023-20078 provides little useful information necessary for exploitation. However, by combining Cisco Security Advisories, Release Notes and Product Documentation with firmware analysis, it is possible to derive how to trigger the vulnerability. With this knowledge in hand, there are multiple avenues for acquiring a shell on the device
https://securityintelligence.com/x-force/cve-2023-20078-technical-analysis/
Threat Actors Exploit Multiple Vulnerabilities in Ivanti Connect Secure and Policy Secure Gateways
CISA and friends (including the us) put out this important message..
Of particular concern, the authoring organizations and industry partners have determined that cyber threat actors are able to deceive Ivanti’s internal and external Integrity Checker Tool (ICT), resulting in a failure to detect compromise.
https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/cybersecurity-advisories/aa24-060b
Tooling and Techniques
Low level tooling and techniques for attack and defence researchers…
LAST
James Berthoty and friends release this interesting tool.. will be interested in feedback on the value for those of you who take it for a spin..
Use AI to Scan Your Code from the Command Line for security and code smells. Bring your own keys. Supports OpenAI and Gemini
https://github.com/latiotech/LAST
PaXtest 0.10.0 Release
A useful work aid to find those weird regressions and/or things which don’t work as one might expect.
PaXtest is a set of programs, originally meant to test various aspects of the userland-focused features of the PaX patch (now part of grsecurity) which, over time, partly emerged in some form in upstream Linux and other operating systems, namely address space layout randomization (ASLR), exclusive memory protection (PAGEEXEC and MPROTECT, NX bit in x86-64 CPUs, W^X in *BSD, DEP in Windows).
PaXtest 0.10.0 also gained new tests, probing various forms of huge-page mappings, in particular:
Anonymous huge page mappings,
huge-page sized file mappings,
position independent executables with text sections requiring huge-page alignment and
shared libraries with text sections requiring huge-page alignment.
Cases 1 to 3 are completely under control of the kernel and the amount of entropy provided gets directly mirrored by the returned address. Case 4, however, is largely subject to the runtime linker
ld-linux.so.
https://grsecurity.net/paxtest_release
SMM isolation - SMI deprivileging (ISRD)
Satoshi Tanda provides valuable knowledge which I suspect will lead to medium term pain..
Details the inner workings of System Management Mode (SMM) isolation on the Intel platform and interaction with Windows.
https://tandasat.github.io/blog/2024/02/29/ISRD.html
Footnotes
Some other small (and not so small) bits and bobs which might be of interest.
Aggregate reporting
Threat Actor group activities based on data and information collected from 21 November 2023 to 20 December 2023 - published Feb 27th 2024
Cybersecurity Disclosure Report - Many prominent companies have already filed their 2023 10Ks. These early 10-K filers provide insight into disclosures about Cybersecurity required by new S-K Item 106.
Tales Of Valhalla – March 2024 - insights into evasive threats that we’ve seen in the wild
Q4 2023 Cyber Threat Landscape Report: Threat Actors Breach the Outer Limits
The Cyber Initiative: Looking back at a decade of cyberpolicy
Network topology facilitates internet traffic control in autocracies
Lloyds Bank issues warning on impersonation scams as they rise 13%
Secure by Design: Google's Perspective on Memory Safety - which mentions CHERI
Artificial intelligence
ArtPrompt: ASCII Art-based Jailbreak Attacks against Aligned LLMs
Rainbow Teaming: Open-Ended Generation of Diverse Adversarial Prompts
aiocrioc: An LLM and OCR based Indicator of Compromise Extraction Tool
ComPromptMized: Unleashing Zero-click Worms that Target GenAI-Powered Applications
Examining Malicious Hugging Face ML Models with Silent Backdoor
Books
Cyber and the City - Presents the first history of computer security in finance, from the perspective of the banks. Offers a mixture of broad overview chapters that set the scene, alongside more detailed case-study chapters. Provides insights from unseen/unused archival material from various banks, and the London Metropolitan Archives
Events
Nothing this week
Unless stated otherwise, linked or referenced content does not necessarily represent the views of the NCSC and reference to third parties or content on their websites should not be taken as endorsement of any kind by the NCSC. The NCSC has no control over the content of third party websites and consequently accepts no responsibility for your use of them.
This newsletter is subject to the NCSC website terms and conditions which can be found at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/terms-and-conditions and you can find out more about how will treat your personal information in our privacy notice at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/privacy-statement.