CTO at NCSC Summary: week ending November 3rd
The new normal...
Welcome to the weekly highlights and analysis of the blueteamsec subreddit (and my wider reading). Not everything makes it in, but the best bits do.
Operationally this week nothing overly of note, which is likely more symptomatic of what we consider normal now as opposed to it being tranquil as you will see from the reporting below.
In the high-level this week:
Cyber Resilience Audit (CRA) scheme launches for assured CAF-based audits -NCSC announces - “NCSC-assured CRA service now offering Cyber Assessment Framework based audits and more applications invited from potential service providers.”
Five Eyes launch shared security advice campaign for tech startups - NCSC and friends announces - “Today members of the Five Eyes intelligence partnership launched shared security guidance Secure Innovation to help protect emerging technology companies from a range of threats, particularly those from nation-state actors. “
Organisations need to do more to help people affected by data breaches - Information Commissioner challenges - “urges people to “stop the negative ripple effect” and improve data protection for people in vulnerable situations”
Written questions, answers and statements - UK Parliament publishes - a discussion on code in kernel for cyber security
Cyber Essentials impact evaluation - Department of Science Innovation and Technology publishes -”An evaluation by Such et al (2015) provides evidence as to the efficacy of Cyber Essentials, with 99% of internet-originating vulnerabilities mitigated using the technical controls and none mitigated without them”
National Cyber Threat Assessment 2025-2026 - The Canadian Centre for Cyber Security publishes - “Over the past four years, at least 20 networks associated with Government of Canada agencies and departments have been compromised by PRC cyber threat actors.”
Defence Industrial Base Vulnerability Disclosure Program - Department of Defence Cyber Crime Centre announces - "The DIB-VDP Pilot was born out of the desire to bring the lessons learned by the DoD VDP to DIB companies based on the strong recommendation from Carnegie Mellon University Software Engineering Institute"
FY2025-2026 CISA International Strategic Plan - CISA publishes - “The CISA International Strategic Plan goals are to:
1. Bolster the Resilience of Foreign Infrastructure on Which the U.S. Depends.
2. Strengthen Integrated Cyber Defense.
3. Unify Agency Coordination of International Activities.”
Managed security services - European Parliamentary Research Service briefs - “As some Member States have begun adopting certification schemes for managed security services that are divergent or inconsistent, there is a need to avoid fragmentation in the internal market. The present proposal therefore includes targeted amendments to the scope of the Cybersecurity Act, seeking to enable managed security services schemes by means of Commission implementing acts.”
Aussie Department of Home Affairs 2023-24 Annual Report - - 93 incidents reported under the Security of Critical Infrastructure Act 2018
Operationalizing Japan-U.S. Cooperation on Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity and Resilience - Center for Strategic & International Studies studies - in essence says more needs to be done…
Laying down rules for the application of Directive (EU) 2022/2555 as regards technical and methodological requirements of cybersecurity risk-management measures and further specification of the cases in which an incident is considered to be significant with regard to DNS service providers, TLD name registries, cloud computing service providers, data centre service providers, content delivery network providers, managed service providers, managed security service providers, providers of online market places, of online search engines and of social networking services platforms, and trust service providers - European Union publishes - “Taking account of the cross-border nature of their activities and in order to ensure a coherent framework for trust service providers, this Regulation should, with respect to trust service providers, further specify the cases in which an incident shall be considered to be significant, in addition to laying down the technical and the methodological requirements of the cybersecurity risk-management measures.”
A Guide to Securing Your Supply Chain Ecosystem - Office of the Director of National Intelligence, National Counterintelligence and Security Center publishes - “This resource guide highlights Security-focused supply chain risk management (SCRM) policies, procedures, and best practices that can be integrated into an organization’s overall risk management framework.”
The Case for Bitcoin as a Reserve Asset - Matthew Ferranti, "an economist for the US Intelligence Community asserts - “Bitcoin possesses some unique investment characteristics that could help central banks diversify against several risks, including those related to inflation, geopolitical tensions, capital controls, sovereign default, bank failures, and financial sanctions. To the extent that gold is a reserve asset, so is Bitcoin."
Semiconductors
China Tightens Its Hold on Minerals Needed to Make Computer Chips - New York Times reports - “As of Oct. 1, exporters must provide the authorities with detailed, step-by-step tracings of how shipments of rare earth metals are used in Western supply chains.”
Huixi Intelligent's first chip, Guangzhi R1, is released: 7nm automotive-grade process, integrating 45 billion transistors - IT Home reports - “provides more than 500 TOPS of deep learning computing power and more than 420kDMIPS of CPU computing power, and has 24 built-in Arm Cortex-A78AE cores.”
China detains first South Korean on alleged espionage charges - The Chosun Daily reports - “Ex-Samsung Electronics employee detained in China on suspicion of "leaking semiconductor information to Korea" … “China’s revised anti-espionage law broadened the scope of espionage from “stealing state secrets and information” to include the transfer of any materials related to “national security and interests.”
Reporting on/from China
Statement on People's Republic of China reconnaissance of Canadian systems - Canadian Centre for Cyber Security states - “[We] aware that a sophisticated state-sponsored threat actor from the People’s Republic of China has performed broad based reconnaissance scanning over several months against numerous domains in Canada.”
Inside a Firewall Vendor's 5-Year War With the Chinese Hackers Hijacking Its Devices = Wired reports - “Sophos' report ties those multiple hacking campaigns—with varying levels of confidence—to Chinese state-sponsored hacking groups including those known as APT41, APT31, and Volt Typhoon, the latter of which is a particularly aggressive team”
Beyond the great firewall: EU and US responses to the China challenge in the global digital economy - University of Dundee analyses - “This paper investigates how growing perceptions of China-based threats in the digital domain have shaped EU (including Member State-level) and US policies.”
Commissars with keyboards: the lingering relevance of the military-political origins of Chinese and Russian psychological warfare - National Defence University researches - “The political officers, or commissars, who staffed these directorates played a large role in shaping the development of psychological warfare beyond the Cold War and into the information age. This article summarizes this history and demonstrates its relevance to modern PLA and Russian military psychological warfare.”
A three-pronged new development model for overcoming the middle-technology trap in China - The Chinese University of Hong Kong researches - “This study introduces a strategic approach through a new development model, emphasizing the synergy among three core systems: basic scientific research, applied technology, and financial support.”
Biometric (Data) Governance and Digital Surveillance: A Comparative Analysis of Biopolitics in India and China - GITAM Deemed to Be University analyses - “The objective is to examine how India and China, being different regime types, could adopt a similar biometric (data) governance, in the guise of providing welfare and national security. This chapter brings out a non-western experience of the surveillance state from global south”
Artificial intelligence
US finalizes rules to curb AI investments in China, impose other restrictions - Reuters reports - Reuters reports - “The new rules are effective Jan. 2 and will be overseen by Treasury's newly created Office of Global Transactions. Treasury said the "narrow set of technologies is core to the next generation of military, cybersecurity, surveillance, and intelligence applications."
AgiBot X1 is a modular humanoid robot with high dof developed and open-sourced by AgiBot. It is built upon AgiBot's open-source framework
AimRTas middleware and using reinforcement learning for locomotion control - they have released the Training set
Cyber proliferation
Removed from U.S. blacklist: Waterloo, Ont. tech company promises major changes, watchdogs remain hesitant - CTV New Kitchener reports - “It seemed the promises were enough for the U.S. Department of Commerce though due to the decision to remove Sandvine from the Entity List.”
Bounty Hunting
Japanese Man Convicted of Making Virus Using AI; Likely 1st Person in Japan to be Convicted in Criminal Case for Abusing Generative AI - The Japan News reports - “A 25-year-old man was found guilty of making a computer virus and was given a three-year prison sentence, which will be suspended for four years, on Friday. The virus was created through the use of interactive generative artificial intelligence.”
A court in St. Petersburg has announced sentences for several defendants in the “REvil case” - Kommersant publishes - “Zayets and Malozemov were sentenced to 4.5 and 5 years in a general regime penal colony, respectively. Khansvyarov and Puzyrevsky received 5.5 and 6 years, respectively.”
Operation Magnus - Dutch National Police announces - “On the 28th of October 2024 the Dutch National Police, working in close cooperation with the FBI and other partners of the international law enforcement task force Operation Magnus, disrupted operation of the Redline and META infostealers”
U.S. Joins International Action Against RedLine and META Infostealers - Department of Justice announces
Defining Cyber War: The Impact of Insurance on Cyber Norms - RUSI publishes
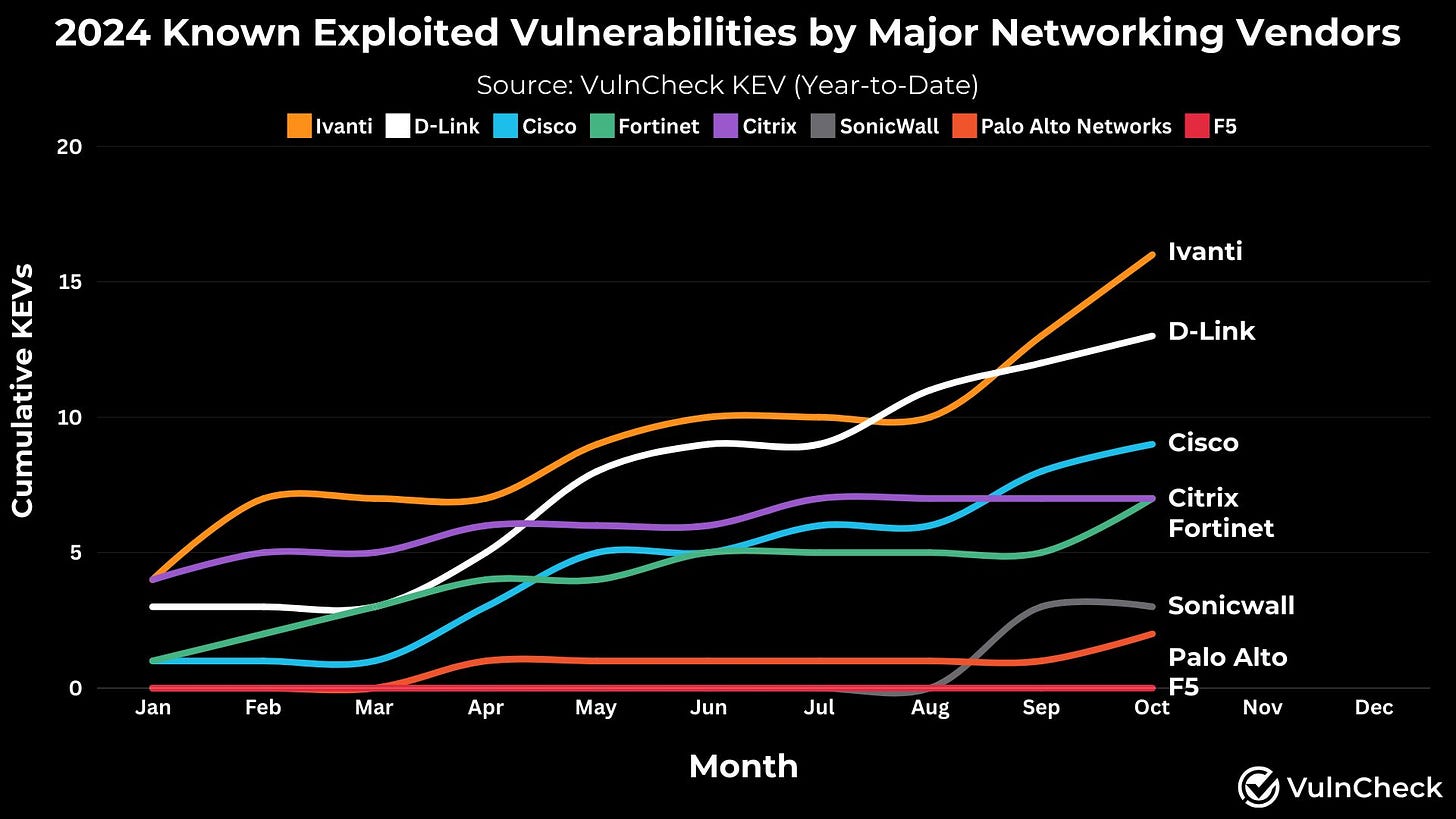
Reflections this week is this graph..
Then building on last weeks reflection on the application of AI to vulnerability discovery clearly being a thing, even if not material, we have this week Methodology for Leveraging LLMs for 0-day discovery (18+ vulns including on Netflix, Hulu, and Salesforce) and From Naptime to Big Sleep: Using Large Language Models To Catch Vulnerabilities In Real-World Code. Both show that we could indeed be experiencing a boiling frog moment..
Think someone else would benefit? Share:
All attribution is by others and not the UK Government unless specifically stated as such, please see the legal text at the end.
Have a lovely Saturday..
Ollie
Cyber threat intelligence
Who is doing what to whom and how allegedly.
Reporting on Russia
Hybrid Russian Espionage and Influence Campaign Aims to Compromise Ukrainian Military Recruits and Deliver Anti-Mobilization Narratives
Google Threat Intelligence Group detail a campaign which they allege is Russia. Notable for using paid promoted posts on Telegram.
UNC5812’s malware delivery operations are conducted both via an actor-controlled Telegram channel
@civildefense_com_uaand website hosted atcivildefense[.]com.ua. The associated website was registered in April 2024, but the Telegram channel was not created until early September 2024, which we judge to be when UNC5812’s campaign became fully operational. To drive potential victims towards these actor-controlled resources, we assess that UNC5812 is likely purchasing promoted posts in legitimate, established Ukrainian-language Telegram channels.
On September 18th 2024, a legitimate channel with over 80,000 subscribers dedicated to missile alerts was observed promoting the "Civil Defense" Telegram channel and website to its subscribers.
An additional Ukrainian-language news channel promoting Civil Defense’s posts as recently as October 8th, indicating the campaign is probably still actively seeking new Ukrainian-language communities for targeted engagement.
Channels where "Civil Defense" posts have been promoted advertise the ability to reach out to their administrations for sponsorship opportunities. We suspect this is the likely vector that UNC5812 is using to approach the respective legitimate channels to increase the operation’s reach.
Beyond Their Intended Scope: Uzing into Russia
Doug Madory details what might be a faux par or might of been something more malicious leading to BGP leaks re-routing traffic to places it should have not gone..
Beginning at 06:25 UTC on September 26, 2024, Uztelecom (AS28910), incumbent of the former Soviet republic of Uzbekistan, began leaking routes from its peers through one of its transit providers, Rostelecom (AS12389), Russia’s state telecom. First reported by our friends over at Qrator, the incident involved the leak of over 3,000 routes lasting about 40 minutes misdirecting traffic from a dozen countries.
Another prefix sucked into the leak (162.158.84.0/24) belonged to Cloudflare.
https://www.kentik.com/blog/beyond-their-intended-scope-uzing-into-russia/
Midnight Blizzard conducts large-scale spear-phishing campaign using RDP files
Microsoft Threat Intelligence further details a campaign which was covered here last week which they allege is Russia. Their reporting gives a sense of the scale of the campaign.
The spear-phishing emails in this campaign were sent to thousands of targets in over 100 organizations and contained a signed Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) configuration file that connected to an actor-controlled server. In some of the lures, the actor attempted to add credibility to their malicious messages by impersonating Microsoft employees. The threat actor also referenced other cloud providers in the phishing lures.
Reporting on China
Chinese threat actor Storm-0940 uses credentials from password spray attacks from a covert network
Microsoft Threat Intelligence details a covert network which appears to be retooling to avoid detection in support of a threat actor they allege is the Chinese state.
Since August 2023, Microsoft has observed intrusion activity targeting and successfully stealing credentials from multiple Microsoft customers that is enabled by highly evasive password spray attacks. Microsoft has linked the source of these password spray attacks to a network of compromised devices we track as CovertNetwork-1658, also known as xlogin and Quad7 (7777).
After successfully gaining access to a vulnerable router, in some instances, the following steps are taken by the threat actor to prepare the router for password spray operations:
Download Telnet binary from a remote File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server
Download xlogin backdoor binary from a remote FTP server
Utilize the downloaded Telnet and xlogin binaries to start an access-controlled command shell on TCP port 7777
Connect and authenticate to the xlogin backdoor listening on TCP port 7777
Download a SOCKS5 server binary to router
Start SOCKS5 server on TCP port 11288
..
Microsoft assesses that CovertNetwork-1658 has not stopped operations as indicated in recent activity but is likely acquiring new infrastructure with modified fingerprints from what has been publicly disclosed.
Pacific Rim: Inside the Counter-Offensive—The TTPs Used to Neutralize China-Based Threats
Sophos detail the timeline in this campaign they attribute to China which I count involved at least five zero-days over five years. Sophos should be applauded for the transparency here.
Throughout the campaigns, the actors became increasingly adept at hiding their activities from immediate discovery by blocking telemetry from being sent from the device to Sophos.
As early as April 2020, the attackers made efforts to sabotage the hotfix mechanism of devices they compromised. Later, they added targeting of the telemetry system of devices to prevent Sophos from getting early warning of their activity.
The actors also discovered and blocked telemetry-gathering on their own test devices after Sophos X-Ops utilized that capability to collect data on exploits while they were being developed.
Additionally, the operational security practices of the exploit developers improved over time. X-Ops saw the trail of data we could follow with open-source intelligence practices shrink considerably from earlier attacks.
https://news.sophos.com/en-us/2024/10/31/pacific-rim-neutralizing-china-based-threat/#conclusions
CloudScout: Evasive Panda scouting cloud services
Anh Ho details a cloud campaign which they allege is Chinese in origination. This is what contemporary threat actor tradecraft looks like in 2024.. Note the regional targeting.
The CloudScout toolset was detected in Taiwan, between 2022 and 2023, in the network of a religious institution and at a government entity.
CloudScout utilizes stolen cookies, provided by MgBot plugins, to access and exfiltrate data stored at various cloud services.
We analyzed three CloudScout modules, which aim to steal data from Google Drive, Gmail, and Outlook. We believe that at least seven additional modules exist.
Hardcoded fields in CloudScout’s web requests for stealing Outlook email messages suggest that the samples involved were crafted to target Taiwanese users.
Each CloudScout module, programmed in C#, is deployed by an MgBot plugin, programmed in C++.
https://www.welivesecurity.com/en/eset-research/cloudscout-evasive-panda-scouting-cloud-services/
LightSpy: Implant for iOS
Threat Fabric show that a threat actor they allege is in China was able to leverage various old-days in their Apple iOS capability. Of note is the sophistication and investment made here.
The threat actor expanded support for the iOS platform, targeting up to version 13.3. They utilized the publicly available Safari exploit CVE-2020-9802 for initial access and CVE-2020-3837 for privilege escalation.
The actor ran multiple campaigns with varying sets of plugins. One particular campaign included plugins that could disrupt the operating system’s stability, with capabilities to freeze the device or even prevent it from booting up.
Finally, an interesting observation was found in the location plugin. The plugin contains a function that recalculates location coordinates according to a system used exclusively in China, strongly indicating that LightSpy operators are likely based in China.
https://www.threatfabric.com/blogs/lightspy-implant-for-ios
Reporting on North Korea
Jumpy Pisces Engages in Play Ransomware
Unit 42 highlights a trend which if their allegation is true that this is the North Korean state should be a warning to all organisations. That is further alleged state involvement in ransomware..
Unit 42 has identified Jumpy Pisces, a North Korean state-sponsored threat group associated with the Reconnaissance General Bureau of the Korean People's Army, as a key player in a recent ransomware incident. Our investigation indicates a likely shift in the group’s tactics. We believe with moderate confidence that Jumpy Pisces, or a faction of the group, is now collaborating with the Play ransomware group (Fiddling Scorpius).
This change marks the first observed instance of the group using existing ransomware infrastructure, potentially acting as an initial access broker (IAB) or an affiliate of the Play ransomware group. This shift in their tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) signals deeper involvement in the broader ransomware threat landscape.
https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/north-korean-threat-group-play-ransomware/
APT Group - Konni Launches New Attacks on South Korea
Threat Book detail what they alleged is a North Korean campaign. The thing of note in this reporting is the use of automation to mass-produce the implant samples.
lFrom mid-April to early July 2024, the Konni group launched attacks on South Korea’s RTP engineering department and personnel involved in tax and North Korea market analysis. The group used malicious samples with Korean themes such as “meeting materials,” “tax evasion,” and “market prices” for the attack;
lThe Konni group used automated tools to mass-produce malicious samples, all of which were generated at the same moment on December 25, 2023, at 11:39:35, but were delivered at different times in 2024. It is speculated that a script tool was used to generate malicious samples based on templates, and the actual number of delivered samples may be large, but only six in-the-wild samples have been discovered so far. This type of sample delivery is still very active, with the latest in-the-wild sample discovered on July 6th;
lThe malicious samples used by the Konni group host the core payload on a compromised website in the execution chain. Although the core payload’s lifespan is extremely short, the malicious samples have been persistent on the infected host, so it cannot be ruled out that the group will reuse the core payload in the future. In addition, the core payload uses AutoIt3 scripts for evasion, which is very effective. Since the core payload was submitted in April 2024, it has not been detected by multiple engines.
https://threatbook.io/blog/id/1094
Reporting on Iran
New Tradecraft of Iranian Cyber Group Aria Sepehr Ayandehsazan aka Emennet Pasargad
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), U.S. Department of Treasury, and Israel National Cyber Directorate warn of new cyber tradecraft of the Iranian cyber group Emennet Pasargad, which has been operating under the company name Aria Sepehr Ayandehsazan (ASA) and is known by the private sector terms Cotton Sandstorm, Marnanbridge, and Haywire Kitten.
FBI also acquired information indicating that since approximately mid-2023, ASA has used several cover hosting providers for infrastructure management and obfuscation. These two providers are ”Server-Speed” (server-speed[.]com) and ”VPS-Agent” (vps-agent[.]net8). Whereas actors typically procure virtual infrastructure from hosting resellers, ASA set up its own resellers and procured server space from Europebased providers, including the Lithuania-based company BAcloud and Stark Industries Solutions/PQ Hosting (located in the United Kingdom and Moldova, respectively). ASA then leverages these cover resellers to provision operational servers to its own cyber actors for malicious cyber activities. FBI has also observed ASA using these cover re-sellers to provide technical support to identified Lebanon-based individuals, including with hosting for HAMAS-affiliated or themed websites.
https://www.ic3.gov/CSA/2024/241030.pdf
Reporting on Other Actors
Inside Intelligence Center: LUNAR SPIDER Enabling Ransomware Attacks on Financial Sector with Brute Ratel C4 and Latrodectus
EclecticIQ Threat Research Team detail a criminal campaign which has it all. Malvertising, use of a commercial implant framework and then the group continuing despite their leader being extradited.
In October 2024, EclecticIQ analysts observed a malvertising campaign employing an obfuscated JavaScript downloader known as Latrodectus to deliver a malicious payload associated with Brute Ratel C4 (BRc4) Analysts assess with high confidence that this campaign is very likely linked to LUNAR SPIDER, a Russian-speaking, financially motivated threat actor group active since at least 2009. LUNAR SPIDER is responsible for developing several high-profile malware families, including IcedID and Latrodectus. IcedID malware is often distributed via malware-as-a-service (MaaS) offerings, enabling affiliates, such as the ALPHA SPIDER/BlackCat ransomware group, to leverage these services for initial compromise.
Despite his extradition to the United States and sentencing to 18 years in prison in 2024, LUNAR SPIDER continues to operate, adapting to leadership changes and law enforcement actions with resilience.
Katz and Mouse Game: MaaS Infostealers Adapt to Patched Chrome Defenses
Jia Yu Chan, Salim Bitam, Daniel Stepanic, Samir Bousseaden, Cyril François and Seth Goodwin detail a campaign which integrated an open source capability which predicted would likely be used to continue their capability.
Latest versions of infostealers implement bypasses around Google’s recent cookie protection feature using Application-Bound Encryption
Techniques include integrating offensive security tool ChromeKatz, leveraging COM to interact with Chrome services and decrypt the app-bound encryption key, and using the remote debugging feature within Chrome
https://www.elastic.co/security-labs/katz-and-mouse-game?utm_source=organic-social
Discovery
How we find and understand the latent compromises within our environments.
Silencing the EDR Silencers
Jonathan Johnson provides a potential detection technique for those who are trying to silence EDR telemetry.
Now, it’s good to note that with Windows AV turned on, Defender does block firewall rules being made against MsMpEng.exe. However, the key point is that this can be done against any EDR, and if they’re not monitoring, the network communications will be cut off. When these firewall rules are created, they’re actually stored in the registry
https://www.huntress.com/blog/silencing-the-edr-silencers
Defence
How we proactively defend our environments.
Enable passkeys in Microsoft Authenticator (preview)
Microsoft inching the word towards passwordless authentication..
steps to enable and enforce use of passkeys in Authenticator for Microsoft Entra ID. First, you update the Authentication methods policy to allow end users to register and sign in with passkeys in Authenticator. Then you can use Conditional Access authentication strengths policies to enforce passkey sign-in when users access a sensitive resource.
Reference Architecture for Confidential Data Processing in a Trusted Execution Environment
Google details their reference architecture..
TEE (Trusted Execution Environment) based solutions offer robust security, privacy and transparency for personal data and computations.
They achieve this through a layered architecture:
Hardware Foundation
Hardware Isolation: The TEE operates within a physically and logically isolated section of the main processor. This creates a cryptographic barrier between the operations within the TEE and potential threats in the broader system.
Operator and Insider Protection: TEE’s isolate processing such that even those with administrative privileges to the main system cannot directly access or manipulate the TEE's contents. This safeguards against both external attacks and misuse by privileged users.
Attestation: The TEE can generate cryptographic proof of its identity and the code it's running. This allows external systems to verify the TEE's identity at runtime. It should be noted that this identity is immutable and tamper proof.
Data Protection
Encryption/Decryption: Data entering or leaving the TEE is encrypted, ensuring its confidentiality outside the protected environment. Within the TEE, the data can be decrypted but is isolated and protected from anyone per the protections outlined above.
Attestation-Based Key Management: Decrypting data relies on attestation and policy evaluation. If the TEE's code or configuration isn't as expected per participant controlled policy, decryption keys are withheld which prevents unauthorized access.
Online Attestation: Attestation offers a critical security layer for clients who need to communicate confidentially with a TEE. By establishing the TEE’s identity via cryptographic attestation, clients can independently validate the code and configuration the TEE runs on. This validation process ensures the TEE is genuine and secure, allowing for trustworthy data exchange.
A deep dive into Linux’s new mseal syscall
Alan Cao details a new Linux mitigation which landed in 6.10 which will have a range of applications..
Memory sealing allows developers to make memory regions immutable from illicit modifications during program runtime. When a virtual memory address (VMA) range is sealed, an attacker with a code execution primitive cannot perform subsequent virtual memory operations to change the VMA’s permissions or modify how it is laid out for their benefit.
https://blog.trailofbits.com/2024/10/25/a-deep-dive-into-linuxs-new-mseal-syscall/
Incident Writeups & Disclosures
How they got in and what they did.
How I Accessed Microsoft’s ServiceNow
Moblig shows how a low privileged user and lack of comprehensive multi-factor authentication can ever impact some of the most resourced firms..
By using the REST API endpoints I was able to determine that the affected user was not high-privileged, but I was able to access two key endpoints:
through which I was able to access:
Thousands of support ticket attachments, which included sensitive data such as internal email requests, support ticket transcripts, incidents & live agent support chats.
Over 250,000+ Employee emails, including personal details such as email addresses
Vulnerability
Our attack surface.
Nothing this week
Offense
Attack capability, techniques and trade-craft.
Chrome App Bound Encryption Decryption
Alex releases a tool which we can expect to be used maliciously is 3..2..
This tool decrypts App-Bound Encrypted (ABE) keys stored in the Local State file of supported Chromium-based browsers, including Google Chrome, Brave, and Microsoft Edge. ABE, introduced in Chrome version 127, binds decryption capabilities to specific applications to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data such as cookies (and potentially passwords and payment information in the future). This tool leverages the internal COM-based IElevator service, unique to each browser, to retrieve and decrypt these keys.
https://github.com/xaitax/Chrome-App-Bound-Encryption-Decryption
Exploitation
What is being exploited..
Increased Fog and Akira Ransomware Activity Linked to SonicWall SSL VPN
Steven Campbell, Akshay Suthar, and Stefan Hostetler show that old-days are being exploited by criminals..
Arctic Wolf has observed an influx of at least 30 Akira and Fog intrusions across a variety of industries since early August, each involving SonicWall SSL VPN early in the cyber kill chain.
Malicious VPN logins originated from IP addresses associated with VPS hosting, providing defenders with a viable mechanism for early detection and prevention.
None of the affected SonicWall devices were patched against CVE-2024-40766, which SonicWall indicates is potentially under active exploitation.
Shared IP infrastructure was seen across several Akira and Fog intrusions.
A short interval between initial SSL VPN account access and ransomware encryption was observed, often within the same day.
CVE-2024-8956, CVE-2024-8957: How to Steal a 0-Day RCE (With a Little Help from an LLM)
Konstantin Lazarev applies LLMs to detect an in the wild exploited zero-day which is sadly as complex as command injection!
ValueHD Corporation (VHD) is a supplier of a white-label AV equipment, including hefty-priced pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) cameras equipped with Network Device Interface (NDI).
Known affected software / hardware: VHD PTZ camera firmware < 6.3.40 used in PTZOptics, Multicam Systems SAS, and SMTAV Corporation devices based on Hisilicon Hi3516A V600 SoC V60, V61, and V63.
https://www.labs.greynoise.io/grimoire/2024-10-31-sift-0-day-rce/
Tooling and Techniques
Low level tooling and techniques for attack and defence researchers…
emulator: 🪅 Windows User Space Emulator
Maurice Heumann shows was a 10x engineer can achieve..
A high-performance Windows process emulator that operates at the syscall level, providing full control over process execution through comprehensive hooking capabilities.
Syscall-Level Emulation: Instead of reimplementing Windows APIs, the emulator operates at the syscall level, allowing it to leverage existing system DLLs
Advanced Memory Management: Supports Windows-specific memory types including reserved, committed, built on top of Unicorn's memory management
Complete PE Loading: Handles executable and DLL loading with proper memory mapping, relocations, and TLS
Exception Handling: Implements Windows structured exception handling (SEH) with proper exception dispatcher and unwinding support
Threading Support: Provides a scheduled (round-robin) threading model
State Management: Supports both full state serialization and fast in-memory snapshots
Debugging Interface: Implements GDB serial protocol for integration with common debugging tools (IDA Pro, GDB, LLDB, VS Code, ...)
https://github.com/momo5502/emulator
Footnotes
Some other small (and not so small) bits and bobs which might be of interest.
Aggregate reporting
Reading between the lies: using leak sites to analyse ransomware trends
EV code signing with .pfx in 2024 - describes the process for kernel signing code certs
Artificial intelligence
Nothing this week
China
Books
Events
Nothing this week
Unless stated otherwise, linked or referenced content does not necessarily represent the views of the NCSC and reference to third parties or content on their websites should not be taken as endorsement of any kind by the NCSC. The NCSC has no control over the content of third party websites and consequently accepts no responsibility for your use of them.
This newsletter is subject to the NCSC website terms and conditions which can be found at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/terms-and-conditions and you can find out more about how will treat your personal information in our privacy notice at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/privacy-statement.