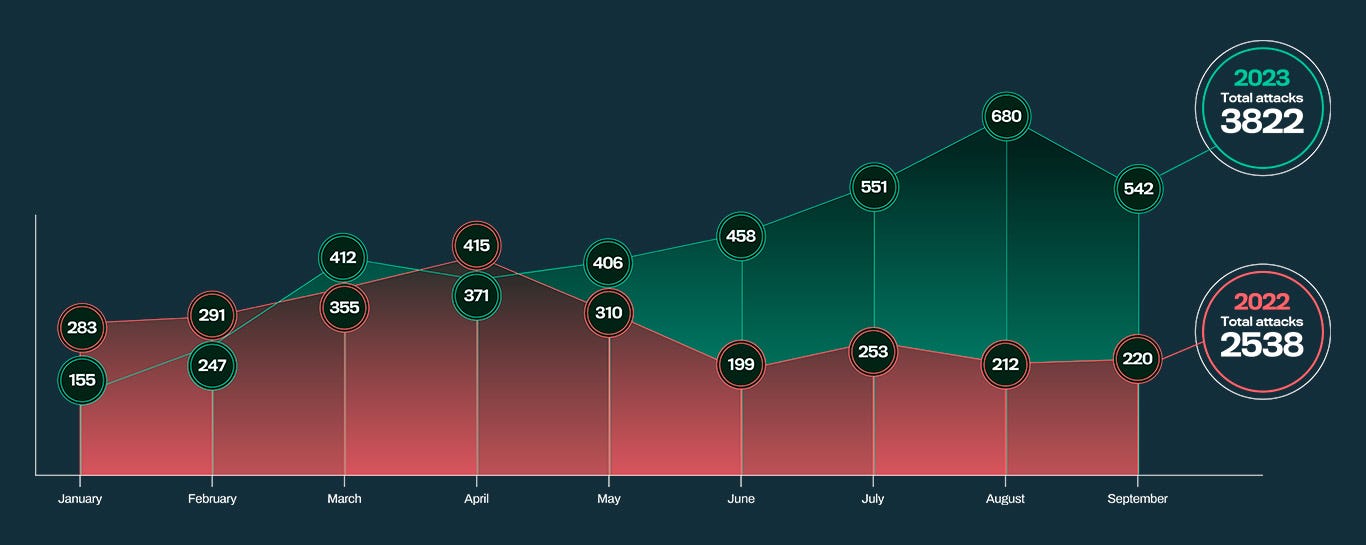
CTO at NCSC Summary: week ending November 26th
Making the UK the most hostile place to target, infiltrate and dwell online...
Welcome to the weekly highlights and analysis of the blueteamsec subreddit (and my wider reading). Not everything makes it in, but the best bits do.
Operationally this week the only thing I would draw your attention to is the alleged financials service focus on the part of a ransomware operation.
In the high-level this week:
UK and Republic of Korea issue warning about DPRK state-linked cyber actors attacking software supply chains - UK’s National Cyber Security Centre and Republic of Korea’s National Intelligence Service warn that such attacks are growing in sophistication and volume
An RFC on IoCs – playing our part in international standards - how we at NCSC contributed to a more secure internet with industry partners - also includes a call to action to get involved by the cyber defence community.
Thanking the vulnerability research community with NCSC UK Challenge Coins - how we are recognising contributions by this valuable community.
2023-2030 Australian Cyber Security Strategy - Each shield provides an additional layer of defence against cyber threats and places Australian citizens and businesses at its core:
Strong businesses and citizens
Safe technology
World-class threat sharing and blocking
Protected critical infrastructure
Sovereign capabilities
Resilient region and global leadership.
DOD Announces Release of 2023 Strategy for Operations in the Information Environment - The 2023 DOD SOIE will improve the Department's ability to plan, resource, and apply informational power toward integrated deterrence, campaigning, and building enduring advantage as described in the 2022 National Defense Strategy. This will enable the DOD to deter challenges to U.S. vital national interests in any arena or domain.
Australian Cyber law shake-up to shield companies - Businesses reporting cyber attacks will be afforded new legal protections, have red tape slashed when liaising with regulators and be required to work with government investigators post-incident to forensically probe significant hacking events.
Lockbit Gang Behind ICBC Attack Hacks Into Chicago Trading Company - The criminal ransomware gang behind the recent attack on the Industrial & Commercial Bank of China Ltd. has claimed responsibility for two more hacks on US financial firms.
Former chief operating officer of a cybersecurity company has pleaded guilty - to hacking two hospitals, part of the Gwinnett Medical Center (GMC), in June 2021 to boost his company's business
NERC’s GridEx VII Tests Rapid and Innovative Response Capabilities - This year’s scenario reflected real-world cyber and physical threats and was designed to stress-test crisis response and recovery plans. Hosted every two years by NERC’s Electricity Information Sharing and Analysis Center (E-ISAC), GridEx is the largest grid security exercise in North America.
Cybersecurity Investment: Spotlight on Vulnerability Management - The new report of the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) confirms investment continues to grow but stresses the importance of vulnerability management.
‘I employ a lot of hackers’: how a stock exchange chief deters cyber-attacks - Six Group counts its profit in millions, but the financial pipework it controls moves billions. “I employ a lot of hackers,” he says, tapping the table sharply. “Sometimes it takes one to know one.”. Six Group has invested in three tranches of cybersecurity, Dijsselhof says: walls to stop people getting in; containment systems for if they do get in; and recovery functions for when someone is “holding hostage” any part of the business.
Barclays flags Treasuries central clearing cybersecurity risks after ICBC hack - A key reform proposed by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission to boost the use of central clearing for U.S. Treasuries could leave the market more exposed to cybersecurity risks, Barclays said, referring to the cyber hack of Industrial and Commercial Bank of China's U.S. broker-dealer last week. Because the Fixed Income Clearing Corporation (FICC), a subsidiary of the Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation (DTCC), is currently the only central clearing platform for repo and Treasuries, activity on the FICC platform will more than double with the proposed reform, Joseph Abate, a strategist at Barclays, said in a note on Tuesday.
Europol sets up OSINT taskforce to support investigations into war crimes committed in Ukraine - This Taskforce aims to help identify suspects and their involvement in war crimes, crimes against humanity or genocide crimes committed in Ukraine through the collection and analysis of open source intelligence (OSINT).
Binance chief Changpeng Zhao pleads guilty to money laundering charges - Binance must now report suspicious activity to federal authorities. - "This will advance our criminal investigations into malicious cyber activity and terrorism fundraising, including the use of cryptocurrency exchanges to support groups such as Hamas,"
Russian and Moldovan National Pleads Guilty to Operating Illegal Botnet Proxy Service that Infected Tens of Thousands of Internet-Connected Devices Around the World - According to online reports, the botnet infrastructure had infected Windows systems then further expanded to infect Linux, Mac, and Android devices, victimizing computers and other electronic devices around the world, including in Asia, Europe, North America and South America.
Is the Fear of Cyberwar Worse Than Cyberwar Itself? - Unrealistic cyberwar expectations could hold the insurance industry back, and that’s the real economic security problem.
FTC Takes Action Against Global Tel*Link Corp. for Failing to Adequately Secure Data, Notify Consumers After Their Personal Data Was Breached - Proposed order to require provider of communication services to prisons and jails to notify users and facilities of any future security breaches
Elon Musk’s X Loses Bid to Scrap FTC Privacy Order - The government said the increased requests for information were because Musk “directed at least five rounds of terminations, layoffs or other reductions in X Corp.’s workforce, which affected the security, governance, risk and compliance team,” according to a legal filing.
Towards a sustainable, multilateral, and universal solution for international data transfers - It encourages a call to action globally to start a constructive conversation and lay foundations for a future global framework for trusted and responsible flows of personal data that benefits everyone.
related Trusted Cross-Border Data Flows: A National Security Priority - To avoid a fragmented world divided by digital barriers, the U.S. government must press ahead to develop a trusted framework for cross-border data flows.
Customary international law, national law, and considering data as objects - from Westpoint - [In cyberspace] the essential elements of customary international law—State practice and opinio juris—remain relatively limited, and their interpretation can sometimes be controversial. Given how frequently cyber operations are unobserved by the public eye, ascertaining State practice and opinio juris can be challenging. Domestic judgements may, therefore, fill the gap when governmental statements are unclear or moreover “give voice” to States that have not made any public statement.
note: there is another legal paper in the footnotes section.
The Mob's IT Department - How two technology consultants helped drug traffickers hack the Port of Antwerp - from 2015 but resurfaced from the below reporting on the operations this month
Inside Job: How a Hacker Helped Cocaine Traffickers Infiltrate Europe’s Biggest Ports - Court records and other documents obtained by reporters reveal how a man in the Netherlands hacked IT systems at the ports of Rotterdam and Antwerp and sold valuable data to aid cocaine traffickers.
NATO and Japan deepen cooperation on emerging security challenges - Deepening NATO-Japan cooperation on cyber defence, cutting edge technologies and defence against hybrid threats
Reporting on/from China
Tianfu Cup 2023: Still a Thing - Tianfu Cup (TFC) 2023, China’s prestigious answer to the annual hacking competition Pwn2Own, took place from October 31 to November 1 in Chengdu, Sichuan Province this year… The TFC 2023 webpage has removed the English-language version… Of particular interest is the new focus on discovering vulnerabilities and exploits in domestic products, not just foreign ones. Among the 26 listed competition targets that participants could try to crack, only five of the targets were foreign products: Chrome browser, Adobe PDF Reader, VMware Workstation, VMware ESXi, and Windows 11.
Artificial intelligence
The Department of State Unveils its First-Ever Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Strategy - Signed by Secretary Blinken, the EAIS establishes a centralized vision for artificial intelligence (AI) innovation, infrastructure, policy, governance, and culture by inaugurating Department-wide guidance for the responsible and ethical design, development, acquisition, and appropriate application of AI.
Nvidia challenger Sapeon unveils new AI chip for data centers - Sapeon Inc., a semiconductor startup backed by South Korea’s second-largest conglomerate SK Group, on Thursday unveiled a new artificial intelligence chip for data centers to join the global race in the sector and challenge the world’s chip design leader Nvidia Corp.
Germany, France and Italy reach agreement on future AI regulation - The three governments are in favour of binding voluntary commitments for both large and small AI providers in the European Union.
Product Liability In The Age Of AI – New Technologies Are Calling For New Concepts - The incorporation of truly strict liability for manufacturers and supplementary liability for commercial users into the defect-based product liability system would create a fair and efficient liability framework
RAI Toolkit: The Responsible Artificial Intelligence (RAI) Toolkit provides a centralized process that identifies, tracks, and improves alignment of AI projects to RAI best practices and the DoD AI Ethical Principles, while capitalizing on opportunities for innovation.
Deepfakes and Human Subjects Protection - How is the Department of Defense beginning to use deepfakes?
A Framework for the Unsupervised and Semi-Supervised Analysis of Visual Frames - A framework to analyze the content of visual material through unsupervised and semi-supervised methods. It details the implementation of a tool from the computer vision field, the Bag of Visual Words (BoVW), for the definition and extraction of “tokens” that allow researchers to build an Image-Visual Word Matrix which emulates the Document-Term matrix in text analysis.
Cyber proliferation
Dual-use and cyber-surveillance: EU policies and current practices
Council for Civil Liberties (ICCL) reports reveal serious security threat to the EU and US - reveals widespread trade in data about sensitive European personnel and leaders that puts them at risk of blackmail, hacking and compromise, and undermines the security of their organisations and institutions.
How a startup hacked the world - investigation found that the company grew from an educational startup to a hack-for-hire powerhouse that stole secrets from executives, politicians, military officials and wealthy elites around the globe. Appin alumni went on to form other firms that are still active.
Hacker-For-Hire Sentenced To 80 Months In Prison For Involvement In Massive Spearphishing Campaign - [He] played a major role in orchestrating and facilitating an international hacking-for-hire spearphishing campaign. The conspiracy targeted individuals and companies in the U.S. and abroad, resulting in the theft of data and netting Azari over $4.8 million in criminal proceeds.
Reflections this week come from SANS CyberThreat 2023 in London. The essence of the talk I gave was we need to force market changes through buying power, not accept security as a premium feature and work together as cyber defenders if we are to achieve our aims. The warm response and resulting discussion has provided a resulted in a glow this week.. also thanks for all the ❤️ that this ask got..
Enjoying this? Don’t get via e-mail? Subscribe:
Think someone else would benefit? Share:
All attribution is by others and not the UK Government, please see the legal text at the end.
Have a lovely Thursday
Ollie
Cyber threat intelligence
Who is doing what to whom and how.
Reporting on Russia
Malware Spotlight - Into the Trash: Analyzing LitterDrifter
A USB worm which appears to have spread relatively far. If it was intended I doubt we will ever know.
Gamaredon continues to focus on wide variety Ukrainian targets, but due to the nature of the USB worm, we see indications of possible infection in various countries like USA, Vietnam, Chile, Poland and Germany. In addition, we’ve observed evidence of infections in Hong Kong. All this might indicate that much like other USB worms, LitterDrifter have spread beyond its intended targets.
The group recently started deploying LitterDrifter, a worm written in VBS, designed to propagate through removable USB drives and secure a C2 channel.
Gamaredon’s infrastructure remains extremely flexible and volatile, while at the same time maintaining previously reported characteristics and patterns.
https://research.checkpoint.com/2023/malware-spotlight-into-the-trash-analyzing-litterdrifter/
Reports of APT29 attacks against Embassies using CVE-2023-38831
There has been prior reporting on this campaign. Now more details from the Ukrainian government have emerged. Initial access tradecraft is defendable against.
The attack methodology entailed the use of phishing emails equipped with enticing lures, portraying BMW car sales, which is a tactic previously employed by APT29 in attacks on embassies in Kyiv. This campaign, consisting of over 200 targeted email addresses, accentuates the evolving nature of cyber threats in the international arena.
APT29's persistence in using the BMW car for sale theme as a lure in their phishing attacks has taken on a new dimension with the deployment of a thematically named RAR archive, "DIPLOMATIC-CAR-FOR-SALE-BMW.rar." This archive contains a recently disclosed and exploitable vulnerability, CVE-2023-38831. This vulnerability, which came to light in April 2023, is rooted in the mishandling of ZIP archives that seemingly contain innocuous files, like standard .PDF documents, and folders sharing identical names.
Discovery of NTC Vulkan Infrastructure
Matt Lembright highlights some potential linkages between information in the leaks and websites they have attributed to the company online. A cover of cyber defence operations being used for offensive capability it would appear.
After discovering these NTC Vulkan hosts, [Our] researchers enumerated all NTC Vulkan certificates, both current and expired.
[We] found raccoonsecurity[.]ru within the CN of the certificate subject and the SANs.
While these services are branded in a defensive manner on the website, their utility matches leaked NTC Vulkan contract initiatives. This includes Krystal-2B, a training environment for attacking operational technology, which could be enabled by conducting and learning from the services offered above. This also includes Scan-V which aimed to identify vulnerabilities on devices identified globally, coinciding with the verbiage above of “identify implementation errors and vulnerabilities in critical products and systems.”
https://censys.com/discovery-of-ntc-vulkan-infrastructure/
Reporting on China
Stately Taurus Targets the Philippines As Tensions Flare in the South Pacific
Note the targeting of a regional cyber security product in this reporting.
[We] observed three Stately Taurus campaigns during the month of August. These campaigns are assessed to have targeted entities in the South Pacific including the Philippines government. The campaigns leveraged legitimate software including Solid PDF Creator and SmadavProtect (an Indonesian-based antivirus solution) to sideload malicious files. Threat authors also creatively configured the malware to impersonate legitimate Microsoft traffic for command and control (C2) connections.
https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/stately-taurus-targets-philippines-government-cyberespionage/
Reporting on North Korea
Diamond Sleet supply chain compromise distributes a modified CyberLink installer
Another alleged North Korean supply chain attack which is reported as getting some traction, but apparently caught early.
[We] uncovered a supply chain attack by the North Korea-based threat actor Diamond Sleet (ZINC) involving a malicious variant of an application developed by CyberLink Corp., a software company that develops multimedia software products. This malicious file is a legitimate CyberLink application installer that has been modified to include malicious code that downloads, decrypts, and loads a second-stage payload. The file, which was signed using a valid certificate issued to CyberLink Corp., is hosted on legitimate update infrastructure owned by CyberLink and includes checks to limit the time window for execution and evade detection by security products. Thus far, the malicious activity has impacted over 100 devices in multiple countries, including Japan, Taiwan, Canada, and the United States.
Hacking Employers and Seeking Employment: Two Job-Related Campaigns Bear Hallmarks of North Korean Threat Actors
Reporting which alludes to a modus operandi previously attributed by others to North Korea that is still in use but in an evolved form. Note the heavy use of social engineering and rapport building.
[We] discovered two separate campaigns targeting job-seeking activities linked to state-sponsored threat actors associated with the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK), commonly known as North Korea.
We call the first campaign “Contagious Interview,” where threat actors pose as employers (often anonymously or with vague identities) to lure software developers into installing malware through the interview process. This malware creates the potential for various types of theft. We attribute with moderate confidence that Contagious Interview is run by a North Korea state-sponsored threat actor.
We call the second campaign “Wagemole,” where threat actors seek unauthorized employment with organizations based in the US and other parts of the world, with potential for both financial gain and espionage. We attribute with high confidence that Wagemole is a North Korea state-sponsored threat. Activity from both campaigns remains an ongoing active threat.
https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/two-campaigns-by-north-korea-bad-actors-target-job-hunters/
Korean National Cyber Security Center has detected influence operations exploiting “disguised websites"
Now this is some interesting reporting where PR like newswires as being used for an alleged influence operation.
It is unclear whether the Chinese companies created these websites as a form of fraud to deceive Chinese corporate and institutional clients who purchase press release distribution services, or for other purposes, but it cannot be ruled out that if malicious actors exploit these websites, they may intentionally create and distribute content with a specific purpose as if it were a legitimate article from a Korean media outlet and use it to shape public opinion in Korea.
As of now, three Chinese promotional agencies and newswire service operators are engaged in the continuous creation and operation of websites disguised as Korean media, namely Haimai, Haixun, and World Newswire.
Reporting on Iran
Nothing this week
Reporting on Other Actors
HrServ web shell analysis
The reporting hints it might be Chinese, but that link is weak. Nevertheless a web shell to go looking for. Also interesting they were not able to attribute given their holdings.
The TTPs analyzed in this investigation are not associated with any known threat actors we are tracking, but there are a few things that we observed:
the GET parameters used in the hrserv.dll file, which is used to mimic Google services, include “hl”. This specifies the host language of the user interface. Although this parameter has no functionality within the attack vector, the assigned value “en-TW” specifies that the Google search interface should be displayed in English, but the search results should be displayed in Traditional Chinese:
https://securelist.com/hrserv-apt-web-shell/111119/
The ALPHV/BlackCat Ransomware Gang is Using Google Ads to Conduct Operations on Organisations and Public Entities
More malvertising use by the criminal eco-system. This technique continues to gain traction. It will be interesting to see how the platforms respond - especially noting some use stems from breached advertiser accounts.
This affiliate is taking out Google ads promoting popular software, such as Advanced IP Scanner, Slack, WinSCP and Cisco AnyConnect, to lure business professionals to attacker-controlled websites. Thinking they are downloading legitimate software, the business professionals are actually downloading the Nitrogen malware. Nitrogen is initial-access malware that leverages Python libraries for stealth. This foothold provides intruders with an initial entry into the target organization’s IT environment. Once the hackers have that initial foothold, they can then infect the target with the malware of their choosing. In the case with this attack campaign, the target victims are being infected with the ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware
Hunting a Hack-For-Hire Group
From this reporting we get a sense of the scale of this hack-for-hire operation, which one might describe as material. I somehow doubt this be the last of these types of outfits that we see.
[We] garnered new intelligence pertaining to the activities of the Appin Security Group, a renowned entity in the realm of hack-for-hire services.
Our comprehensive analysis has unearthed information on numerous global cyber intrusions, encompassing instances of espionage, surveillance, and disruptive actions. Furthermore, our findings establish a high level of confidence in attributing intrusions in various countries, including Norway, Pakistan, China, and India, among others.
The landscape of hack-for-hire enterprises has undergone a transformation, diversifying the array of services available to both private enterprises and government entities. Notwithstanding previous public disclosures, the internal methodologies governing the creation of malware, exploits, and network infrastructure have persisted in obscurity. Our investigative efforts contribute crucial insights, shedding light on the intricate processes underlying these operations.
https://www.sentinelone.com/labs/elephant-hunting-inside-an-indian-hack-for-hire-group/
CISA Advisory AA23-320A: Scattered Spider
Formal US Government reporting which confirms what industry has been saying around the use of these blended techniques by criminal threat actors. A great example socio-technical challenges we face with regards to cyber security.
Scattered Spider (also known as Starfraud, UNC3944, Scatter Swine, and Muddled Libra) engages in data extortion and several other criminal activities. Scattered Spider threat actors are considered experts in social engineering and use multiple social engineering techniques, especially phishing, push bombing, and subscriber identity module (SIM) swap attacks, to obtain credentials, install remote access tools, and/or bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA).
https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/cybersecurity-advisories/aa23-320a
2023’s ransomware rookies are a remix of Conti and other classics
Adam Pilkey shares data that shows a trend that is going in the wrong direction. Also of note is the almost teenage like relationships that ebb and flow in the cyber criminal eco-system.
Old groups, however, are still very significant in multiple ways. For starters, most groups don’t last that long. Only 6 of the 60 tracked in the analysis were active every month. These groups start, stop, fold, rebrand themselves, etc. Only a few seem to have successful, sustainable operations.
Understanding the Phobos affiliate structure and activity
Guilherme Venere provides some deep insight around this activity. Reading between the lines it is almost as if there is a getting started manual which is leading to tradecraft overlap. Noting we have seen such manuals before in other groups..
[We] recently identified the most prolific Phobos variants, common affiliate tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs), and characteristics of the Phobos affiliate structure, based on observed Phobos activity and analysis of over 1,000 Phobos samples from VirusTotal dating back to 2019.
We assess with moderate confidence Eking, Eight, Elbie, Devos and Faust are the most common Phobos variants, as they appeared most frequently across the samples we analyzed.
The affiliates use similar TTPs to deploy Phobos and commonly target high-value servers, likely to pressure victims into paying the ransom.
We assess with moderate confidence that the Phobos ransomware is closely managed by a central authority, as there is only one private key capable of decryption for all campaigns we observed.
There are also indications that Phobos may be sold as a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS). We discovered hundreds of contact emails and IDs associated with Phobos campaigns, indicating the malware has a dispersed affiliate base, which is commonly seen among RaaS affiliates.
https://blog.talosintelligence.com/understanding-the-phobos-affiliate-structure/
Discovery
How we find and understand the latent compromises within our environments.
The Spelling Police: Searching for Malicious HTTP Servers by Identifying Typos in HTTP Responses
Margit Hazenbroek brings some science to HTTP header analysis and that spelling mistakes alone are not sufficient to identify the bad.
Our study reveals that typos in HTTP responses are not as rare as one might assume. Despite the crucial role that appropriate implementation of HTTP response headers plays in the security and safety of websites and web services, our research suggests that textual errors in HTTP responses are surprisingly widespread, even in the outputs of servers from legitimate organizations. Although these deviations from standard naming conventions could potentially indicate an attempt to disguise a malicious server, they do not always signify nefarious activity. The internet is simply too messy.
Our research concludes that typos alone are insufficient to identify malicious servers. Nevertheless, they retain potential as part of a broader detection framework. We propose advancing this research by combining the presence of typos with additional metrics. One approach involves establishing a baseline of common anomalous HTTP responses, and then flagging HTTP responses with new typos as they emerge.
Defence
How we proactively defend our environments.
ETW internals for security research and forensics
Yarden Shafir goes deep on ETW which will be of use to both red and blue.
In this deep dive, we’re not just discussing ETW’s functionalities; we’re exploring how ETW works internally so you can conduct novel research or forensic analysis on a system. Security researchers and malware authors already target ETW.
https://blog.trailofbits.com/2023/11/22/etw-internals-for-security-research-and-forensics/
Configure the Attack Surface Reduction rules
Does what it says on the tin..
This tool will help you configure the Attack Surface Reduction rules in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
amides: An Adaptive Misuse Detection System
Applied use of machine learning here which is of some value.
The Adaptive Misuse Detection System (AMIDES) extends conventional rule matching of SIEM systems by applying machine learning components that aim to detect attacks evading existing SIEM rules as well as otherwise undetected attack variants. It learns from SIEM rules and historical benign events and can thus estimate which SIEM rule was tried to be evaded.
https://github.com/fkie-cad/amides
HavocExploit
A counter capability which is illegal to use for most.
A remote unauthenticated DOS POC exploit that targets the authentication implementation of Havoc
https://github.com/syncwithali/HavocExploit
Incident Writeups
How they got in and what they did.
None this week
Vulnerability
Our attack surface.
Touch of Pwn
Headache..
[We evaluated] the security of the top three fingerprint sensors embedded in laptops and used for Windows Hello fingerprint authentication - revealed multiple vulnerabilities that our team successfully exploited, allowing us to completely bypass Windows Hello authentication on all three laptops..
https://blackwinghq.com/blog/posts/a-touch-of-pwn-part-i/
The Ticking Supply Chain Attack Bomb of Exposed Kubernetes Secrets
Yakir Kadkoda and Assaf Morag show that there are many low hanging fruits which remain that could have high impact. Expect threat actors to explore this and similar..
We conducted a search using GitHub's API to retrieve all entries containing .dockerconfigjson and .dockercfg. The initial query yielded over 8,000 results, prompting us to refine our search to include only those records that contained user and password values encoded in base64. This refinement led us to 438 records that potentially held valid credentials for registries. Out of these, 203 records, approximately 46%, contained valid credentials that provided access to the respective registries.
https://blog.aquasec.com/the-ticking-supply-chain-attack-bomb-of-exposed-kubernetes-secrets
Passive SSH Key Compromise via Lattices
Keegan Ryan, Kaiwen He, George Arnold Sullivan and Nadia Heninger highlight the real-world implications of poorly implemented cryptography. An optimisation here the implications of which we will need to see.
We demonstrate that a passive network attacker can opportunistically obtain private RSA host keys from an SSH server that experiences a naturally arising fault during signature computation. In prior work, this was not believed to be possible for the SSH protocol because the signature included information like the shared DiffieHellman secret that would not be available to a passive network observer. We show that for the signature parameters commonly in use for SSH, there is an efficient lattice attack to recover the private key in case of a signature fault. We provide a security analysis of the SSH, IKEv1, and IKEv2 protocols in this scenario, and use our attack to discover hundreds of compromised keys in the wild from several independently vulnerable implementation
https://eprint.iacr.org/2023/1711.pdf
FortiSIEM - OS command injection in Report Server
Patch..
An improper neutralization of special elements used in an OS Command vulnerability [CWE-78] in FortiSIEM report server may allow a remote unauthenticated attacker to execute unauthorized commands via crafted API requests.
https://www.fortiguard.com/psirt/FG-IR-23-135
DIALStranger: details about DIAL protocol vulnerabilities
Interesting due to the time period needed to get the patches deployed. Likely also a long tail of vulnerable devices out in the wild and probably some of which are really hard or cost prohibitive to replace (think big advertising screens).
Discovery and Launch (DIAL) is a protocol co-developed by Netflix and YouTube with help from Sony and Samsung. It is used for videos to be played on TVs and other devices easily.
This is a research from 2019. I found protocol doesn't cover some basic security features and most of TV vendors didnt implement protocol correctly. Hackers can play any video on the TVs with or without user interaction.
Because of nature of protocol vulnerabilities - we saw for CallStranger CVE-2020-12695 - it takes forever to patch all the systems. I think waiting 4 years is enough for this vulnerability
https://github.com/yunuscadirci/DIALStranger
Offense
Attack capability, techniques and trade-craft.
.NetConfigLoader: .net config loader
Pain for blueteams, but something to go hunting for.
List of .Net application signed by Microsoft that can be used to load a dll via a .config file. Ideal for EDR/AV evasion and execution policy bypass
https://github.com/Mr-Un1k0d3r/.NetConfigLoader
CoSetProxyBlanket: to call dump function in SentinelAgent.exe to dump a PID to disk
Round 1, expect some mitigations - requires local administrator.
gist.github.com/adamsvoboda/8e248c6b7fb812af5d04daba141c867e
DumpKernel-S1.ps1: Dumps the Kernel via SentinelOne
Round 2..
gist.github.com/adamsvoboda/8f29e09d74b73e1dec3f9049c4358e80
Exploitation
What is being exploited.
Zimbra 0-day used to target international government organizations
Clement Lecigne and Maddie Stone detail the volume of variance in actors exploiting this vulnerability.
In June 2023, [we] discovered an in-the-wild 0-day exploit targeting Zimbra Collaboration, an email server many organizations use to host their email. Since discovering the 0-day, now patched as CVE-2023-37580, [we] observed four different groups exploiting the same bug to steal email data, user credentials, and authentication tokens. Most of this activity occurred after the initial fix became public on Github. To ensure protection against these types of exploits, [we] urge users and organizations to keep software fully up-to-date and apply security updates as soon as they become available.
LockBit 3.0 Ransomware Affiliates Exploit CVE 2023-4966 Citrix Bleed Vulnerability
CISA et al warning the world..
Citrix Bleed, known to be leveraged by LockBit 3.0 affiliates, allows threat actors to bypass password requirements and multifactor authentication (MFA), leading to successful session hijacking of legitimate user sessions on Citrix NetScaler web application delivery control (ADC) and Gateway appliances. Through the takeover of legitimate user sessions, malicious actors acquire elevated permissions to harvest credentials, move laterally, and access data and resources.
https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/cybersecurity-advisories/aa23-325a
Tooling and Techniques
Low level tooling and techniques for attack and defence researchers…
Chromium VRP Money Tree
Which bits of source have had the most cash paid out on them for vulnerabilities.
https://lyra.horse/misc/chromium_vrp_tree.html#
GWP-ASan: Sampling-Based Detection of Memory-Safety Bugs in Production
Kostya Serebryany, Chris Kennelly, Mitch Phillips, Matt Denton, Marco Elver, Alexander Potapenko, Matt Morehouse, Vlad Tsyrklevich, Christian Holler, Julian Lettner, David Kilzer and Lander Brandt show how many people it takes to add an if and come up with likely the best abstract ever.
Despite the recent advances in pre-production bug detection, heap-use-after-free and heap-buffer-overflow bugs remain the primary problem for security, reliability, and developer productivity for applications written in C or C++, across all major software ecosystems. Memory-safe languages solve this problem when they are used, but the existing code bases consisting of billions of lines of C and C++ continue to grow, and we need additional bug detection mechanisms.
This paper describes a family of tools that detect these two classes of memory-safety bugs, while running in production, at near-zero overhead. These tools combine page-granular guarded allocation and low-rate sampling. In other words, we added an "if" statement to a 36-year-old idea and made it work at scale.
We describe the basic algorithm, several of its variants and implementations, and the results of multi-year deployments across mobile, desktop, and server applications.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.09394
entdb: Host your own macOS Entitlement Database
For the researchers out there looking to understand attack surface.
Self-hosted entitlement database, on macOS only. No 3rd-party dependency except
codesignfrom macOS.
cli.pyto create database. Seequery.pyfor making queries.
https://github.com/chichou/entdb
Footnotes
Some other small (and not so small) bits and bobs which might be of interest.
Aggregate reporting
Key Takeaways from the 2023 Kubernetes Security Report - based on scans of over 200,000 cloud accounts
The song remains the same: The 2023 Active Adversary Report for Security Practitioners
Ransomware Dwell Time Hits Low of 24 Hours - The Threat Report shows ransomware median dwell time has dropped from 4.5 days to less than 24 hours in a year
New cyber security awareness video from Institute of Cyber Security for Society (iCSS) - CSS is releasing a new animated video “Why does cyber security matter for everyone?” for raising awareness of all on cyber security risks we are all facing in today’s highly digitalised and networked world. The video is part of an iCSS-led cyber security awareness campaign for all staff and students of the University of Kent.
Unpacking due diligence in cyberspace - published November 3 - There is controversy as to whether due diligence in cyberspace is required as the result of a general rule in international law – namely, that States must not allow their territory to be used for acts contrary to the rights of other States – or because of a voluntary norm of responsible State behaviour, i.e. something that is expected but not legally required. This paper analyses the legal status and content of due diligence in the cyber context, including with reference to position statements published by a growing number of States on these issues.
Artificial intelligence
Adversarial Attacks on LLMs - a walk through
Deep Neural Networks Can Learn Generalizable Same-Different Visual Relations - potential deepfake / unauthenticate behaviour applications
Comparing Humans, GPT-4, and GPT-4V On Abstraction and Reasoning Tasks
Beyond neural scaling laws: beating power law scaling via data pruning
Books
None this week
Events
Program Agenda: 2023 FIRST Cyber Threat Intelligence Conference - TLP Clear presentations available now
Velociraptor DEATHcon 2023 - Watch the video and / or walk through the lab descriptions
Billington CyberSecurity - videos, this is session 5 including Chris Inglis
Security for Space Systems Conference, May 27th/28th in the Netherlands - call for papers
Unless stated otherwise, linked or referenced content does not necessarily represent the views of the NCSC and reference to third parties or content on their websites should not be taken as endorsement of any kind by the NCSC. The NCSC has no control over the content of third party websites and consequently accepts no responsibility for your use of them.
This newsletter is subject to the NCSC website terms and conditions which can be found at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/terms-and-conditions and you can find out more about how will treat your personal information in our privacy notice at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/privacy-statement.