CTO at NCSC Summary: week ending November 12th
Post Quantum Crypt: start your engines.. especially for the long tail of those complex systems..
Welcome to the weekly highlights and analysis of the blueteamsec subreddit (and my wider reading). Not everything makes it in, but the best bits do.
Operationally this week nothing overly of note, although year-on-year you can see capability available to all appears to be getting more sophisticated.
In the high-level this week:
The UK’s National Cyber Security Centre has released its Next steps in migrating to post-quantum cryptography - Many legacy and sector-specific protocols, including those used in critical national infrastructure (CNI) will also need to transition to PQC. Additional challenges in these use cases include having to run cryptography on devices with constrained resources, and on legacy systems that are hard to upgrade.
UK and Singapore secure agreement against ransomware payments - Members of the CRI have signed a joint statement pledging that central government funds should not be used to pay ransoms to cyber criminals.
Cybersecurity in 2023 and the challenges ahead - I wrote something on my thoughts for the new publication BindingHook from the European Cyber Conflict Research Initiative (ECCRI).
Four Arrested and Multiple Russian Nationals Charged in Connection with Two Schemes to Evade Sanctions and Send U.S. Technology Used in Weapons Systems to Russia - Over $7 Million Worth of Semiconductors, Integrated Circuits, and Other Electronics Unlawfully Exported to Russian End-Users Affiliated with the Russian Military
US, South Korea, Japan to launch consultative group on North's cyber threats - Anne Neuberger, U.S. deputy national security adviser for cyber and emerging technologies, held talks with her South Korean and Japanese counterparts in Washington last week. They agreed to hold quarterly meetings under the new framework, the presidential office said.
FBI Warned Of Threats By Iranian Cyber Group, Offers $10mn Reward - The FBI has warned that the Iranian cyber group Emennet Pasargad is conducting hack-and-leak operations involving a combination of hacking and theft of data.
Treasury Designates Virtual Currency Money Launderer for Russian Elites and Cybercriminals - Zhdanova also provided services to individuals connected with the Russian Ryuk ransomware group. In 2021, Zhdanova laundered over $2.3 million of suspected victim payments on behalf of a Ryuk ransomware affiliate.
Two Russian Nationals Charged For Conspiring To Hack The Taxi Dispatch System At JFK Airport - They used their unauthorized access to alter the Dispatch System and move specific taxis to the front of the line, thereby allowing drivers of those taxis to skip other taxi drivers waiting in the line. ABAYEV and LEYMAN charged taxi drivers $10 each time they were advanced to the front of the line and transferred part of their profits to SHIPULIN and DEREBENETC.
'Active' cyber insurers to combat scourge of ransomware - Based in claims so far, global head of cyber at Allianz Commercial Scott Sayce said he expected a 25 per cent rise in the number of claims in 2023.
Taiwan faces highest number of cyberattacks globally: Cybersecurity report - In September, Taiwan's Minister of Economic Affairs Wang Mei-hua (王美花) and United States National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Director Laurie E. Locascio enhanced bilateral cybersecurity cooperation. The two agreed to establish a joint cybersecurity supply chain under the U.S.-Taiwan Technology Trade and Investment Collaboration framework.
Governor Hochul Announces Updates To New York’s Nation-leading Cybersecurity Regulations As Part Of Sweeping Effort To Protect Businesses And Consumers From Cyber Threats - The new rules strengthen the Department of Financial Services’ (DFS) risk-based approach to ensure that cybersecurity is integrated into regulated entities’ business planning, decision-making, and ongoing risk management
Singapore to table new law reviewing ‘significant investments’ in critical entities - These requirements will apply to specified entities, with only “a handful” expected to be so designated under the law, said Trade and Industry Minister Gan Kim Yong.
Announcing Microsoft Secure Future Initiative to advance security engineering - post the incident recommitment to cyber resilience, reminiscent of the original Bill Gates memo in 2002
Answering the Call to Build the Nation’s Cyber Workforce (USA) - In October alone, some of the nation’s largest companies have stepped up to accelerate and expand training and apprenticeship programs, committing to reach up to 225,000 people, and have built cybersecurity competitions to challenge new expertise and bring talent into leading cybersecurity companies.
Reporting on China
China critic says he's the target of deepfake 'spamouflage' attack by Beijing - The video is a deepfake creation according to Liu and an Australian security think-tank that analyzed it, and is part of an extensive "spamouflage" campaign that Global Affairs Canada believes is connected to China.
Huawei and Tencent spearhead China's hold on cybersecurity patents - As of August, IBM led the rankings with 6,363 patents. Huawei Technologies came in second with 5,735 patents and Tencent Holdings placed third with 4,803.
China aims to launch nearly 13,000 satellites to ‘suppress’ Elon Musk’s Starlink, researchers say - The project, code-named ‘GW’, would provide internet services and could be used to spy on rival networks and carry out anti-Starlink missions, paper says
Artificial intelligence
UK Prime Minister's speech on AI: 26 October 2023 - Now, doing the right thing, not the easy thing, means being honest with people about the risks from these technologies.
Bletchley Declaration - Leading AI nations have reached a world-first agreement at Bletchley Park establishing a shared understanding of the opportunities and risks posed by frontier AI.
Remarks of EU President von der Leyen at the Bletchley Park AI Safety Summit
German Giants Pour Over $500 Million Into AI Startup Aleph Alpha - A consortium of German industrial giants and financial investors have committed more than $500 million to Aleph Alpha GmbH, an artificial intelligence startup trying to build a European rival to the large language models created OpenAI and Google.
Human Subjects Protection in the Era of Deepfakes -With respect to trust, deepfake technology, unlike other AI, is uniquely concerning from a privacy and ethical standpoint due to the volume and type of biometric data needed.
Time to Act: Building the Technical and Institutional Foundations for AI Assurance - Assurance for AI systems presents unique challenges. While traditional software allows engineers to develop mental models of its behavior, guiding testing and evaluation procedures, AI often includes corner cases, where a system behaves in an unexpected way when presented with new situations, which can be difficult to predict and incorporate into a testing regime - as anyone who works in vulnerability research sees it, software also has corner cases.
Hacking Google Bard - From Prompt Injection to Data Exfiltration - Indirect Prompt Injection attacks via Emails or Google Docs are interesting threats, because these can be delivered to users without their consent.
Cyber proliferation
Podcast: Cyber mercenaries and the global surveillance-for-hire market
Spyware could destroy our democracies - MEP Sophie in t’ Veld, who led the European Parliament’s investigations into spyware, sounds the alarm on their dangers
“Predator Files”: the text messages that embarrass the Greek Prime Minister’s right-hand man - French language reporting - Mediapart and its partners reveal that the telephone number of Grigoris Dimitriadis, nephew and former secretary general of Prime Minister Kyriákos Mitsotákis, was used to attack the phones of eleven eminent Greek personalities with the Predator spyware. The person concerned denies any involvement.
Request for Information on Open-Source Software Security: Areas of Long-Term Focus and Prioritization - The Office of the National Cyber Director (ONCD), the Cybersecurity Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), the National Science Foundation (NSF), the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), and the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) invite public comments on areas of long-term focus and prioritization on open-source software security - comments closed in October, but to be aware more than anything.
Brief reflection this week is anyone who yearns for national impact on cyber resilience should seriously consider working for their Government. The opportunity to have meaningful impact is very real as a policyist, scientist or technologist and especially a cyber policyist, scientist or technologist..
On the interesting job/role front (thanks to those sending me these):
Spring 2024 Young Global Professionals Program - Cyber Statecraft Initiative, Atlantic Council
Enjoying this? Don’t get via e-mail? Subscribe:
Think someone else would benefit? Share:
All attribution is by others and not the UK Government, please see the legal text at the end.
Have a lovely Thursday
Ollie
Cyber threat intelligence
Who is doing what to whom and how.
Reporting on Russia
The results of a complex operation carried out by the SIS (Moldova), in the context of hybrid warfare
Reporting from the Romanian government’s intelligence services. No technical details but the breadth is of note.
The conclusions of the information presented indicate that the Republic of Moldova is subject to hybrid attacks of an unprecedented scale. Manipulation, propaganda and disinformation, attempts to change the government through violence, cyber attacks, false bomb alarms, attempts to enter the country of foreign citizens with military training to carry out subversive operations, massive financing of an organized criminal group that corrupts voters, deputies, political leaders and candidates, all to compromise the entire system of democratic governance of the country to pass it into the sphere of influence of the Russian Federation.
Reporting on China
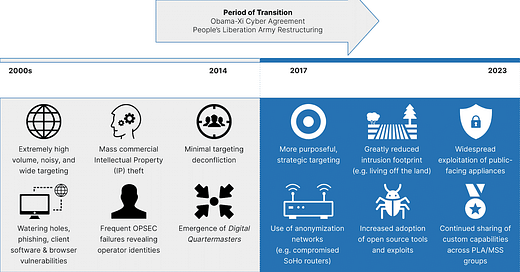
Charting China’s Climb as a Leading Global Cyber Power
Third party reporting which summarises the evolution based on commercial assessment. It highlights the growing sophistication.
Over the past five years, Chinese state-sponsored cyber operations have evolved into a more mature and coordinated threat, focusing on exploiting both known and zero-day vulnerabilities in public-facing security and network appliances. They have also placed a strong emphasis on operational security and anonymity, making it harder to detect their activities. These changes have been influenced by both internal factors like military restructuring and changes in domestic regulations, as well as external factors including reporting by Western governments and the cybersecurity community. This evolution has made it more challenging for organizations, governments, and the cybersecurity community to defend against these threats
https://www.recordedfuture.com/charting-chinas-climb-leading-global-cyber-power
Chinese APT Targeting Cambodian Government
Reporting on alleged enduring regional targeting. Of note is the operational security trying to avoid interaction from certain sources.
[We] identified malicious Chinese APT infrastructure masquerading as cloud backup services. Monitoring telemetry associated with two prominent Chinese APT groups, we observed network connections predominately originating from the country of Cambodia, including inbound connections originating from at least 24 Cambodian government organizations.
We assess with high confidence that these Cambodian government entities were targeted and remain compromised by Chinese APT actors. This assessment is due to the malicious nature and ownership of the infrastructure combined with persistent connections over a period of several months.
..
We have also observed IP filtering on this infrastructure. Specifically, we have observed the blocking of connections from the following:
Known Palo Alto Networks IP ranges
Some VPS and cloud hosting providers
IP ranges from a number of Big Tech and other cybersecurity companies
https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/chinese-apt-linked-to-cambodia-government-attacks/
Reporting on North Korea
North Korea's evolving cyber attack status and response
Reporting out of a South Korean think tank.
Until the second quarter of this year, the number of cryptocurrency attacks worldwide increased significantly compared to the same period last year.
It is known that North Korea accounts for close to 30% of this.
However, the amount of cryptocurrency earned by North Korea through cyber hacking by the third quarter of 2023 is about $340 million, a decrease compared to 2022, when it recorded the highest amount ever.
It is being counted. The decline in income through North Korea's cryptocurrency hacking led to a sharp decline in cryptocurrency prices,
It is believed that this is due to strengthening monitoring and sanctions in each country and difficulties in laundering stolen money.
However, despite these difficulties, North Korea responded to the crisis through various methods.
First, in addition to direct attacks on cryptocurrency, ransomware second, through Russian cryptocurrency exchanges, third, strengthen cooperation between existing hacking groups to track and trace stolen funds. Trying to get away In response to North Korea's evolving cyber attacks, South Korea the government enacts laws, imposes sanctions on domestic companies for violating security, imposes independent sanctions against North Korea in the cyber sector, and implements cyber sanctions against North Korea.
We are implementing various measures, such as sharing threat-related information. But more than anything else counter hacking to prevent money laundering and recover assets stolen through hacking by improving our capabilities, we will fundamentally block North Korea's illegal acquisition of foreign currency funds and reducing cyber activity is of utmost importance.
BlueNoroff strikes again with new macOS malware
Ferdous Saljooki details an alleged evolved capability targeting maOS which appears to follow on a theme targeting this operating system.
[We] discovered a new later-stage malware variant from BlueNoroff that shares characteristics with their RustBucket campaign
The standalone binary, labeled
ProcessRequest, is ad-hoc signed
https://www.jamf.com/blog/bluenoroff-strikes-again-with-new-macos-malware/
Warning Against HWP Documents Embedded with Malicious OLE Objects
Regional software targeting by unattributed threat actor. Phishing and other social engineering techniques seem the order of the day.
[We] found HWP documents that were embedded with OLE objects, targeting individuals in specific sectors such as the national defense and the press. The malware is presumed to be distributed mainly through download URLs or attachments in emails. The file names of the distributed documents are relevant to the areas of national defense, unification, education, and broadcasting, suggesting that the malware targets professionals involved in these areas.
https://asec.ahnlab.com/en/58335/
Malicious code created by Kimsuky targeting North Korean officials
A campaign from May which uses Compiled HTML files. Nothing overly of note beyond the entities which were being spoofed.
https://wezard4u.tistory.com/6645
North Korean Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures for Revenue Generation
From the US Government in July, a worthwhile reference to understand where cyber fits in.
https://www.dni.gov/files/CTIIC/documents/products/North-Korean-TTPs-for-Revenue-Generation.pdf
Reporting on Iran
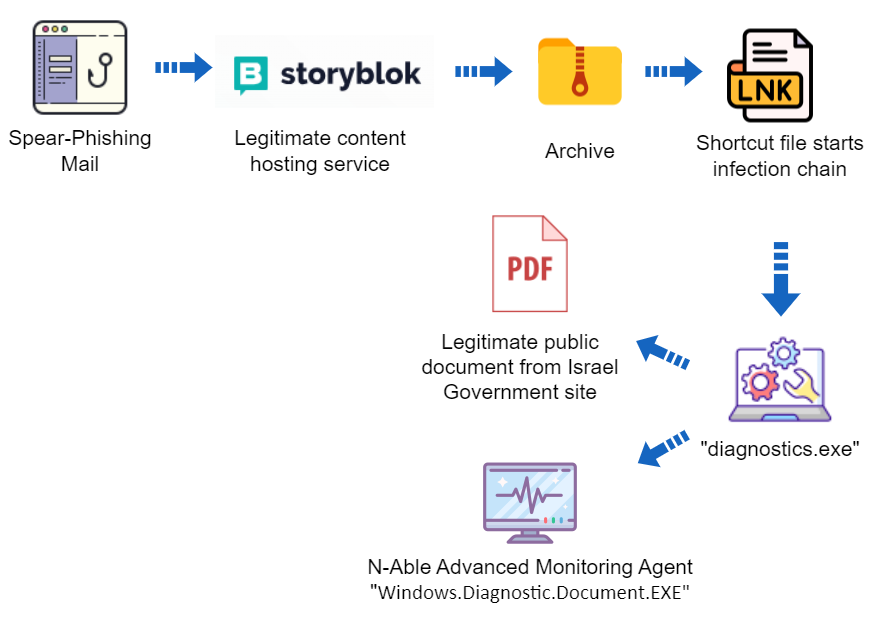
MuddyWater eN-Able spear-phishing with new TTPs
Simon Kennan outlines a suspected Iranian campaign. Note the use of a phishing combined with a third party services to host the payloads.
[We] identified a new campaign from the “MuddyWater” group
The campaign has been observed attacking two Israeli targets
The campaign exhibits updated TTPs to previously reported MuddyWater activity
https://www.deepinstinct.com/blog/muddywater-en-able-spear-phishing-with-new-ttps
Reporting on Other Actors
Analysis of activities of suspected APT-C-36 (Blind Eagle) organization launching Amadey botnet Trojan
Chinese reporting on a suspected Columbia originating threat actor. The point of note here is the use of capability which appears to originate from the Russian criminal underground.
we discovered that the APT-C-36 organization recently attempted to add the Amadey botnet Trojan to its usual PDF spear phishing attack flow. The Amadey botnet Trojan is a modular botnet Trojan that appeared for sale on Russian hacker forums around October 2018. It has the capabilities of intranet traversal, information theft, remote command execution, script execution, and DDoS attacks.
CloudKeys in the Air: Tracking Malicious Operations of Exposed IAM Keys
William Gamazo and Nathaniel Quist show what a persistent threat actor looks like. What real-time exposure exploitation looks like in 2023…
We found that the actor was able to detect and use the exposed IAM credentials within five minutes of their initial exposure on GitHub. AWS’s automatically applied quarantine policy limited the actor’s ability to operate, but by removing that policy we gained deep insight into the design and automation behind this campaign.
https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/malicious-operations-of-exposed-iam-keys-cryptojacking/
Popping Blisters for research: An overview of past payloads and exploring recent developments
Mick Koomen provides reporting showing some of the more advanced tradecraft of cyber criminals. The use of environment keying hints at their ability to do the required recognisance.
The overview shows that since its support for environmental keying, most samples have this feature enabled, indicating that attackers mostly use Blister in a targeted manner. Furthermore, there has been a shift in payload type from Cobalt Strike to Mythic agents, matching with previous reporting. Blister drops the same type of Mythic agent which we thus far cannot link to any public Mythic agents. Another development is that its developers started obfuscating the first stage of Blister, making it more evasive.
Who killed Mozi? Finally putting the IoT zombie botnet in its grave
Ivan Bešina, Michal Škuta and Miloš Čermák identify an interesting disruption which occurred against an IoT botnet.
In August 2023, the notorious Mozi botnet, infamous for exploiting vulnerabilities in hundreds of thousands of IoT devices each year, experienced a sudden and unanticipated nosedive in activity. First observed in India on August 8th, 2023 and a week later in China on August 16th, this mysterious disappearance stripped Mozi bots of most of their functionality.
..
Our investigation into this event led us to the discovery of a kill switch on September 27th, 2023. We spotted the control payload (configuration file) inside a user datagram protocol (UDP) message that was missing the typical encapsulation of BitTorrent’s distributed sloppy hash table (BT-DHT) protocol. The person behind the takedown sent the control payload eight times, each time instructing the bot to download and install an update of itself via HTTP.
GhostSec offers Ransomware-as-a-Service Possibly Used to Target Israel
Reporting on a commercial offering which is allegedly focusing on a specific region. This threat actor is interesting as they have previously shown capability to go after industrial PLC systems yet claim to be hacktivists.
The hacker collective called GhostSec has unveiled an innovative Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) framework called GhostLocker. They provide comprehensive assistance to customers interested in acquiring this service through a dedicated Telegram channel. Presently, GhostSec is focusing its attacks on Israel. This move represents a surprising departure from their past activities and stated agenda.
https://www.uptycs.com/blog/ghostlocker-ransomware-ghostsec
Discovery
How we find and understand the latent compromises within our environments.
Detecting DNS over HTTPS
Showing the challenges, but also the opportunity DNS becomes encrypted - a common defensive tradecraft data source.
While DoH encrypts the content of DNS queries, certain characteristics can still be used as signatures for detection
https://detect.fyi/detecting-dns-over-https-30fddb55ac78?gi=a33a25e04cbe
Integration of THOR in Velociraptor
Paul Hager extends an already powerful platform to further enrich with detection capability. The fact that a lot of this is open source is something to be celebrated.
We’ve created three Velociraptor artifacts for using and leveraging THOR:
Generic artifact for THOR (enterprise) forensic scanner. Works for all major operating systems and licenses endpoints on the fly.
Artifact which is used best in combination with THOR Lite. Expects a ZIP file with THOR Lite (as downloaded from our servers) and a THOR Lite license. Works for all major operating systems.
Artifact for our newest member in the THOR family: THOR Cloud
K-means Clustering for Lateral Movement Detection
Alicja Dobrzeniecka and Marvin Straathof shows the iterative journey one can go on when doing anomaly detection using unlabeled data by a team just start
[W]e have shown a simple first approach to anomaly detection with unlabelled network data. We start with something simple, with the goal of improving it with more complexity in subsequent iterations as the data and scope are better understood. Such an approach allows us not to get stuck in a problem space that is too complex at the beginning, but to slowly move from simple and sometimes naive methods to more complex ones as we learn more about the data and the domain itself.
https://www.huntandhackett.com/blog/kmeans-clustering-for-lateral-movement-detection
VEDRANDO: A Novel Way to Reveal Stealthy Attack Steps on Android through Memory Forensics
Jennifer Bellizz, Eleonora Losiouk, Mauro Conti, Christian Colombo and Mark Vella deliver some academic work which will be interesting to see which if any handset OEMs pick up and incorporate.
We present VEDRANDO, an enhanced EDR for Android that accomplishes (i) the challenge of timely collection of volatile memory artefacts and (ii) the detection of a class of stealthy attacks that hijack benign applications. VEDRANDO leverages memory forensics and app virtualization techniques to collect timely evidence from memory, which allows uncovering attack steps currently uncollected by the state-of-the-art EDRs. The results showed that, with less than 5% CPU overhead compared to normal usage, VEDRANDO could uniquely collect and fully reconstruct the stealthy attack steps of ten realistic messaging hijack attacks using standard anomaly detection techniques, without requiring device or app modification.
https://www.mdpi.com/2624-800X/3/3/19
Measuring CDNs susceptible to Domain Fronting
Karthika Subramani, Roberto Perdisci and Pierros Skafidas show the scale of the challenge that enterprise security teams have when they can’t terminate and inspect TLS connections where they don’t have endpoint coverage.
To better understand whether domain fronting can still be effectively used, we propose a systematic approach to discover CDNs that are still prone to domain fronting. To this end, we leverage passive and active DNS traffic analysis to pinpoint domain names served by CDNs and build an automated tool that can be used to discover CDNs that allow domain fronting in their infrastructure. Our results reveal that domain fronting is feasible in 22 out of 30 CDNs that we tested.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.17851
Defence
How we proactively defend our environments.
Introducing Raven: Open Source Vulnerability Scanner for CI/CD
Oreen Livni release a work aid for those tasked with securing modern CI/CD pipelines.
Raven scans GitHub workflows and breaks them down into individual components. These components are then inserted into a Neo4j database as distinct types of nodes, with relationships established between them. This allows for effortless scanning and identification of vulnerabilities in workflows.
https://cycode.com/blog/introducing-raven/
First handset with MTE on the market
Mark Brand details the first Android handset which has shipped with this countermeasure. These silicon enabled defense again memory corruption are how we impose cost and complexity on adversaries.
The ability of MTE to detect memory corruption exploitation at the first dangerous access is a significant improvement in diagnostic and potential security effectiveness. The availability of MTE on a production handset for the first time is a big step forward, and I think there's real potential to use this technology to make 0-day harder.
https://googleprojectzero.blogspot.com/2023/11/first-handset-with-mte-on-market.html
Incident Writeups
How they got in and what they did.
Unauthorized Access to Okta's Support Case Management System: Root Cause and Remediation
David Bradbury provides a conclusion to an incident which sent shockwaves around the industry but whose impact appears thankfully contained a small number of victim, albeit important ones.
The unauthorized access to Okta’s customer support system leveraged a service account stored in the system itself. This service account was granted permissions to view and update customer support cases. During our investigation into suspicious use of this account, Okta Security identified that an employee had signed-in to their personal Google profile on the Chrome browser of their Okta-managed laptop. The username and password of the service account had been saved into the employee’s personal Google account. The most likely avenue for exposure of this credential is the compromise of the employee’s personal Google account or personal device.
On Friday, November 3rd, 2023, Sumo Logic discovered evidence of a potential security incident
Rotate those secrets..
We recommend that customers rotate credentials that are either used to access Sumo Logic or that you have provided to Sumo Logic to access other systems. Specifically:
What we advise you rotate immediately:
Sumo Logic API access keys (If you need assistance with this, please contact Sumo Support at https://support.sumologic.com/support/s/)
What you could also rotate as an additional precautionary measure:
Sumo Logic installed collector credentials
Third-party credentials that have been stored with Sumo for the purpose of data collection by the hosted collector (e.g., credentials for S3 access)
Third-party credentials that have been stored with Sumo as part of webhook connection configuration
User passwords to Sumo Logic accounts
https://www.sumologic.com/security-response-center/#eede153a-8f3f-4eff-858d-1b653eaff457
Vulnerability
Our attack surface.
Cisco Firepower Management Center Software Command Injection Vulnerability
Patch..
This vulnerability is due to insufficient authorization of configuration commands that are sent through the web service interface. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by authenticating to the FMC web services interface and sending a crafted HTTP request to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute certain configuration commands on the targeted FTD device. To successfully exploit this vulnerability, an attacker would need valid credentials on the FMC Software.
Hunting Vulnerable Kernel Drivers
Takahiro Haruyama shows that there are still show shallow vulnerabilities to be found in Windows kernel drivers. It will be interesting to see if detecting this class of issue will be introduced into the signing process or not.
[We] discovered 34 vulnerable drivers (30 WDM, 4 WDF) with firmware access, including ones made by major chip/BIOS/PC makers. This is the number based on the unique filenames. Practically, there are 237 file hashes in the wild. All discovered drivers give full control of the devices to non-admin users. TAU could load them all on HVCI-enabled Windows 11 except five drivers.
https://blogs.vmware.com/security/2023/10/hunting-vulnerable-kernel-drivers.html
Offense
Attack capability, techniques and trade-craft.
The Wiki-Slack Cyberattack Analysis
Keegan Keplinger and Joe Stewart detail a novel technique where threat actors can co-opt Wikipedia which when shared can turn malicious. This highlights the complexity.
A threat actor selects a subject in Wikipedia that they believe will interest the type of business professionals they are targeting. For example, if the cybercriminals are targeting publicly traded companies, they might select a Wikipedia entry detailing the latest Securities and Exchange Commission’s (SEC) cybersecurity regulations that are being implemented. Because these regulations are necessary for compliance, organizations may be likely to visit the Wikipedia page – a first step in executing the Wiki-Slack attack.
Once the threat actors select a topic in Wikipedia, they will go to the first page of the Wikipedia entry and edit the page, adding a legitimate referenced footnote to the article. The footnote itself is not malicious but it paves the way for a formatting error when the article is shared in Slack. Once certain additional conditions are met – made easy by small grammatical changes to the Wikipedia article, Slack will render a link that is not visible in the original Wikipedia article.
Once a business professional copies and pastes that Wikipedia entry in a Slack channel, the malicious link is rendered. If the grammar around the link is crafted well enough, Slack users are enticed to click it, leading them to an attacker-controlled website where browser-based malware lays in wait.
https://www.esentire.com/blog/the-wiki-slack-attack
Nuclei templates for honeypots detection
Sheila A. Berta releases a capability which will be interesting to see if it adopted by threat actors.
This repository contains Nuclei templates to detect several well-known open-source honeypots, such as: ADBHoney, Conpot, Cowrie, Dionaea (multiple services), ElasticPot, Mailoney, Redis Honeypot, Snare, among others.
https://github.com/UnaPibaGeek/honeypots-detection
JS-Tap: Weaponizing JavaScript
Drew Kirkpatrick provides a universal Cross-Site-Scripting payload which will exfiltrate useful information for the threat actor.
https://trustedsec.com/blog/js-tap-weaponizing-javascript-for-red-teams
https://github.com/hoodoer/JS-Tap
Phishing With Dynamite: Cuddlephish is an open-source, point-and-shoot implementation of BitM for penetration testers
Forrest Kasler provides tooling we should expect will be misused by threat actors who are seeking to circumvent multi factor authentication etc.
Token stealing is getting harder. Instead, stealing whole logged-in browser instances may be an easier and more generic approach. One attack, known as “browser-in-the-middle” (BitM), makes it possible to virtually place a user in front of our browser and request them to log in for us.
Cuddlephish is an open-source, point-and-shoot implementation of BitM for penetration testers.
https://medium.com/@fakasler/phishing-with-dynamite-7d33d8fac038
Exploitation
What is being exploited.
CVE-2023-20273: IOS XE root priv escalation
Provides a walkthrough the end-to-end payload.
https://blog.leakix.net/2023/10/cisco-root-privesc/
Confluence to Cerber: Exploitation of CVE-2023-22518 for Ransomware Deployment
Patch!
In addition to observations from other organizations. [We] can confirm active exploitation starting on November 3 post patch release.
Bypassing Android 13 Restrictions with SecuriDropper
How Android security features are being bypassed in the real-world.
[We] look at how threat actors are bypassing the "Restricted Settings" security measure introduced by Google in Android 13 to help protect against malware by taking a closer look at SecuriDropper, the first example of a widely distributed dropper bypassing this security measure.
https://www.threatfabric.com/blogs/droppers-bypassing-android-13-restrictions
Exploitation of CVE-2023-46604 Leading to Ransomware
Stefan Hostetler, Markus Neis, Christopher Prest, Hady Azzam, Joe Wedderspoon, and Ross Phillips detail a campaign where this vulnerability appears to be exploited by cyber crimnials.
[We] observed active exploitation in the wild as of October 10, 2023 for CVE-2023-46604, a RCE vulnerability in Apache ActiveMQ.
Binary analysis of the ransomware payload identified similarities with the TellYouThePass ransomware variant.
The IP address, Domains, and the Bitcoin wallet address observed in these recent intrusions also had overlap with the TellYouThePass ransomware variant.
Tooling and Techniques
Low level tooling and techniques for attack and defence researchers…
macho_similarity: Conceptual Methods for Finding Commonalities in Macho Files
Greg Lesnewich provides a work aid to
In this repository are 2 scripts of mostly identical functionality - one based on lief, the other ktool
The goal is to parse batch of Macho files to try and mine them for similarity based on hashes of the dylibs, the imports, or the exports (And eventually, hopefully, signature-based things like names or entitlements)
https://github.com/g-les/macho_similarity
Footnotes
Some other small (and not so small) bits and bobs which might be of interest.
Aggregate reporting
Cross Market Operational Resilience Group (CMORG) - for financial services - cyber publications
A survey and characterization of Close Access Cyberspace Operations
Saving face in the cyberspace: responses to public cyber intrusions in the Gulf - academic work - This article explores the rhetorical strategies used by governments in response to a public cyber intrusion they suffered.
Artificial intelligence
Idempotent Generative Network - We propose a new approach for generative modeling based on training a neural network to be idempotent. An idempotent operator is one that can be applied sequentially without changing the result beyond the initial application.
Books
None this week
Events
How can we protect people from cyberattacks? Live premiere, November 8th.
Inclusive Cybersecurity: Widening the Horizons, November 28th, London, UK
Amsterdam 2024 FIRST Technical Colloquium, March 5-7, 2024 - call for papers
Workshop on SOC Operations and Construction (WOSOC 2024) - call for papers
Unless stated otherwise, linked or referenced content does not necessarily represent the views of the NCSC and reference to third parties or content on their websites should not be taken as endorsement of any kind by the NCSC. The NCSC has no control over the content of third party websites and consequently accepts no responsibility for your use of them.
This newsletter is subject to the NCSC website terms and conditions which can be found at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/terms-and-conditions and you can find out more about how will treat your personal information in our privacy notice at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/privacy-statement.