CTO at NCSC Summary: week ending November 5th
AI is our future.. with what level of resilience is our choice..
Welcome to the weekly highlights and analysis of the blueteamsec subreddit (and my wider reading). Not everything makes it in, but the best bits do.
Operationally this week you will see it is very busy indeed on all fronts. In terms of specific operations the Citrix Bleed vulnerability (see reporting) has resulted in one vendor “currently tracking four distinct uncategorized (UNC) groups involved in exploiting this vulnerability”.
In the high-level this week:
The UK’s National Cyber Security Centre has launched Protective DNS for schools - The service will be completely free, and the phased rollout will start now and will progress into next year.
International Counter Ransomware Initiative 2023 Joint Statement - CRI members endorsed a statement that relevant institutions under our national government authority should not pay ransomware extortion demands.
The SEC charged the CISO of SolarWinds with fraud - As the complaint alleges, SolarWinds’ public statements about its cybersecurity practices and risks were at odds with its internal assessments, including a 2018 presentation prepared by a company engineer and shared internally, including with Brown, that SolarWinds’ remote access set-up was “not very secure” and that someone exploiting the vulnerability “can basically do whatever without us detecting it until it’s too late,” which could lead to “major reputation and financial loss” for SolarWinds.
Committee formed to suggest ways for tackling cyber crime effectively, says (Indian) Home Minister - Home Minister G. Parameshwara said on Sunday, October 29, that the government has formed a committee to suggest legal measures required to tackle cyber crime effectively by amending the Information Technology Act.
What the !#@% is a Passkey? and Passkeys and Privacy - by the EFF
Taking cyber warfare training to new heights - In the first classified-level cyber exercise of its kind, Australian and US military cyber experts joined forces to battle simulated network attacks in Canberra
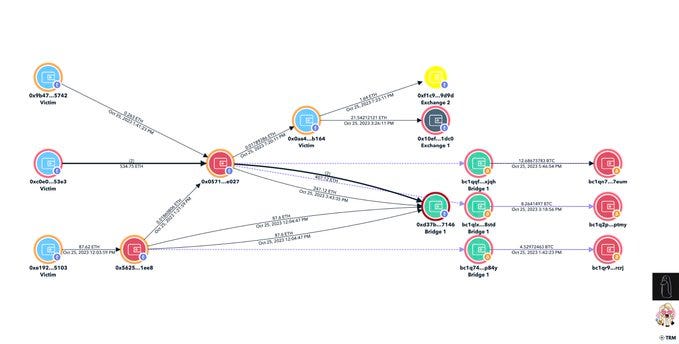
Mapping the Ransomware Payment Ecosystem: A Comprehensive Visualization of the Process and Participants - It presents a novel, comprehensive ransomware payment map and orients the reader to the actors and entities adapting to the ransomware threat.
Security recommendations for UK parliamentarians - This short paper intends to assess current security apparatus, and offer recommendations to the relevant authorities in line with best practice. Ahead of a General Election, where interference activities are expected to increase, there is an urgent need to increase capacity - by the Inter-Parliamentary Alliance on China
FACT SHEET: Delivering on the Next Generation of Innovation and Partnership with Australia - Together, the United States and Australia intend to engage Pacific Island nations and the private sector to explore developing and deploying a pilot initiative in the region to increase national cyber resilience.
Biden-Harris Administration Designates 31 Tech Hubs Across America - Designation is an endorsement of the region’s plans to supercharge their respective technological industries to create jobs, strengthen U.S. competitiveness, and protect national security.
New quantum computing architecture achieves electron charge qubit with 0.1 millisecond coherence time - They have extended the coherence time for their novel type of qubit to an impressive 0.1 milliseconds—nearly a thousand times better than the previous record - some way to go, but impressive progress.
New EU rules needed to make digital platforms less addictive - Calls for ban on addictive techniques like endless scrolling or automatic play - you have to wonder what any productivity boot would be.
SIM Swappers Are Working Directly with Ransomware Gangs Now - Hackers connected to “the Comm,” a nebulous group that includes SIM swappers, are working with ALPHV, a ransomware group that has impacted some of the biggest companies on the planet, including MGM Casinos.
China
Shanghai opens data economy industrial park in pilot free-trade zone Lingang amid China’s AI push - The International Data Economy Industrial Park aims to draw more than 100 leading data firms with a combined output of over 100 billion yuan by 2025
The Emergence of China’s Smart State - This series brings together the latest research from international relations scholars—particularly those working across disciplines—to challenge and extend our understanding of world politics in the Information Age.
Chinese AI start-up claims to beat US rivals in processing long text - claims to beat Anthropic, OpenAI with model that can process 350,000 Chinese characters
China’s YMTC makes world’s most advanced memory chip in ‘surprise technology leap’ - has manufactured the “world’s most advanced” 3D NAND memory chip known to be in a consumer device in a “surprise technology leap”
Artificial intelligence
The Bletchley Declaration by Countries Attending the AI Safety Summit, 1-2 November 2023 - we resolve to sustain an inclusive global dialogue that engages existing international fora and other relevant initiatives and contributes in an open manner to broader international discussions, and to continue research on frontier AI safety to ensure that the benefits of the technology can be harnessed responsibly for good and for all.
FACT SHEET: President Biden Issues Executive Order on Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence - New Standards for AI Safety and Security
’Poison’ AI threat to national security, cyber centre warns - Australia’s Cyber Security Cooperative Research Centre has sounded alarm over the potential for hackers to exploit data that AI systems including ChatGPT rely on, feeding false information into platforms used for everyday activities like medical and financial advice
First of its kind Generative AI Evaluation Sandbox for Trusted AI by AI Verify Foundation and IMDA - Over 10 global players join Sandbox to develop evaluation benchmarks for trusted Gen AI
Skating to Where the Puck Is Going - Anticipating and Managing Risks from Frontier AI Systems
Data Equity: Foundational Concepts for Generative AI - Data equity is not a new concept; it is grounded in human rights and part of ongoing work on data privacy, protection, ethics, Indigenous data sovereignty and responsibility. The intersection of data equity and genAI, however, is new and presents unique challenges.
This new data poisoning tool lets artists fight back against generative AI - The tool, called Nightshade, messes up training data in ways that could cause serious damage to image-generating AI models.
Prompt-Specific Poisoning Attacks on Text-to-Image Generative Models - the underpinning academic work
Chatbot Hallucinations Are Poisoning Web Search - Untruths spouted by chatbots ended up on the web—and Microsoft's Bing search engine served them up as facts. Generative AI could make search harder to trust.
UK DSIT competitions on Collaborative AI Solutions to improve productivity in key sectors and AI Solutions to improve productivity in key sectors
Artificial intelligence, services globalisation and income inequality - Drawing from a rich data set that covers 86 countries over 2010–19, this paper presents high-level cross-country evidence on how AI-related investment is associated with economic outcomes, including real incomes and income shares across different income groups.
Cyber proliferation
EU Parliament resurrects spyware discussion with second inquiry committee on the horizon - The most contentious issue in the Commission’s reply to PEGA committee, is the ‘non-legislative’ nature of the proposed actions in response to the Parliament’s calls in May for common EU standards regulating the use of spyware by member state bodies.
How Europe became the Wild West of spyware - The lack of EU rules on who can use spyware, and how, also means that a swath of governments across the bloc — from education ministries to national revenue agencies and law enforcement — have access to some of the most intrusive surveillance technologies available.
Request for Comment on Software Identification Ecosystem Option Analysis - CISA announces the publication of “Software Identification Ecosystem Option Analysis,” which is a white paper on software identification ecosystems and requests public comment on the paths forward identified by the paper and on the analysis of the merits and challenges of the software identifier ecosystems discussed. Additionally, CISA requests input on analysis or approaches currently absent from the paper.
Reflections this week stem from the spectrum of activity in relation to AI and specifically in the cyber domain. You will read in the above the high-level aspects, then at the end you will see emergent application to offensive cyber operations, vulnerability discovery in the guise of fuzzing through to the first steps in application to code verification. It is increasingly clear that we have a set of parallel developments occurring in many sub domains of cyber and doing so at very different speeds. This cadence mismatch will cause challenges for priority calls I suspect. Exciting..
On the interesting job/role front (thanks to those sending me these):
Interpretable Machine Learning-based Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) - Funded PhD in the UK
Project Manager Cybersecurity Policy at the Swiss Government
Enjoying this? Don’t get via e-mail? Subscribe:
Think someone else would benefit? Share:
All attribution is by others and not the UK Government, please see the legal text at the end.
Have a lovely Thursday
Ollie
Cyber threat intelligence
Who is doing what to whom and how.
Reporting on Russia
How Russian government-controlled hacking groups shift their tactics, objectives and capacities: forecast
Reporting that further evidences the importance of supply chain security.
The SSSCIP specialists anticipate an increase in high-complexity supply chain attacks. Companies engaged in software development for critical infrastructure and the military are going to suffer from active targeted cyberattacks in the long run.
Over the Kazuar’s Nest: Cracking Down on a Freshly Hatched Backdoor Used by Pensive Ursa (Aka Turla)
Daniel Frank and Tom Fakterman show that this adversary continues to invest in their operational security in an attempt to squeeze enduring value out of their implants.
As the code of the upgraded revision of Kazuar reveals, the authors put special emphasis on Kazuar’s ability to operate in stealth, evade detection and thwart analysis efforts. They do so using a variety of advanced anti-analysis techniques and by protecting the malware code with effective encryption and obfuscation practices.
https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/pensive-ursa-uses-upgraded-kazuar-backdoor/
Campagnes d’attaques du mode opératoire APT28 depuis 2021 - APT28 modus operandi attack campaigns since 2021
French government reporting which highlights the fact that adversaries are dwelling in places where there isn’t the observability coverage. This should be a warning to cyber defence team to ensure they have coverage even if only at a network level in the first instance.
During its investigations, ANSSI analyzed several APT28 attack mode of attack (MOA) compromise chains used for espionage purposes. Some campaigns have been directed against French organizations, including government entities, businesses, universities, as well as research institutes and think tanks.
If attackers continue their brute force attack and vulnerability exploitation campaigns, ANSSI also notes that attackers reduce the risk of detection by compromising equipment that is poorly monitored and located on the edge of the network (routers, gateways and mail servers, firewalls). In some cases, no backdoors are dropped on the compromised network.
NKCC at the National Security and Defense Council of Ukraine experienced a sharp growth of cyberattacks of Russian cybercriminals using malware Smokeloader
Reporting from the Ukrainian government around an uptick in activity. The aspect of note is the use of financial themes in the lures.
Reporting on North Korea
The IT company that stole 3.4 billion Korean currency through ransomware was in league with North Korean hackers
Reporting out of Korea which intimates a rather sophisticated inter-relationship with what appears to be a front company which was then backed off to a criminal group. This is the first time I have read of this type of relationship and an interesting example which likely warrants further study.
The National Police Agency's National Security Investigation Unit charged five people, including the CEO and employees of data recovery agency A, who collected 3.4 billion won in recovery costs from 778 victims whose computers were infected with ransomware over a four-year period from October 2018 to September last year, for violating the Information and Communications Network Act. It was announced on the 27th that it had been handed over to the prosecution on charges of aiding and abetting extortion
…
Company A is said to have previously received a manual to unlock ransomware by collaborating with North Korean hackers.
DPRK passing out KANDYKORN
Colson Wilhoit, Rricardo Ungureanu, Seth Goodwin and Andrew Pease highlight continued interest in crypto assets by going after engineers associated with the asset class. The numerous stages in these deployments and the transition between different services appears on the face of it increasing and complicating analysis.
Threat actors lured blockchain engineers with a Python application to gain initial access to the environment
This intrusion involved multiple complex stages that each employed deliberate defense evasion techniques
The intrusion set was observed on a macOS system where an adversary attempted to load binaries into memory, which is atypical of macOS intrusions
https://www.elastic.co/security-labs/elastic-catches-dprk-passing-out-kandykorn
A cascade of compromise: unveiling Lazarus' new campaign
Seongsu Park provides reporting which further highlights the level of sophistication through a multistage campaign. Of note is that the threat actor went back into the victim software vendor on multiple occasions. Putting the P is Persistent as it were.
A software vendor was compromised through the exploitation of another high-profile software.
The SIGNBT malware used in this attack employed a diverse infection chain and sophisticated techniques.
LPEClient used in this attack was observed executing a range of targeted attacks associated with the Lazarus group.
Upon further investigation, we discovered that the software vendor that developed the exploited software had previously fallen victim to Lazarus several times. This recurring breach suggested a persistent and determined threat actor with the likely objective of stealing valuable source code or tampering with the software supply chain, and they continued to exploit vulnerabilities in the company’s software while targeting other software makers.
https://securelist.com/unveiling-lazarus-new-campaign/110888/
Evidence Leads to Lazarus as the VMConnect Supply Chain Attack Continues
We have see reporting of a variety of threat actors employing this technique in the past. A rather broad campaign which raises the risk of complex victimology emerging.
[We] analyzed the fraudulent PyPI package ‘VMConnect,’ developed to imitate the authentic VMware vSphere connector module closely, ‘vConnector,’ but actually contains a malicious code
..
During the investigation, the team discovered hints that led to the Lazarus outfit, a North Korean advanced persistent threat (APT) outfit that has been connected to a number of sophisticated operations.
FastViewer Variant Merged with FastSpy and disguised as a Legitimate Mobile Application
Youngjae Shin and Sebin Lee hypothesize that there is a campaign going after mobile devices by using social engineering for initial deployment. The tightening up of post compromise detection is interesting.
The variant has been in production since at least July 2023 and, like the initial version, is found to induce installation by distributing repackaged APKs that include malicious code in legitimate apps.
The exact distribution route of the malicious app has not been identified, but it is believed to be the same as last year, disguised as a legitimate app through spearphishing emails or smishing to trick targets into running it.
In the past, FastViewer was responsible for downloading and loading the FastSpy, which is the actual remote control module, but the newly identified variant integrates some of the functionality of FastViewer with FastSpy and does not download additional malware.
Analysis of the relationship between Kimsuky APT group's Storm operation and BabyShark Family
South Korean reporting which shows a specific focus in terms of sectoral targeting of the diplomatic and humanitarian spheres. Initial access tradecraft is phishing..
Impersonating a public official belonging to the Peace Regime Department of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Humanitarian Affairs Department of the Ministry of Unification, etc., approached under the pretense of having a closed-door meeting.
BabyShark attack toolkit discovered for reconnaissance and infiltration by the infamous Kimsuky APT group
Cyber espionage was carried out targeting specific people in the fields of diplomacy and unification, including experts on North Korean issues.
Reporting on China
i-SOON: Another Company in the APT41 Network
Reporting on a business disagreement by an alleged APT. Not something one might expect..
This court case is an intellectual property dispute in which the company known as Chengdu 404 – which allegedly stands behind Chinese state hacking operation known as APT41 – sued a company known as Sichuan i-SOON. The case, which pitted Chengdu Silingsi (404) Network Technology Company (成都市肆零肆网络科技有限公司) as the plaintiff against Sichuan i-SOON Information Technology Company(四川安洵信息技术有限公司) as the defendant, centered on a software development contract dispute.
..
the CEO of i-SOON, Wu Haibo (吴海波) , a.k.a shutdown, is a well-known first-generation red hacker or Honker (红客) and early member of Green Army (绿色兵团) which was the very first Chinese hacktivist group founded in 1997.
nattothoughts.substack.com/p/i-soon-another-company-in-the-apt41
New APT organization "Double Different Rats" launches large-scale cyber attacks against China
Reporting from China that a previously unknown APT is operating in China using n-days and reported false flag techniques. Both aspects of tradecraft are noteworthy..
The signature attack method of the Shuangyirat organization is to first gain continuous control over a large number of public network security devices through N-day vulnerabilities, then scan and detect the intranet to confirm the value of each compromised target, and design different follow-up attacks for different targets. Or use methods to steal data and files of high-value targets.
…
The organization's independence comes from its special attack mode that is not identical to that of known APT organizations (see Chapter 4 of this report for details), its unique attack weapons, and its special "false flag" strategy that is implemented throughout the attacker's actions .
Reporting on Iran
From Albania to the Middle East: The Scarred Manticore is Listening
Reporting which is noteworthy for both its aggression and relative sophistication. The apparent evolution in tradecraft and continued investment in capability are of note.
an ongoing Iranian espionage campaign by Scarred Manticore, an actor affiliated with the Ministry of Intelligence and Security (MOIS).
The attacks rely on LIONTAIL, an advanced passive malware framework installed on Windows servers. For stealth purposes, LIONTIAL implants utilize direct calls to Windows HTTP stack driver HTTP.sys to load memory-residents payloads.
The current campaign peaked in mid-2023, going under the radar for at least a year. The campaign targets high-profile organizations in the Middle East with a focus on government, military, and telecommunications sectors, in addition to IT service providers, financial organizations and NGOs.
Scarred Manticore has been pursuing high-value targets for years, utilizing a variety of IIS-based backdoors to attack Windows servers. These include a variety of custom web shells, custom DLL backdoors, and driver-based implants.
While the main motivation behind Scarred Manticore’s operation is espionage, some of the tools described in this report have been associated with the MOIS-sponsored destructive attack against Albanian government infrastructure (referred to as DEV-0861).
Reporting on Other Actors
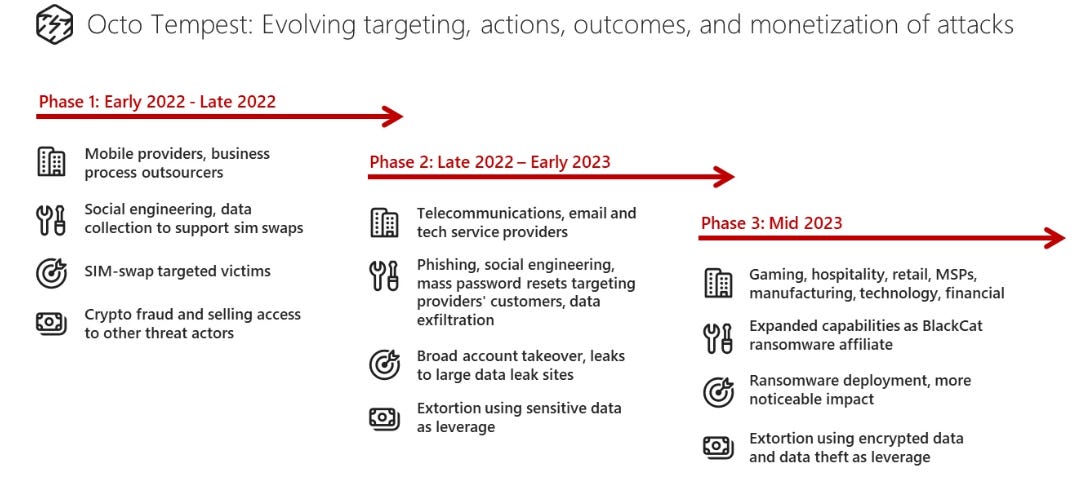
Octo Tempest crosses boundaries to facilitate extortion, encryption, and destruction
A suspected criminal actor evolves their tradecraft as they learn and become bolder. The blend of tradecraft to incorporate social engineering and other techniques to enable initial access shows the importance of whole system thinking when we think about defence.
Octo Tempest is a financially motivated collective of native English-speaking threat actors known for launching wide-ranging campaigns that prominently feature adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) techniques, social engineering, and SIM swapping capabilities. Octo Tempest, which overlaps with research associated with 0ktapus, Scattered Spider, and UNC3944, was initially seen in early 2022, targeting mobile telecommunications and business process outsourcing organizations to initiate phone number ports (also known as SIM swaps). Octo Tempest monetized their intrusions in 2022 by selling SIM swaps to other criminals and performing account takeovers of high-net-worth individuals to steal their cryptocurrency.
GHOSTPULSE haunts victims using defense evasion bag o' tricks
Salim Bitam and Joe Desimone highlight further social engineering and search engine priming to achieve initial access.
In a common attack scenario, we suspect the users are directed to download malicious MSIX packages through compromised websites, search-engine optimization (SEO) techniques, or malvertising. The masquerading themes we’ve observed include installers for Chrome, Brave, Edge, Grammarly, and WebEx to highlight a few.
https://www.elastic.co/security-labs/ghostpulse-haunts-victims-using-defense-evasion-bag-o-tricks
Sidecopy joins the CVE-2023-38831 vulnerability exploit attack queue
Chinese reporting on a suspected South Asian threat actor who is using the WinRAR exploit for their initial access.
BiBi-Linux: A New Wiper Dropped By Pro-Hamas Hacktivist Group
Reporting on a possible destructive payload being used against Linux hosts. Not the first Linux wiper, but a noteworthy event nevertheless.
Hamas affiliated hacktivist group broke into Israeli companies and deployed a new cyberweapon to destroy their infrastructure
Notably, they decided to hardcode the name of Israeli PM in the malware name and in every destroyed file's extension
The attack had no ransom note or C2 servers which increased our confidence that the malware tracked as BiBi-Linux is indeed a Wiper aimed for data destruction
https://www.securityjoes.com/post/bibi-linux-a-new-wiper-dropped-by-pro-hamas-hacktivist-group
Malvertising via Dynamic Search Ads delivers malware bonanza
Jérôme Segura shows that complexity and innovation within the advertising ecosystem are creating new and novel attack paths.
Most, if not all malvertising incidents result from a threat actor either injecting code within an existing ad, or intentionally creating one. Today, we look at a different scenario where, as strange as that may sound, malvertising was entirely accidental.
The reason this happened was due to the combination of two separate factors: a compromised website and Google Dynamic Search Ads.
Unbeknownst to the site owner, one of their ads was automatically created to promote a popular program for Python developers, and visible to people doing a Google search for it. Victims who clicked on the ad were taken to a hacked webpage with a link to download the application, which turned out to install over a dozen different pieces of malware instead.
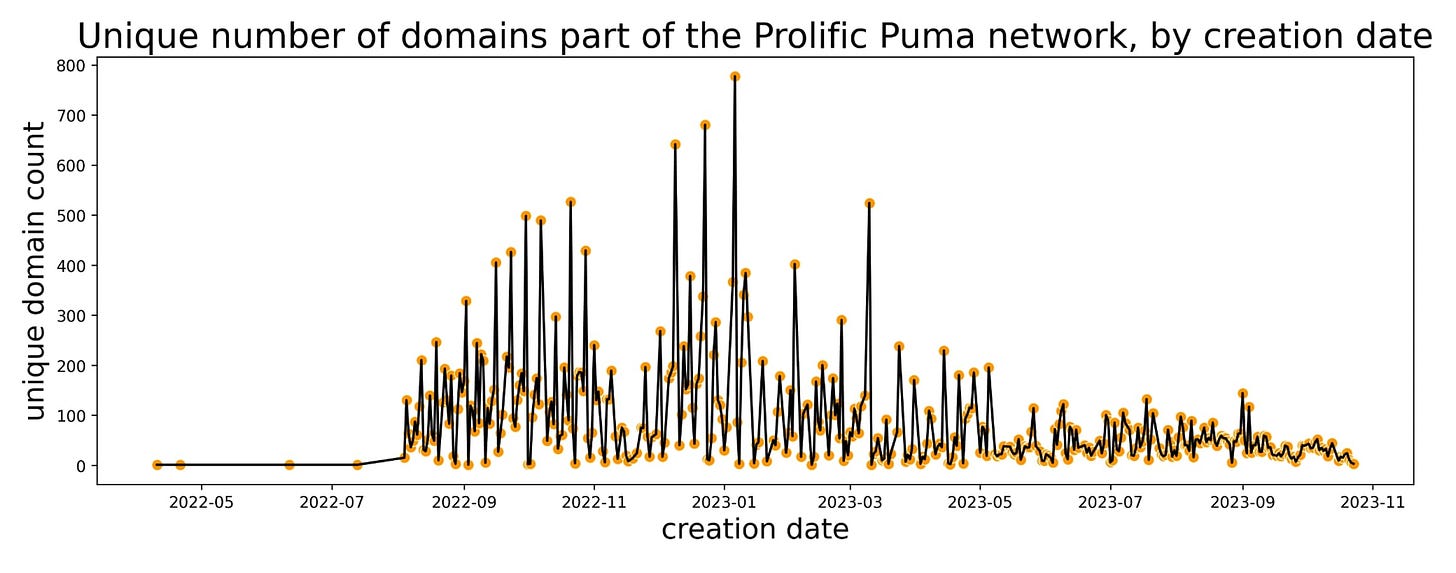
To Aid and Abet: Prolific Puma Helps Cybercriminals Evade Detection
The mantra in start-ups is at times ‘do one thing well’. Transpires the cyber crime eco system is sufficiently complex to warrant similar behaviours. The fact there is a dedicated cyber criminal link shortening service will be noteworthy. The stats show some scale..
The cybercrime economy is the world’s third largest, with an estimated $8 trillion value in 2023, and Prolific Puma is part of the supply chain.1 They create domain names with an RDGA and use these domains to provide a link shortening service to other malicious actors, helping them evade detection while they distribute phishing, scams, and malware.
https://krebsonsecurity.com/2023/10/us-harbors-prolific-malicious-link-shortening-service/
Discovery
How we find and understand the latent compromises within our environments.
Fifteen Months in the Life of a Honeyfarm
Cristian Munteanu, Said Jawad Saidi, Oliver Gasser, Georgios Smaragdakis and Anja Feldmann show that the Internet is not even when it comes to honeypot interactions. Hypothesis on a postcard as to why..
We analyze data of about 400 million sessions over a 15-month period, gathered from a globally distributed honeyfarm consisting of 221 honeypots deployed in 55 countries. Our analysis unveils stark differences among the activity seen by the honeypots-some are contacted millions of times while others only observe a few thousand sessions.
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3618257.3624826
How to Operate a Meta-Telescope in your Spare Time
Daniel Wagner, Sahil Ashish Ranadive, Harm Griffioen, Michalis Kallitsis, Alberto Dainotti, Georgios Smaragdakis and Anja Feldmann provide a fascinating capability which will be interesting to observe how it survives when more people adopt its use.
Network telescopes have been used for many years to monitor such unsolicited traffic. Unfortunately, they are limi the available address space for such tasks and, thus, limited to specific geographic and/or network regions.
In this paper, we introduce a novel concept to broadly capture unsolicited Internet traffic, which we call a "meta-telescope". A meta-telescope is based on the intuition that, with the availability of appropriate vantage points, one can (i) infer which address blocks on the Internet are unused and (ii) capture traffic towards them-both without having control of such address blocks. From this intuition, we develop and evaluate a methodology for identifying unlikely to be used Internet address space and build a meta-telescope that has very desirable properties, such as broad coverage of dark space both in terms of size and topological placement. Such meta-telescope identifies and captures unsolicited traffic to more than 350k /24 blocks in more than 7k ASes.
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3618257.3624831
Pushing Alias Resolution to the Limit
Taha Albakour, Oliver Gasser and Georgios Smaragdakis provide some capabilities which will be useful to those hunting and corelating adversary infrastructure.
In this paper, we show that utilizing multiple protocols offers a unique opportunity to improve IP alias resolution and dual-stack inference substantially. Our key observation is that prevalent protocols, e.g., SSH and BGP, reply to unsolicited requests with a set of values that can be combined to form a unique device identifier. More importantly, this is possible by just completing the TCP hand-shake. Our empirical study shows that utilizing readily available scans and our active measurements can double the discovered IPv4 alias sets and more than 30× the dual-stack sets compared to the state-of-the-art techniques. We provide insights into our method's accuracy and performance compared to popular techniques.
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3618257.3624840
Collection of Remote Management Monitoring tool artifacts
J Schell provides a collection for forensic artefacts which will be useful to hunt teams. This builds on previous alerts from the US Government as to the misuse of these tools.
This collection of Remote Management Monitoring tool artifacts is focused on providing defenders and investigators with up-to-date indicators and context.
https://github.com/jischell-msft/RemoteManagementMonitoringTools
Defence
How we proactively defend our environments.
Joint guide to outline phishing techniques malicious actors
US Government advisory on various phishing tradecraft thematic for various parties involved in defence. Highlights the risk for example of prompt bombing..
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), National Security Agency (NSA), Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), and Multi-State Information Sharing and Analysis Center (MS-ISAC) are releasing this joint guide to outline phishing techniques malicious actors commonly use and to provide guidance for both network defenders and software manufacturers. This will help to reduce the impact of phishing attacks in obtaining credentials and deploying malware.
https://www.ic3.gov/Media/News/2023/231018.pdf
CISA Announces New Release of Logging Made Easy
CISA have picked up our original Logging Made Easy platform for which we are extremely grateful.
WASHINGTON – The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) announces a new release of Logging Made Easy, a Windows-based, free and open log management solution designed to help organizations more effectively use available security data to detect and address cyber threats.
In April 2023, CISA assumed Logging Made Easy from the United Kingdom’s National Cyber Security Centre (UK-NCSC). Following a period of transition and enhancement, it is now available with step-by-step installation instructions for both legacy and new users.
https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/news/cisa-announces-new-release-logging-made-easy
Conducting Robust Learning for Empire Command and Control Detection
Qian Feng, Chris Navarrete, Yanhui Jia, Yu Fu, Iris Dai, Nina Smith and Brad Duncan share some of their applied machine learning approaches to training on Empire C2 profiles. Having seen some of these types of activities in a former life it does seem we are in the world of the 1980s sound engineer as opposed to the 2000s autotune at the moment - but we are quickly improving.
We categorize our dataset using three labels: “benign,” “non-adv” and “adv.”
“Benign” is C2 traffic from real-world uses, like penetration testing Empire C2 activity. “Non-adv” stands for non-adversarial attacks, indicating the datasets are from default profiles. Finally, the “adv” datasets are from simulated adversarial attack profiles.
We balanced our model detection on both “non-adv” and “adv” categories, designing our loss function to consider these labels. Our loss function is designed to increase the number of “adv” samples we create, which should increase our detection rate for adversarial attacks.
We employed a periodic training approach, relying on the feedback from our data quality monitoring engine. Whenever our data quality monitoring engine generated a signal, we captured the newly generated C2 traffic for model retraining.
The model is retrained on the new “adv” samples with the original dataset. Since our loss function will pay more attention to “adv” samples, the retrained model is guaranteed to have a good detection rate on adversarial (“adv”) samples.
https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/empire-c2-helps-train-machine-learning-framework/
Dealing with Noisy Behavioral Analytics in Detection Engineering
Sean Hutchinson provides shows what happens when you apply enrichment and data science. Valuable lessons in here for overburdened Security Operation Centres.
If the immediate context is insufficient to distill patterns and/or discern benign behavior, detection engineers can almost always supplement it with automated enrichments and/or baselines. Automated enrichments are more common for external, Internet-accessible assets and may be harder to come by for internal entities, but baselines can typically be built using the data you’re already collecting.
https://insights.sei.cmu.edu/blog/dealing-with-noisy-behavioral-analytics-in-detection-engineering/
Common Cybersecurity Misconfigurations in Networks
Singapore’s Cyber Security Agency provides a summary of their most commonly observed misconfigurations.
This advisory describes the most common types of network misconfigurations and provides recommended mitigation measures for organisations to implement in order to improve their security posture and enhance overall cybersecurity.
https://www.csa.gov.sg/alerts-advisories/Advisories/2023/ad-2023-022
Advancing iMessage security: iMessage Contact Key Verification
Apple enhance the security of iMessage contact verification.
iMessage Contact Key Verification displays detected key validation errors in the Messages conversation transcript and allows users to compare short verification codes to verify they're messaging with whom they intend.
https://security.apple.com/blog/imessage-contact-key-verification
Secure PLC Coding
Documentation and guidance to practice secure coding for various PLC vendors - this is Industry Control Systems/OT.
https://github.com/Fortiphyd/Secure_PLC_Coding
Introducing HAR Sanitizer: secure HAR sharing
Building on the Okta challenges reported last week, Kenny Johnson and team release a sanitizer to reduce credential proliferation.
https://blog.cloudflare.com/introducing-har-sanitizer-secure-har-sharing/
Incident Writeups
How they got in and what they did.
Netsupport Intrusion Results in Domain Compromise
From the team at the DFIR Report who provide insight into a historic compromise from the start of the year. Initial access was email and malicious zip file..
NetSupport Manager is one of the oldest third-party remote access tools still currently on the market with over 33 years of history. This is the first time we will report on a NetSupport RAT intrusion, but malicious use of this tool dates back to at least 2016. During this report, we will analyze a case from January 2023 where a NetSupport RAT was utilized to infiltrate a network. The RAT was then used for persistence and command & control, resulting in a full domain compromise.
https://thedfirreport.com/2023/10/30/netsupport-intrusion-results-in-domain-compromise/
Vulnerability
Our attack surface.
CVE Crowd
CVEs being discussed in the Fediverse.
CVE-2023-46747: BIG-IP Configuration utility unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerability
Don’t expose your control plane to the internet is the re-enforced lesson here.
This vulnerability may allow an unauthenticated attacker with network access to the BIG-IP system through the management port and/or self IP addresses to execute arbitrary system commands. There is no data plane exposure; this is a control plane issue only.
https://my.f5.com/manage/s/article/K000137353
CVE-2023-22518: Improper Authorization Vulnerability In Confluence Data Center and Confluence Server
All versions affected.
Offense
Attack capability, techniques and trade-craft.
Data-bouncing
John Carroll and Dave find that many third party services do DNS resolution. These services can these be used in a domain-front-esq manner as an exfiltration technique.
by directing web requests to certain domains that process hostnames in headers, you can relay small pieces of data to your DNS listener, allowing you to collect and reconstruct data, be it strings, files, or anything else.
https://thecontractor.io/data-bouncing/
Ghost Task: hiding Windows tasks
Chris Au creates some detection headaches with this tool which weaponizes tradecraft originally seen in the wild. Expect use by adversaries…
The tool offers the following features:
Creates scheduled tasks with a restrictive security descriptor, making them invisible to all users.
Establishes scheduled tasks directly via the registry, bypassing the generation of standard Windows event logs.
Provides support to modify existing scheduled tasks without generating Windows event logs.
Supports remote scheduled task creation (by using specially crafted Silver Ticket).
Supports to run in C2 with in-memory PE execution module (e.g.,
BruteRatel's memexec)
https://github.com/netero1010/GhostTask
Lateral Movement: Abuse the Power of DCOM Excel Application
Raj Patel build on DCOM lateral movement tradecraft. More generally is serves an example of the scale of the challenge when defending any sufficiently complex system.
an interesting lateral movement technique called ActivateMicrosoftApp() method within the distributed component object model (DCOM) Excel application.
This technique could be used for persistence once we have established a foothold on a machine that has Microsoft Office installed.
https://posts.specterops.io/lateral-movement-abuse-the-power-of-dcom-excel-application-3c016d0d9922
Evasion by Annoyance: When LNK Payloads Are Too Long
The evasion technique is the novelty in this payload which requires the analyst to question the fact and then go deeper.
a LNK payload can be too long to pull just by looking at the file properties
https://montysecurity.medium.com/evasion-by-annoyance-when-lnk-payloads-are-too-long-9bd07ac38f6d
Understanding the New SaaS Cyber Kill Chain
SaaS is complex and Luke Jennings re-runs his Bluehat talk which shows how so..
Exploitation
What is being exploited.
CVE-2023-4966: Investigation of Session Hijacking via Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway Vulnerability
Sebastian Demmer, Nicole JeNaye, Doug Bienstock, Tufail Ahmed, John Wolfram and Ashley Frazer detail exploitation of CVE-2023-4966 or otherwise known as Citrix Bleed. If your organisation management interfaces are exposed to the internet or otherwise reachable via Server Side Request Forgery (SSRG) investigation is warranted.
[We are] currently tracking four distinct uncategorized (UNC) groups involved in exploiting this vulnerability.
https://www.mandiant.com/resources/blog/session-hijacking-citrix-cve-2023-4966
Cisco IOS XE CVE-2023-20198: Deep Dive and POC
James Horseman explains the vulnerability, so any routers not patched are in for a torrid time.
https://www.horizon3.ai/cisco-ios-xe-cve-2023-20198-deep-dive-and-poc/
Tooling and Techniques
Low level tooling and techniques for attack and defence researchers…
LastPass and Bitcoin thefts
Interesting corelation here.
Just on October 25, 2023 alone another ~$4.4M was drained from 25+ victims as a result of the LastPass hack
https://twitter.com/zachxbt/status/1717901088521687330?t=Ra_hP8GE3SRM3_zkzqy1YQ&s=19
shimon: URL fingerprinting made easy
Manabu Niseki reanimates this project which will be of use to cyber defense teams.
https://github.com/ninoseki/shimon
Illuminating Router Vendor Diversity Within Providers and Along Network Paths
Taha Albakour, Oliver Gasser, Robert Beverly and Georgios Smaragdakis do some excellent work here to allow Internet scale measurement of key technologies.
LFP, a tool that improves the coverage, accuracy, and efficiency of router fingerprinting as compared to the current state-of-the-art. We leverage LFP to characterize the degree of router vendor homogeneity within networks and the regional distribution of vendors. We then take a path-centric view and apply LFP to better understand the potential for correlated failures and fate-sharing. Finally, we perform a case study on inter and intra-United States data paths to explore the feasibility to make vendor-based routing policy decisions, i.e., whether it is possible to avoid a particular vendor given the current infrastructure.
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3618257.3624813
EMBERSim: A Large-Scale Databank for Boosting Similarity Search in Malware Analysis
Dragos Georgian Corlatescu, Alexandru Dinu, Mihaela Gaman and Paul Sumedrea impose cost on threat actors who reuse code.
We propose to address the deficiencies in the space of similarity research on binary files, starting from EMBER - one of the largest malware classification data sets. We enhance EMBER with similarity information as well as malware class tags, to enable further research in the similarity space. Our contribution is threefold: (1) we publish EMBERSim, an augmented version of EMBER, that includes similarity-informed tags; (2) we enrich EMBERSim with automatically determined malware class tags using the open-source tool AVClass on VirusTotal data and (3) we describe and share the implementation for our class scoring technique and leaf similarity method.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.01835
Footnotes
Some other small (and not so small) bits and bobs which might be of interest.
Aggregate reporting
“Cyber Attacks: The Apex of Crime-as-a-Service” - by EuroPol from September, but I missed it.
Report: Voice of the SOC 2023 - This year’s data reveals that overall job satisfaction in the SOC remains high — security practitioners love the work they do. However, burnout is taking its toll.
The Global Digital Compact: Progress Towards Digital Cooperation - The proposed Compact represents a response to the challenges posed by digital technologies, which both offer immense opportunities and raise the stakes of responsible behaviour in cyberspace.
Revealing the dark and gray organizations behind VPNs - Chinese analysis of the eco-system
Insect-inspired drones among UK Intelligence Community Postdoc awards
CSIS Launches Program on Intelligence, National Security, and Technology
Multi-factor authentication: a silver cyber bullet? - NHS Digital
Metamorphic Malware and Obfuscation: A Survey of Techniques, Variants, and Generation Kits
Learning about simulated adversaries from human defenders using interactive cyber-defense games
Artificial intelligence
Conducting Robust Learning for Empire Command and Control Detection
Prompt-Specific Poisoning Attacks on Text-to-Image Generative Models
Ranking LLM-Generated Loop Invariants for Program Verification - 'gpt-3.5 or gpt-4) are capable of synthesizing loop invariants for a class of programs in a 0-shot setting, yet require several samples to generate the correct invariants.'
Books
None this week
Events
The Workshop on the Economics of Information Security (WEIS) - CFP closes November
The 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing - December 6 –10. “Resorts World Convention Centre”, Singapore
Past
Objective by the Sea, v6.0 - videos
IMC '23: Proceedings of the 2023 ACM on Internet Measurement Conference - papers - some are covered above, this is the remainder
Unless stated otherwise, linked or referenced content does not necessarily represent the views of the NCSC and reference to third parties or content on their websites should not be taken as endorsement of any kind by the NCSC. The NCSC has no control over the content of third party websites and consequently accepts no responsibility for your use of them.
This newsletter is subject to the NCSC website terms and conditions which can be found at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/terms-and-conditions and you can find out more about how will treat your personal information in our privacy notice at https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/section/about-this-website/privacy-statement.






These are such useful updates! Thanks for sharing them.
Thanks for sharing Ollie - particularly interested in making devices less addictive, that would be great especially for addicted kids!